 In this topic, we will look at
In this topic, we will look at
- Composite and Inverse Functions
- Quadratic Functions and the Discriminant
- Rational Functions
- Transforming Functions
- The Factor and Remainder Theorem
- Sums and Products of Polynomial Equations
Equation of a Straight Line
You will probably recognise the most commonly used form of the equation of a straight line: y = mx + c where m represents the gradient and c represents the y-intercept. It is important not to overlook this topic, as it comes up a lot in work on Functions,
Functions - The Basics
In this page, we will look at the different types of relations including functions. The first step to gaining a good understanding of functions is to think about inputs and outputs. Once that is clear, you should be able to deal with domain...

Quadratics
On this page we will look at quadratic expressions and how the different factorised forms link to the shape of the graph. We will also get an understanding about how the discriminant affects not only the number of roots of a quadratic equation, but also ho
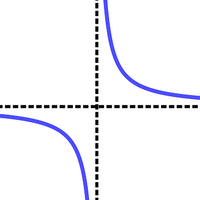
Rational Functions HL
On this page, we will look at the properties of the reciprocal function and rational functions. You may be required to draw a sketch of these functions. In these cases, it is important to know how to find the vertical asymptote, the horizontal...
Transforming Functions HL
For the topic of transforming functions, we need to understand the effect of translating, reflecting and stretching has on functions. You may be asked to describe the transformations, sketch graphs or find the coordinates of points that have been transform
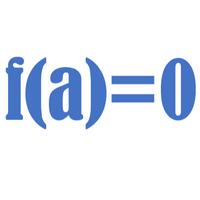
Factor and Remainder Theorem
The factor theorem is a special case of the remainder theorem, in that (x-a) is a factor if and only if P(a)=0

Sums and Products of Roots
On this page, we learn all about roots of polynomial equations and how to use the formulae for the sum of the roots and the product of the roots.


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn