Chemicals which affect synapses
 In these activities students learn how chemicals affect synapses. They answer questions which help to synthesise their knowledge of the structure of membranes, synapses and neurotransmitters. Beginning with a quick review of the role of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, applications of the biological understanding of synapses are then explored. These applications include the treatment of wrinckles, dementia, and the use of neonicotinal pesticides.
In these activities students learn how chemicals affect synapses. They answer questions which help to synthesise their knowledge of the structure of membranes, synapses and neurotransmitters. Beginning with a quick review of the role of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, applications of the biological understanding of synapses are then explored. These applications include the treatment of wrinckles, dementia, and the use of neonicotinal pesticides.
Lesson Description
Guiding Question
Secretion and reabsorption of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine, by neurons commonly occurs in synapses and at neuromuscular junctions.
How can an understanding of this neurotransmitter help to treat human ailments and also kill insects?
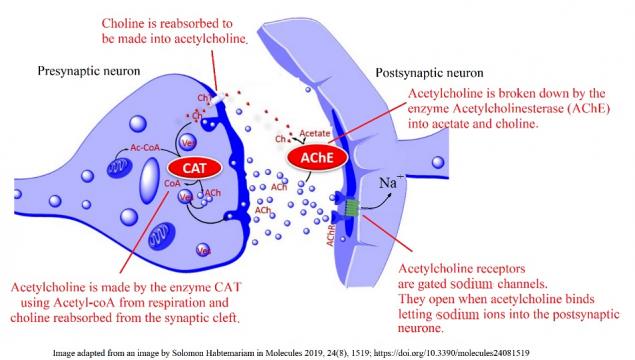
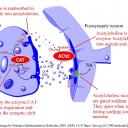
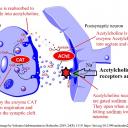
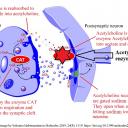
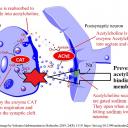
Activity 1 - Acetylcholine in synapses of the brain and at the neuro-muscular junction
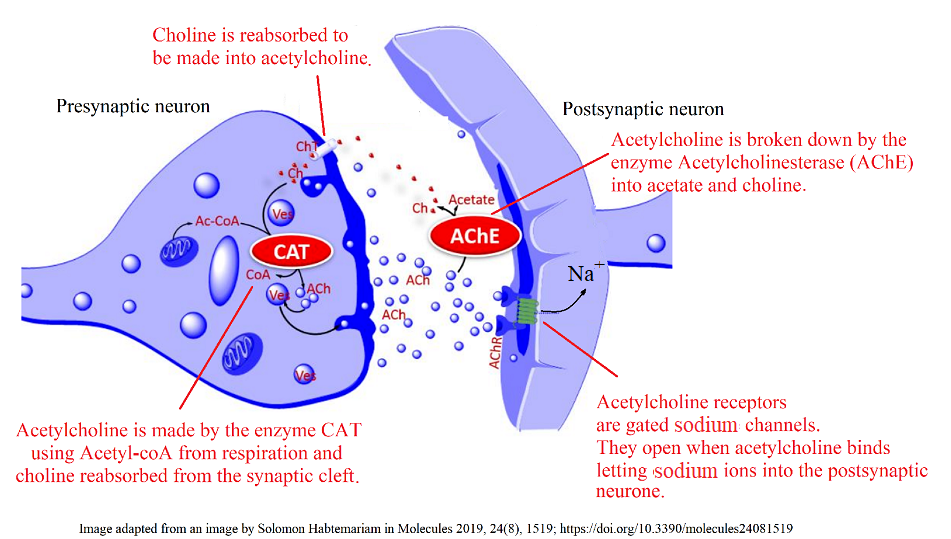
Answer the following questions using the image above and prior knowledge about nerve impulses
Questions
- Acetylcholine diffuses across synapses and binds to receptors. How does this neurotransmitter cause a new impulse in the post-synaptic neurone?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
- Once it has bound to receptors in the post-synaptic membrane acetylcholine is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). What is the effect of this enzyme on the stimulus of nerve impulses?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
- What is the advantage of reabsorbing choline from the synapse for the pre-synaptic neurone?
