Humans Activities for Learning
Lesson Plan Ideas for the Human Health and Physiology Topic
The ideas for learning activities on this page aim to cover the whole of the IB guide for this topic. Where a full lesson plan has been developed it includes resources to use on an interactive whiteboard and worksheets to print. There is a mix of laboratory work, theory lessons, and assessment materials with model answers.
Digestion & absorption- planning 6.1This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
 | Digestion & Enzymes IntroductionTime: 1hr This lesson begins with an experiment to model the hydrolysis of starch by amylase and the absorption of simple sugars using visking tubing. While students wait for diffusion there is an activity to use a textbook, Biodigital human or Zygote body as a research tool to answer some simple questions about the digestive system. The lesson finishes with a collaborative diagram drawing activity. |
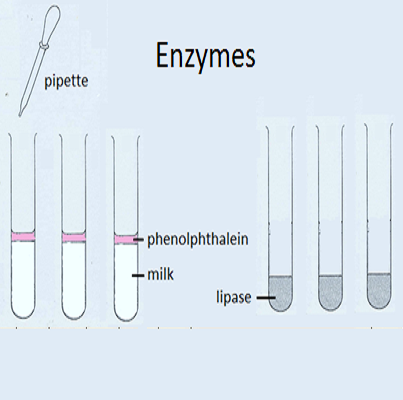 | IA Lipase ExperimentTime: 1hr Enzyme experiments are always excellent for internal assessment and as students need to understand digestion it is worth doing one here. This activity is also a chance to revisit some of the details of biochemistry covered in the earlier topic. |
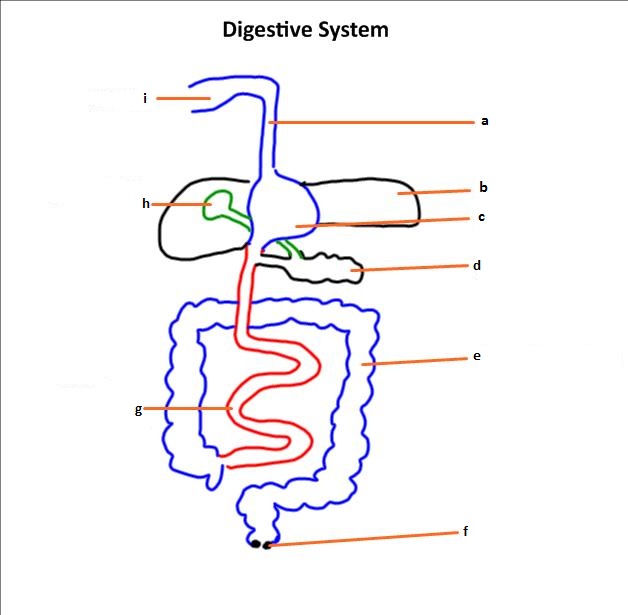 | Structure of the digestive system.Time: 1hr With a short screencast students learn a simple method of drawing a diagram of the digestive system. Annotations are added and students can practice their knowledge using some printable flashcards or a range of online study methods. |
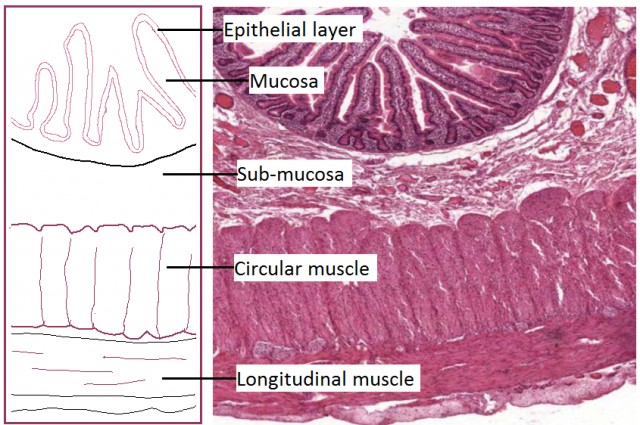 | Small Intestine Structure & Function.Time: 1h After learning to draw an annotated diagram of the digestive system students extend their understanding by looking at details of intestine structure and how they relate to function. This includes identification of muscle layers, mucosa and epithelium as well as villi which help absorbance of nutrients. There is an open-ended assessment task to finish the lesson. |
Blood system - planning 6.2This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
 | Time: 1h A short practical activity to look at the prepared slides of a human blood smear and transverse sections of an artery and vein. With the help of a textbook and these slides students complete the structured notes. |
