SL Practice Paper 1 (1)

 'Mock' Paper 1 multiple choice exam (1)
'Mock' Paper 1 multiple choice exam (1)
To give your students access to this page you will need to change the access from "Filtered student access" to "Direct student access".
Instructions
- Time allowed: 45 minutes
- Answer all the questions.
- For each question choose the answer you consider to be the best.
- Use the periodic table from Section 6 of the data booklet as your only source of reference.
- Do not use a calculator
- If you are not a native speaker of English a simple translating dictionary is allowed.
- At the end of 45 minutes tick the green check box at the bottom of the page.

- Learn from any mistakes you have made.
What is the relative atomic mass of silicon?
The relative atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes occurring naturally in one mole of atoms of the element compared to the mass of 1/12 mol of carbon-12 so has no units.
What is the sum of the integer coefficients when ammonia is oxidized in air in the presence of a catalyst to produce nitrogen(II) oxide and water?
_ NH3(g) + _ O2(g) → _ NO(g) + _ H2O(l)
The balanced equation is 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(l)
What will be the concentration (in mol dm−3) of hydrochloric acid in the solution formed by adding 150 cm3 of 0.20 mol dm−3 HCl(aq) to 250 cm3 of 0.30 mol dm−3 HCl(aq)?
Amount of HCl in 150 cm3 of 0.20 mol dm−3 HCl(aq) = 150/1000 x 0.20 mol
Amount of HCl in 250 cm3 of 0.30 mol dm−3 HCl(aq) = 250/1000 x 0.30 mol
Amount of HCl in 400 cm3 of mixture = (150/1000 x 0.20) + (250/1000 x 0.30) mol
Amount of HCl in 1000 cm3 (1 dm3) of mixture = [(150/1000 x 0.20) + (250/1000 x 0.30)] x 1000/400 = 0.26 mol
What volume of gas, measured at STP, will be remaining when 1.60 g of methane is combusted completely in 12.80 g of oxygen gas? (1 mol of an ideal gas occupies 22.7 dm3 at STP).
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) so 1.60 g (0.1 mol) of methane requires 0.2 mol of oxygen (6.40 g) to combust completely. This means there will be 6.40 g (0.2 mol) of excess oxygen remaining and 0.1 mol of carbon dioxide product present (water is a liquid at STP) which will occupy 3 x 2.27 = 6.81 dm3.
Which is correct for 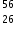 Fe3+?
Fe3+?

The atomic number of Fe is 26 so it will contain 26 protons. Its mass number is 56 so there will be 30 neutrons in the isotope. Fe contains 26 electrons. Three electrons have been removed to form Fe3+ so there will be 23 electrons remaining.
Which transition in the hydrogen spectrum emits the highest energy?
Emission spectra involve excited electrons falling from higher to lower energy levels. Electrons falling to the n = 1 level will have the highest energy as all these transitions occur in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (when electrons fall to the n = 2 level the transitions occur in the visible region).
Which group in the periodic table contains the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p5?
The element has 5 electrons in its incomplete 3p sub-level so is a p block element and will be in group 17. (You can also arrive at the answer by seeing that it has 17 electrons in total so the atomic number must be 17. This means the element is chlorine which is in group 17.)
Which is a correct description of the oxides of period 3?

The oxides of period 3 (Na → Cl) change from basic to acidic moving from left to right across the period with aluminium oxide having both basic and acidic properties.
Which compound contains only ionic bonding?
All four compounds are ionic but the nitrate, sulfate and ammonium ions, (NO3−, SO42− and NH4+) are complex ions which also contain covalent bonding. Potassium nitride, K3N only contains K+ and N3− ions.
Which compound contains a bond angle greater than 109.5o?
CCl4, NH3 and H2O all have four electron domains around the central atom. CCl4 has four bonding pairs of electrons so has a regular tetrahedral shape with bond angles of 109.5o. NH3 has one non-bonding pair of electrons and H2O has two non-bonding pairs of electrons. These non-bonding pairs exert a greater repulsion than bonding pairs so the bond angles are less than 109.5o. BF3 has three electron domains consisting of three bonding pairs of electrons so its shape is trigonal planar with bond angles of 120o.
Which is the correct order of increasing boiling points?
There is no hydrogen bonding between ethanal, CH3CHO molecules so ethanal has the lowest boiling point (20.2 oC). Both ethanol and ethanoic acid have a hydrogen atom bonded directly to an electronegative oxygen atom so exhibit hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bonding will be stronger in the carboxylic acid as the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group also draws electrons away from carbon atom bonded to the -OH group so that the polarity of the O-H bond increases. (Ethanol boils at 78.4 o.C and the boiling point of ethanoic acid is 118.1 oC.)
Which factor significantly increases the strength of metallic bonding?
The three factors which increase the strength of metallic bonding are a decrease in the radius of the metal ion, an increase in the charge on the metal ion (these two factors increase the charge density) and the number of delocalized electrons. An increase in the number of electrons is not the same as an increase in the number of delocalized electrons. Potassium, for example, has 39 electrons whereas lithium only has 3 electrons but both have only one electron in the outer s orbital that can delocalize and the much smaller lithium ion means lithium has a much higher boiling point than potassium.
Consider the following enthalpy values:

Which expression gives the enthalpy value, in kJ mol−1, for the formation of propane, C3H8(g)?

Which is the correct order of increasing bond strength between oxygen atoms in a molecule of the compound?
The O−O bond in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 is a single bond so is the weakest. The O=O bond in oxygen gas is the strongest as it is a double bond and the oxygen to oxygen bond in ozone is in-between as it is a resonance hybrid equivalent to a 1.5 bond.
Which enthalpy value at SATP conditions can be determined using only average bond enthalpies?
Average bond enthalpies refer only to the gaseous state and additional enthalpy terms involving change of state are required for all the reactions except for the reaction between methane and chlorine where all the reactants and products are in the gaseous state.
Which is a correct unit for the rate of a chemical reaction?
Rate of reaction is measured as the change in concentration over time so will have the units of concentration time−1.
The graph shows the reaction pathway for an endothermic reaction with and without a catalyst.

