Cardiac muscle & myogenic control
 The structure of cardiac muscles and conduction of impulses is covered in a short video and some question in activity one. This is followed by a sequencing activity about the events of the cardiac cycle & the myogenic control of heart beat. This is linked to an ECG of normal heartbeat. Finally there are instructions of how to listen to a heart beat and measure blood pressure.
The structure of cardiac muscles and conduction of impulses is covered in a short video and some question in activity one. This is followed by a sequencing activity about the events of the cardiac cycle & the myogenic control of heart beat. This is linked to an ECG of normal heartbeat. Finally there are instructions of how to listen to a heart beat and measure blood pressure.
Lesson Description
Guiding Questions
What makes cardiac muscle different from skeletal muscle?
What does myogenic mean?
Activity 1 - The Cardiac muscle & the Cardiac cycle
Watch the first seven minutes of this video which explains cardiac muscle structure explained.
After 7 minutes the video goes a little beyond the IB guide explaining the biochemistry of action potentials.
Answer the following questions about the structure of cardiac muscle.
Questions
1. What are the two types of action potential in the heart?
..........................................................................................................................................
2. What do skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles have in common?
..........................................................................................................................................
3. Name 3 structural features of cardiac muscles which are not found in skeletal muscles?
..........................................................................................................................................
4. Why are there so many mitochondria in cardiac muscle cells?
..........................................................................................................................................
Stop the video at 7 minutes - unless you really want to understand the biochemistry of cardiac action potentials.
Important details to note about cardiac action potentials
- The heart is made of cardiac muscle.
- Cardiac muscle contracts and conducts electrical signals 'action potentials' - the cells depolarise and contract.
- This conduction of signals is helped by gaps in intercalated disks between cells & branched muscle fibres.
- After contraction cardiac muscles relax, repolarise and become ready to contract again.
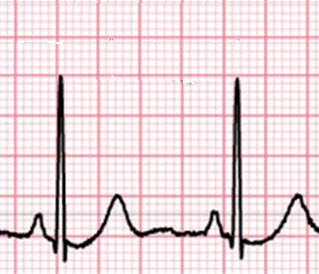
Activity 2 - ECG basics
The myogenic activity of the heart
- the sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker) starts the cardiac cycle
- the SA node sends an 'action potential' through the cardiac muscle to the left and right atrial walls.
- atria contract (depolarise) - this causes the P wave in an ECG.
- the AV node receives the 'action potential' signal to from the SA node?
- the AV node holds signal for 0.1 seconds
- the AV node sends 'depolarisation' signal to bottom of left and right ventricles;
- conducting fibres in the heart's central septum carry the signal rapidly
- ventricles contract - this causes the QRS spike in the ECG.
- The ventricles repolarise - causing the T wave.
- The heart is ready to beat again. (The atria repolarise during the ventricle contraction QRS - so it isn't seen)
Use these statements to label the diagram and the graph on the ![]() ECG basics worksheet below.
ECG basics worksheet below.
Activity 3 - Taking readings about the circulatory system
Carry out the experiments listed below:
1. Listen to the heart using a stethoscope.
This is a great ![]() Video tutorial on using a stethoscope to listen to the heart
Video tutorial on using a stethoscope to listen to the heart
2. Measure blood pressure
If there are no blood pressure cuffs in your lab this is a nice ![]() Blood pressure readings animation showing how blood pressure readings are taken:
Blood pressure readings animation showing how blood pressure readings are taken:
Teacher's notes
The three sections in this activity are quite clear. Activity one focuses on the structure of cardiac muscle, activity two looks at the conduction of impulses during the beating of the heart and activity three includes some practical activities.
This is a review of the cardiac cycle - without mentioning SA & AV nodes.
There is a super animation from Utah medical library
- atrial systole is the contraction of the muscle walls of the atrium
- atia contraction increases pressure and pushes blood into ventricles
- ventricular systole is delayed by 0.1 second to allow full atrial contraction
- atrial diastole is relaxation of atrial walls
- ventricular systole is the contraction of ventricle walls
- blood is pushed up against atrio-ventricular valves
- valves close making 1st heart sound "lubb";
- blood exits the heart by the pulmonary artery and aorta;
- ventricular diastole is relaxation of ventricular walls;
- lower pressure in ventricle draws blood back against semi-lunar valves at base of arteries;
- semi-lunar valves close making 2nd heart sound "dupp";
- cardiac cycle repeats;
This is a nice explanation of the control of myogenic contraction and the SA and AV nodes from a nurse.
(note the test questions are not IB questions)
Key words about the control of the cardiac cycle.
- aorta
- atherosclerosis
- atrial systole
- AV (atrioventricular) node
- cardiac cycle
- cardiac muscle
- conducting fibres
- coronary thrombosis
- diastole
- depolarisation
- repolarisaition
- electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)
- left atrium
- left ventricle
- SA (sinoatrial) node
- ventricular systole

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