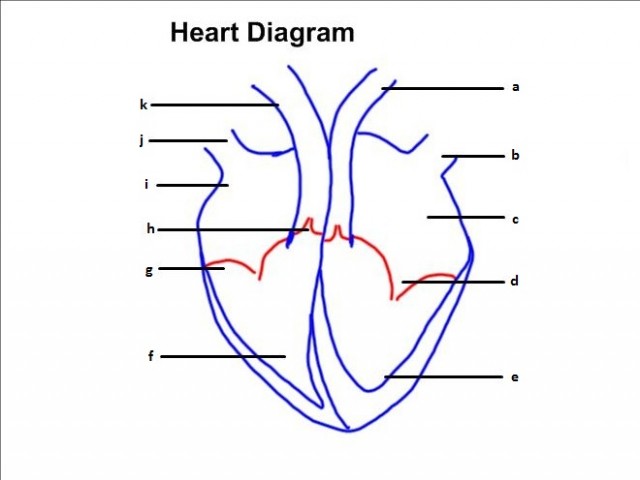 | Heart Dissection & DiagramTime: 1h Using a short screencast students learn a simple method of drawing a diagram of the heart. Annotations are added and students can practice their knowledge using some printable flashcards or a range of online study methods. Students then extend their knowledge by completing a detailed heart dissection. |
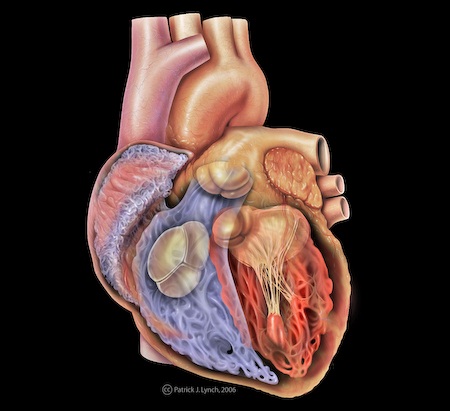 | Controlling HeartbeatTime: 1h The lesson begins with a discussion about the structure and function of the heart using the models, including the 4 chambers, associated blood vessels, valves, route of blood low and wall thicknesses. An activity to establish how the heart beat is controlled follows and student complete their notes using the Heart worksheet. A final plenary challenge is to do a running commentary of this animation? |
Defense against disease - planning 6.3This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
 | Blood clotting and heart diseaseTime: 1h Students complete a SOLO hexagon activity to sequence and explain the chemical cascade which leads to the formation of a blood clot or scab. This is followed by a short activity outlining an application of this understanding, the causes and consequences of blood clot formation in coronary arteries. |
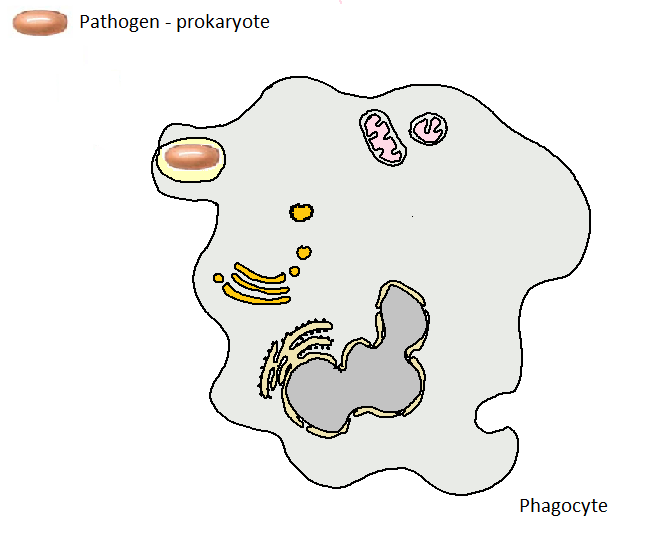
| Immune SystemTime: 1h This lesson contains two constructivist activities. In the first students research and classify microorganisms into pathogens and non pathogens. The second activity is a challenge to narrate a series of images which show the process of phagocytosis. Two short IB style questions conclude the activity |
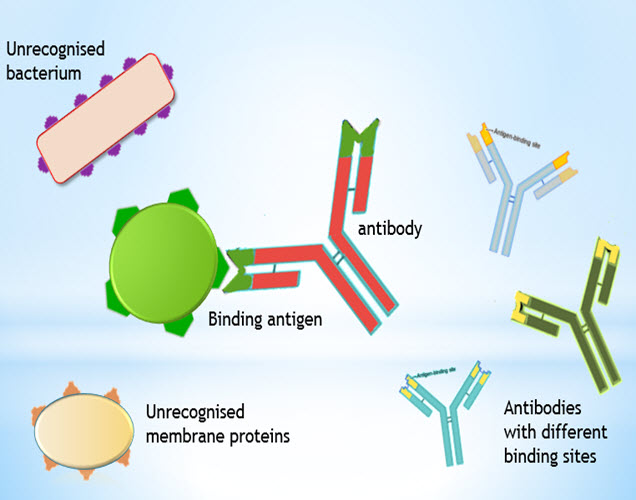 | Antigens and antibodiesTime: 1h A few simple slides help to introduce the basic concepts in this lesson. This is followed by an activity to describe the immune response to an infection of bacteria into a small cut on a student's finger. A final activity asks students to describe the role of the skin as a barrier to infection and to consider how mucus membranes help to protect the body's most vulnerable areas. |
 | HIV and AIDSTime: 1h In today's world it is important to understand the way the HIV virus leads to AIDS and how the virus is transmitted from person to person. This activity begins with a simple explanation of HIV and AIDS. The way that HIV infection reduces the number of antibodies is revealed using some short videos and a structured worksheet. There is also a video showing more detail of the transmission of HIV, and a discussion on the impacts of HIV and AIDS in society. |