Which gives the correct quantitative values?

Ea for the forward catalysed reaction is the difference between the starting energy and the peak of the dotted red line (catalysed pathway), ΔH is the difference in energy between the initial and final states and Ea for the reverse catalysed reaction is the difference between the new starting energy and the peak of the catalysed pathway.
The value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction between hydrogen and iodine to form hydrogen iodide at 500 K is 1.60 x 102.
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g) Kc = 1.60 x 102
What will be the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc’, for the reverse reaction?
HI(g) ⇌ ½H2(g) + ½I2(g) Kc’ = ?
If the first equation is written as ½H2(g) + ½I2(g) ⇌ HI(g) then the equilibrium constant will be √Kc. The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction will be (√Kc)−1, i.e. 1 ÷ √(1.60 x 102).
Which is the conjugate base of ammonia, NH3?
Brønsted-Lowry acids donate a proton to form their conjugate base, so NH2− is the conjugate base of NH3 whereas ammonia itself is the conjugate base of NH4+.
What is the pH of 0.010 mol dm−3 H2SO4(aq)?
Sulfuric acid is a strong diprotic acid so [H+(aq)] will be equal to 2 x 10−2 mol dm−3. pH = − log10[H+(aq)] so the pH will be less than 2 but more than 1 (as [H+(aq) would need to be 10 x 10−2 mol dm−3 for it to be 1). This has assumed that H2SO4 is a strong dibasic acid. In fact the first dissociation to HSO4− is strong but the second dissociation is not completely strong. Even so, the actual concentration of H+(aq) will still be more than 1 x 10−2 (but less than 2 x 10−2 mol dm−3) so the pH will between 1 and 2.
Which oxide cannot be a cause of acid deposition?
All four oxides listed are acidic but carbon dioxide only forms a weak acid in water. As rain water falls through the atmosphere it naturally dissolves carbon dioxide to become acidic but the lowest pH this can reach is about 5.6 so acid precipitation is defined as having a pH lower than 5.6.
Which compound contains sulfur with the highest oxidation state?
The oxidation state of sulfur in sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is +6. In sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3 and in sulfur dioxide, SO2 it is +4 and in hydrogen sulfide, H2S it is −2.
Which is a correct statement about electrochemical cells?
Oxidation always occurs at the anode. In a voltaic cell the anode is the negative electrode and in a electrolytic cell the anode is the positive electrode. For a voltaic cell to produce electrical energy the spontaneous chemical process must be exothermic, not endothermic
Which is a correct statement about the molecule with the structural formula shown?

The molecule has the formula R-CO-R' so it is a ketone. The two functional groups in addition to the carbonyl group are a phenyl group and an alkyl goup.
What is the name of this compound using IUPAC rules?

The compound is an isomer of hexanol, C6H13OH, but the longest chain contains four carbon atoms and there is a hydroxyl group on the second carbon atom. It is also bonded to two methyl groups, one on the second carbon atom and one on the third, so it is 2,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol.
Ethanol can be formed from the reaction of bromoethane with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide.
C2H5Br(l) + NaOH(aq) → C2H5OH(aq) + NaBr(aq)
Which best describes how the hydroxide ion is behaving in this reaction?
The reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution. A nucleophile is an electron-rich species containing a non-bonding pair of electrons that it donates to an electron-deficient carbon. The carbon atom in the C−Br bond is electron deficient as bromine is more electronegative than carbon.
Which organic compound is produced when methanol reacts with methanoic acid in the presence of a sulfuric acid catalyst?
The equation for this esterification reaction is HCOOH + CH3OH ⇌ HCOOCH3 + H2O
An experiment was performed to measure the volume, V (in m3) of exactly 1.0 g of oxygen gas at different temperatures, T (in Kelvin) at a constant pressure of 1.0 x 105 Pa.
Which graph should be plotted from the data obtained to give a straight line with a gradient equal to the value of the gas constant, R (in J K−1 mol−1)? Assume that oxygen behaves as an ideal gas.

The ideal gas equation is pV = nRT. Since Mr of O2 is 32, n = 1/32 mol. P = 1.0 x 105 Pa = 1.0 x 105 Nm−2 and I J = 1 Nm
32 (mol−1) x 1.0 x 105 (Nm−2) x V (m3) = R (J K−1 mol−1) x T (K)
a plot of (3.2 x 106)V against T will give a gradient of R in J K−1 mol−1)
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (molecular formula: C12H4Cl4O2)?

When calculating IHD O atoms count as zero and Cl atoms can be considered to behave as H atoms so the formula can be reduced to C12H8. If it was fully saturated it would be C12H26 so it is 18 H atoms (or 9 H2) short which means that the IHD Is 9. This can also be seen from the structural formula as the two benzene rings each have an IHD of 4 (three for the 'double bonds' and one for the ring) and the additional ring makes a total of 9.
How many different signals will 2-methylbutane give in its 1H NMR spectrum?

The hydrogen atoms are in four different chemical environments. Although not asked for the ratio of the areas under each signal will be 6:3:2:1. The 6 is due to the six H atoms in the two -CH3 groups bonded to the second carbon atom in the chain, the 3 is due to the three H atoms bonded to the fourth carbon atom in the chain, the 2 is due to the two hydrogen atoms bonded to the third carbon atom in the chain and the 1 is due to the single H atom bonded to the second carbon atom in the chain.

 IB Docs (2) Team
IB Docs (2) Team