Taxol questions

 Questions on Taxol - a chiral auxiliary case study
Questions on Taxol - a chiral auxiliary case study
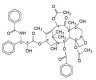
1. A molecule of Taxol contains eleven chiral carbon centres. Ten of the chiral centres are shown. Identify the remaining chiral centre by placing an asterisk (*) in the correct position on the structure below.
2. One of the chiral auxiliaries used in the synthesis of Taxol is trans-2-phenylcyclohexan-1-ol.
.jpg)
A 3-D representation of one of the enantiomers of trans-2-phenylcyclohexan-1-ol
(a) Explain why this is described as the trans isomer of 2-phenylcyclohexan-1-ol.
(b) Draw a 3-D representation of the other enantiomer of trans-2-phenylcyclohexan-1-ol
(c) Explain how chiral auxiliaries are used in organic syntheses to give products with the desired enantiomeric form.
(d) Although the use of chiral auxiliaries mainly gives the desired enantiomer some other enantiomers are likely to also be present in small amounts in the final product as impurities. Explain how a polarimeter can be used to determine the percentage purity of the product.
3. Taxol can be synthesised from 10-deacetylbaccatin, which is a natural product.

During the synthesis of Taxol from 10-deacetylbaccatin, two hydroxyl groups (shown above in red) are replaced by side groups.
Identify the type of reaction that takes place in each case when they react to form Taxol.
Download the Taxol questions ![]() to give to your students
to give to your students
To see the worked answers go to Taxol answers.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team