Gas exchange - planning 6.4This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
 | Alveoli & gas exchangeStudents learn about the structure of the lungs and their alveoli including type I and II pneumocytes. After a short quiz on basic lung structure a short screen cast helps students to complete a diagram of the cells of two alveoli and a capillary. This diagram would be suitable for an answer during an IB exam. Using flashcards students' learn the diagram labels and annotations of their function. A final test of the concepts through some IB style questions with answers further consolidates learning. |
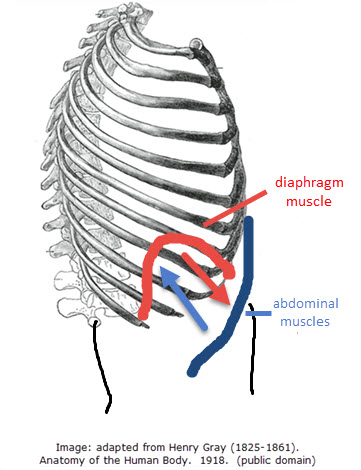 | Ventilation & lung diseaseStudents begin by looking at the muscle contractions which cause the pressure changes inside the thorax that force air in and out of the lungs to ventilate them. This is followed by an experiment to monitor breathing rates (Practical 6) and there is an activity to help prepare students for their IA investigation. Two short videos about lung disease conclude the activities. Students are asked to make links between lung structure and the consequences of these diseases. |
Neurones & synapses - planning 6.5This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
 | Neurones and nerve impulses.Time: 1h Neurones can propagate impulses down the axon at speeds over 300 km/h, as fast as a Bullet train. A quick review of resting potential and action potential is followed by a SOLO card sorting activity where students arrange information to explain the cell processes leading to resting potential and then action potential. There are some interesting web links for further reading. |
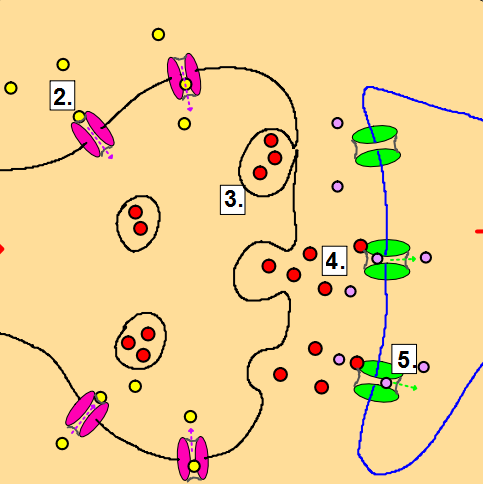 | Synapses.Time: 1h This activity involves lots of discussion and a little competition to help students learn the details of synaptic transmission. First by annotation of simple diagrams showing the structures of a synapse students are introduced to the main points and then in a collaborative activity students take turns in becoming the expert about each step. A final activity is an online multiple choice quiz followed by a plenary writing task. |
Hormones & reproduction - planning 6.6This simple sheet sets out the learning objectives, essential questions and some ideas for assessment for the following activities. | |
