Proteins & enzymes (HL) questions
 Questions on Proteins & enzymes (HL)
Questions on Proteins & enzymes (HL)
1. The graph below shows how the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction varies with the concentration of substrate when there is no inhibitor present, when there is a competitive inhibitor present and in the presence of a non-competitive inhibitor.
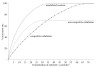
(a) Explain how enzymes are able to catalyse specific biological reactions.
(b) Describe how competitive and non-competitive inhibitors differ in the way that they interact with enzymes.
(c) Calculate the value of the Michaelis-Menten constant, Km, from the graph for the uninhibited reaction.
(d) State and explain how the values of Vmax and Km are affected by the presence of (i) competitive inhibitors and (ii) non-competitive inhibitors.
2. Explain with the help of equations how an amino acid, represented by H2NCH(R)COOH, can act as a buffer in aqueous solution.
3. (a) Explain why an amino acid has two pKa values.
(b) The two pKa value for the amino acid alanine are 2.3 and 9.7. Deduce the ratio of the concentrations of the zwitterion and its conjugate base, the anion H2NCH(CH3)COO−, in a solution with a pH of 9.7.
(c) Calculate the change in pH that occurs when 0.500 g of solid sodium hydroxide is added to 1.00 dm3 of a buffer solution containing 0.500 mol of the zwitter ionic form and 0.200 mol of the cationic form of alanine, H2NCH(CH3)COOH. (Assume there is no volume change when the sodium hydroxide is added).
4. A protein solution of unknown concentration was assayed by measuring its absorbance at λmax using a UV-Vis spectrometer. The absorbance was found to be 0.22. The absorbance of known concentrations of the protein in solution were then measured at the same wavelength and the following calibration curve obtained.

(a) Explain what is meant by λmax.
(b) Determine the concentration of the protein in the assayed sample.
Download the Proteins & enzyme (HL) questions ![]() to give to your students.
to give to your students.
To see the worked answers go to Proteins & enzymes (HL) answers.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team