Condensation polymers answers
 Answers to questions on condensation polymers
Answers to questions on condensation polymers
Answers to Condensation polymers questions.
1. (a) Polyester
(b)
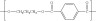
(c) n HOOC−C6H4−COOH + n HO−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH → H−(−O−(CH2)3−OCO−C6H4−CO−)n−OH + (2n−1) H2O
(d) Mr (HOOC−C6H4−COOH) = (8 x 12.01) + (6 x 1.01) + (4 x 16.00) = 166.14
Mr (HO−CH2−CH2−CH2−OH) = (3 x 12.01) + (8 x 1.01) + (2 x 16.00) = 76.11
Total mass of 1000 mol of reactants = 166.14 + 76.11 = 242.25 kg
Total mass of water formed = 1999 x 18.02/1000 = 36.02 kg
Mass of polymer = 242.25 − 36.02 = 206.23 kg
Atom economy = (206.23 ÷ 242.25) x 100 = 85.1 %
2. (a) Polyamide.
(b)

(c) The long polymer chains are able to form a strong 3-dimensional cross linkage to make strong layers due to hydrogen bond formation between the H bonded to the N atom in one peptide linkage with the O of an adjacent peptide linkage.
(d) The acid protonates the O and N atoms in the peptide bonds so they can no longer form hydrogen bond cross linkages. The concentrated acid may also hydrolyse the peptide bond.
Download the Answers to Condensation polymers questions

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team