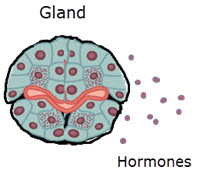 | Hormones introductionTime: 1h Students are introduced to hormones in this lesson using three examples, leptin, thyroxin and melatonin. These examples clearly illustrate the nature of hormones and ideas about homeostasis. After some quick research from four carefully selected webpages students make notes using a sheet of questions and there is a final plenary, a junior doctor speed dating activity. |
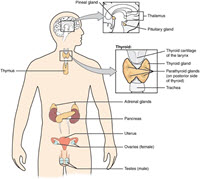 | Homeostasis of Glucose.Time: 1h This lesson introduces the way insulin and glucagon control blood glucose levels. Students arrange SOLO hexagons to explain the homeostasis process and to build on their prior knowledge of insulin or glucose. Negative feedback is essential to the hormonal control of blood glucose and is introduced here. A second set of hexagons give a summary of the two types of diabetes and an IB style question completes the lesson. |
 | Harvey and the 2000 year search for ovaTime: 1hr This lesson includes annotation of reproductive organ diagrams just as biologists, Aristotle, Harvey and de Graaf did in history in their quest to discover the function of the ovary and the existence of ova and sperm cells in mammalian sexual reproduction. Students will participate in a balloon debate and compare each biologist's work, notably the work of William Harvey, who advanced the idea "ex ovo omnia" all life originates from an egg |
 | Hormones and the menstrual cycleTime: 1hr Students are introduced to the functions of the hormones of the menstrual cycle with the aid of a short presentation. This is followed by an activity looking at the effects of hormones on one another and an explanation of positive and negative feedback. There are also some IB style questions and some flashcards to further consolidate learning. |
 | Hormones in IVF and HRTTime 1hr: This short activity rounds off the section on hormones by looking at two medical cases, the use of FSH in the stimulation of ovulation during the first phase of IVF treatment and the use of estrogen and testosterone hormones in hormone replacement therapy. This is also a worksheet to help students to structure their notes. |
 | IA Experiment on Pulse RateTime: 1h This is an experiment which complements practical 6 and may well be useful for IA investigation preparation. |

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team