Electron transport chain
Lesson Description
Guiding Question s
s
What happens to the hydrogen produced in the Krebs cycle?
Which enzyme makes ATP in large amounts in the mitochondria?
Activity 1 - Introductory slides about the Electron transport chain
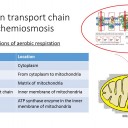
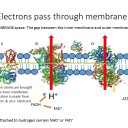
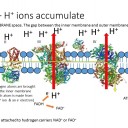
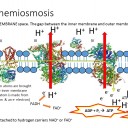
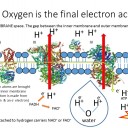
The following slides outline in simple terms the process of electron transport, the pumping of H+ ions and chemiosmosis.
This process makes lots of ATP and as oxygen is the final electron acceptor it also makes metabolic water.
Use this ![]() Electron transport chain summary sheet to review the main points about the process of electron transport. Identify five or six bullet points to learn from the sheet.
Electron transport chain summary sheet to review the main points about the process of electron transport. Identify five or six bullet points to learn from the sheet.
Activity 2 - IB style questions about the Electron transport chain
Then try these ![]() electron transport chain IB style questions
electron transport chain IB style questions
Activity 3 - Extension activity
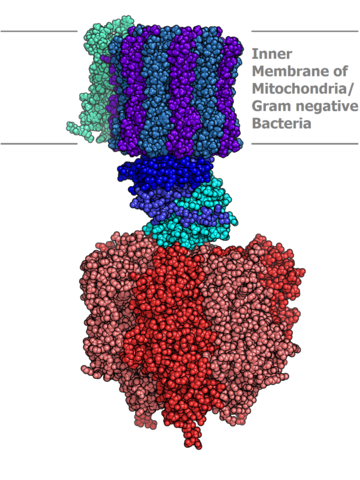
Further information about the electron transport chain is very clearly explained in this HarvardX animation.
While the details are beyond the IB guide, the animation are so clear they make a nice activity for curious students with a keen interest.
Watch the video and discuss the questions below.
Questions
1) Describe the location in a eukaryote cell where the reactions of the electron transport chain take place?
............................................................................................................
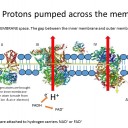
2) The role of the membrane is to provide a barrier to protons allowing a concentration gradient of protons to form.
Where is the concentration of protons high, and where is it low?
............................................................................................................
3) Outline the role of the protein complex called ATP synthase.
............................................................................................................
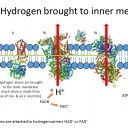
4) The electron transport chain involves four protein complexes which transfer electrons through a series of coupled reactions. What is the name of the molecule which brings electrons to protein complex I ?
............................................................................................................
5) Name the molecules made in protein complex IV.
............................................................................................................
6) Outline why oxygen in complex IV is known as "the final electron acceptor".
............................................................................................................
............................................................................................................
Click the eye icon to see some model answers.
Model answers
1) Describe the location in a eukaryote cell where the reactions of the electron transport chain take place?
The mitochondrion inner membrane
2) The role of the membrane is to provide a barrier to protons allowing a concentration gradient of protons to form.
Where is the concentration of protons high, and where is it low?
The proton concentration is high in the intra-membrane space, and low in the matrix of the mitochondrion
3) Outline the role of the protein complex called ATP synthase.
ATP synthase uses the proton gradient to make ATP
4) The electron transport chain involves four protein complexes which transfer electrons through a series of coupled reactions. What is the name of the molecule which brings electrons to protein complex I ?
Reduced NAD, or NADH
5) Name the molecules made in protein complex IV.
Two water molecules
6) Outline why oxygen in complex IV is known as "the final electron acceptor".
The electrons are not transferred beyond the protein complex IV - they react with the oxygen and four protons to become two water moleculesTeachers notes
Activity 1 is a simple set of slides to help explain what is happening to the hydrogen atoms on the inner membrane of mitochondria during this part of aerobic respiration.
The slides could be used to help students make notes about the process. Although there are actually some quite complicated ideas in this topic, exam questions can be answered successfully without a thorough understanding of the chemistry, e.g. ionisation energies.
It is important for students to understand the difference between hydrogen atoms and ions.
Activity 2 Gives students time to test themselves with some IB style questions
There are some model answers on this page:
Activity 3 shows students some further information about the electron transport chain. While this is detailed it is very clearly explained in this HarvardX animation. The content is partly beyond the IB guide but it may help some students to better understand the processes, as they are described logically, step by step.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team