Introduction to Meiosis
Students begin by sorting cards to outline the process of meiosis, including pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over, followed by two divisions, resulting in four haploid cells. Online flashcards, a PowerPoint activity and a test help to consolidate learning of the stages of meiosis. This lesson concludes with a short practical activity using modeling clay to illustrate how crossing over increases the variation in offspring produced be sexual reproduction.
Lesson Description
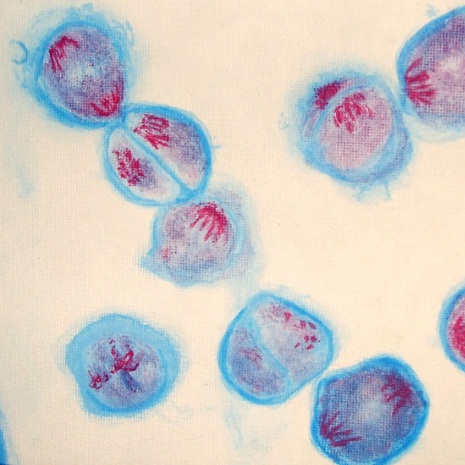
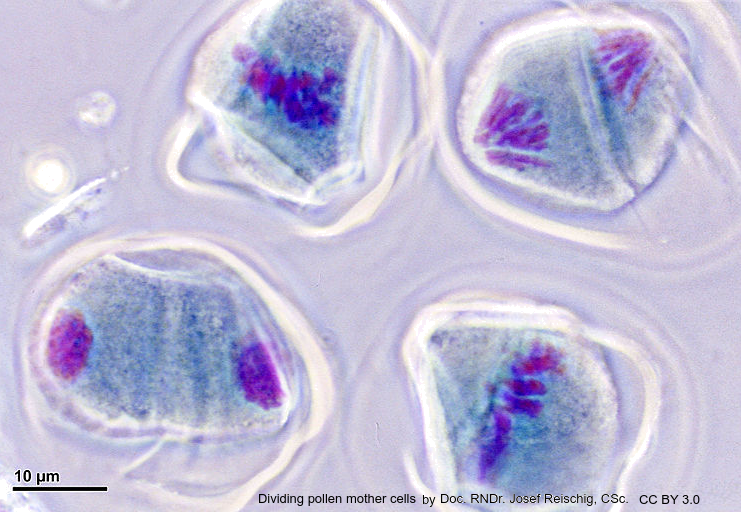 Guiding Questions
Guiding Questions
- What happens to the chromosomes during Meiosis?
- Describe the four pollen mother cells in the image?
(click the image to enlarge it)
Activity 1: Arrange the Flash Cards to tell the story of meiosis
- Use the following cards to try to work out what the order of the stages are. It is best to print a set of
 Meiosis Flashcards and arrange them on the table to show the whole process of meiosis.
Meiosis Flashcards and arrange them on the table to show the whole process of meiosis. - Be sure to match the diagrams with the chromosome movements described for each stage.
- Once you have worked out the process of meiosis then learn the names of the stages.
These online cards on Quizlet or the scatter game is good for this.
Distance learning alternative activity
Instead of printing cards which students sort in lessons I made a set of timeline slides with jumbled images of cells undergoing meiosis and asked students to put images of chromosomes into the correct sequence to show meiosis. Then we annotated the steps of the process and to finish while I presented the slides the students each said a few words about each of their slides in turn.
Activity 2 Describe the stages from memory
Complete the two simple (if you know meiosis) activities on the following PowerPoint.
You can download the file using the options button at the bottom right of the PowerPoint slide.
Alternatively paper and pen will work too.
Activity 3 Quick Test on Meiosis stages
Complete the activity on the ![]() Quick Test on Meiosis worksheet below.
Quick Test on Meiosis worksheet below.
This could be a homework task, or a starter activity for next lesson.
This is an alternative ![]() Worksheet of meiosis questions
Worksheet of meiosis questions
Activity 4 Crossing Over - Modelling Clay Activity
There is one last detail about meiosis which needs a little explanation, crossing over.
Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during prophase I
This process is important for increasing the variation in offspring produced by sexual reproduction.
Remember meiosis makes the sex cells, which form the fertilized egg cell.
Try this ![]() Practical Activity - Modelling Crossing Over
Practical Activity - Modelling Crossing Over
Answer these short IB-style questions on crossing over and meiosis ![]() Meiosis extension questions
Meiosis extension questions
Teachers notes
These resources can be used in a lesson as described or they can be used individually.
Activity 1 The card sort in activity may take as much as 30 minutes, but brighter students, or those who have read the text book will complete this more quickly. The online Quizlet flashcards will keep the faster students busy learning the details.
Activity 2 could be done by students on their computers or on an interactive whiteboard. If there is no computer then the ppt slides can be printed as a worksheet. It should take about 10 minutes. The main aim is to ensure that all students have notes on explaining the process of meiosis.
Activity 3 is a short test, and could be completed in the next lesson, as a quick review, or for homework.
There are model answers here: Meiosis Quick Quiz Answers
Activity 4 requires some modeling clay and some sharp pencils, or mounted needles. Students like using scalpels with modeling clay, and this would make the cut in the crossing over nice and neat. The questions on the worksheet relate to offspring variation, and is useful later in the evolution section, it is also useful for the HL genetics topic.
These are some extra resources which didn't make it into this activity but may be useful.
- Meiosis diagrams with a spoken explanation of meiosis
- Quizlet flashcards for all the genetics theory in this topic
- Meiosis animation from Cells Alive
- Mitosis and meiosis comparison from the Amoeba sisters

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team