........................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................
- When the nerve endings of a motor neuron release acetylcholine into a muscle what happens in the muscle?
........................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................
Click the eye icon to display model answers.
Model answers
- Acetylcholine diffuses across synapses and binds to receptors. How does this neurotransmitter cause a new impulse in the post-synaptic neurone?
Acetylcholine receptors are gated (sodium) channels,
which allow sodium ions to enter the post-synaptic neurone when acetylcholine binds.
The change in membrane potential causes a new action potential.
- Once it has bound to receptors in the post-synaptic membrane acetylcholine is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). What is the effect of this enzyme on the stimulus of nerve impulses?
Acetylcholinesterase stops the stimulus of a nerve impulse by breaking down the acetylcholine.
- What is the advantage of reabsorbing choline from the synapse for the pre-synaptic neurone?
By reabsorbing choline the presynaptic neurone can make more acetylcholine.
- When the nerve endings of a motor neuron release acetylcholine into a muscle what happens in the muscle?
Acetylcholine binds to (nicotinic acetylcholine) receptors in the muscle membrane which results in a muscle contraction.
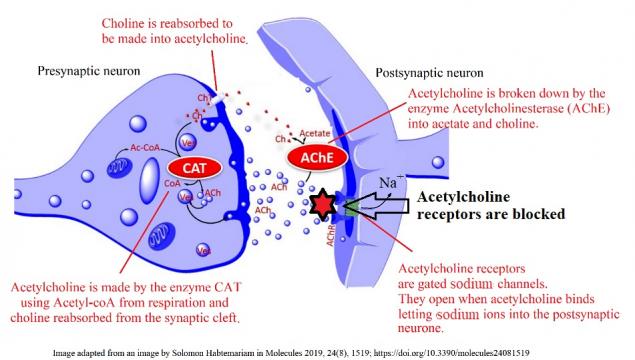
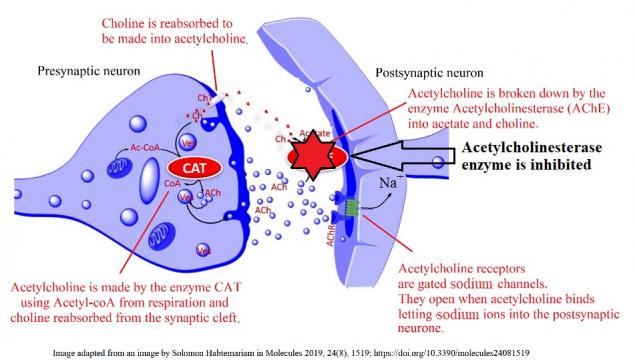
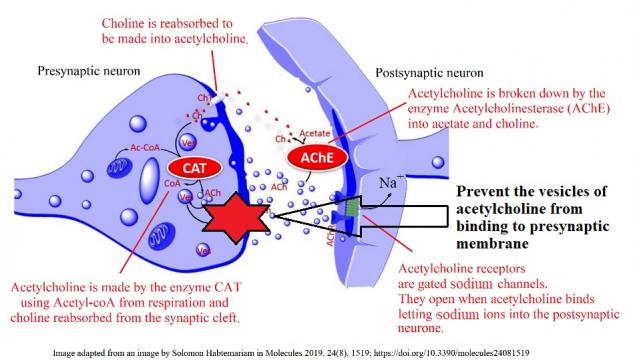
Activity 2 - What would happen if?
The slides below illustrate some different ways in which medicines can affect the functioning of acetylcholine synapses.
Answer the, 'What would happen if ..?' questions in the worksheet below using the information from the slides.
![]() "What would happen if.." questions worksheet.
"What would happen if.." questions worksheet.
Activity 3 - Three treatments - which is which?
The three ways in which medicines can affect the functioning of acetylcholine synapses from Activity 2 are found in three treatments; Botox injections to prevent wrinkles, neonicotinoid pesticides to kill insects, and treatment of Alzheimer's disease to reduce the decline in brain function.
Carry out some research about these treatments using the web links below and decide which of the methods from Activity 3 are used. Make brief notes about each treatment and how it affects acetylcholine in the synapse.
BOTOX Mechanism of Action Video
Mechanism of action animation for BOTOX®.
What Are Botox Injections? | StreamingWell.com
Have you ever thought about getting Botox? Learn about the botulinum injection and what side effects can occur.
The buzz about pesticides - by Nature Video
Bees, the most important pollinators of our crops, are in trouble. All over the world, their populations are decreasing and scientists want to know why. In t...
2-Minute Neuroscience: Alzheimer's Disease
In this video, I discuss Alzheimer's disease---the most common form of neurodegenerative disease. In addition to the widespread neurodegeneration that occurs...
Acetylcholinesterase and Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Blocking cholinesterase enzyme with drugs.
How Close Are We to Curing Alzheimer's?
Researchers are working hard to understand the mechanics of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. So, how close are we to finding a cure? We're co...
Teachers notes
The main idea in this activity is to give students sufficient understanding of acetylcholine synapses and the methods of modifying its action in a synapse for them to be able to match the three treatments in Activity 3 with the mechanisms of action.
Activity 1 is a simple reminder of how acetylcholine works.
Activity 2 uses the "what happens if" questioning approach to explore different aspects of neurotransmitter activity, using acetylcholine as an illustration.
Activity 3 asks student to work out for themselves which mechanism each of the treatments use. This is guided inquiry approach. While there are six videos selected for students to use, any reasearch methods wold be appropriate.
One way to start the lesson and help students to remember the name, "acetylcholine" could be to play this song and invite students to sing along with these silly lyrics.
Choline choline acetyl choline Your beauty is beyond compare Your smile is ….. |
An alternative, or fourth Activity idea
Activity 4 - Understanding chain activity -Three treatments.
This is a method of achieving clear explanations by focusing on the audience for the explanation.
How to Play
- First get a clear picture of the audience - for each treatment this will be different.
- Then brainstorm questions - what do these people really want to know and care about?
Questions are best captured in the voice or thoughts of the audience, as they would ask them.
They may sound like:
- “What’s a benefit of this?
- "Why should I have this treatment?”
- “How is this related to the decline of honey bees?”
- “What makes this a priority?”
Or, they may be more specific:
- “When does the treatment begin to have an effect?”
- “How will it impact my overall health?”
The questions will become the links in the understanding chain.
- Capture the questions on individual sticky notes. (ref: post up game)
- Sort the questions in a horizontal line on a wall or whiteboard.
The group may choose to do one of the following:
Arrange the questions in a simple story format. In this understanding chain, the group clusters questions under three headings, from left to right:
- Situation, which sets the stage, introduces a topic and a conflict
- Complication, in which further conflict is endured and decisions are made
- Resolution, in which a course of action is chosen which leads to a result.
Arrange the questions in an educate-differentiate-stimulate format. In this chain, the group arranges the questions from left to right, moving from:
- Educate, in which a topic or idea and its parts are introduced
- Differentiate, in which parts of the topic are contrasted to create a basis of understanding
- Stimulate, in which actions are asked for or proposed.
Strategy
An understanding chain, like any chain, is only as strong as its weakest link. By examining the questions as a whole, the group may uncover an area that needs work or find the “tough questions” that are not easy to answer. A group that tackles the weak questions, and has the courage to answer the tough ones directly and honestly, will have the best understanding.
The Understanding Chain game was developed by Dave Gray as part of XPLANE’s consulting approach.
A point to remember
*Blocking of synaptic transmission at cholinergic synapses in insects occurs by the binding of neonicotinoid pesticides to acetylcholine receptors. While low activation of acetylcholine receptors promotes nerve signalling, overstimulation results in fatal convulsions and paralysis, more toxic to insects
The use of these pesticides has caused concern to bee keepers.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team