Energy Resources
- Energy resources are large stores of energy that can be transferred from one form into electrical energy that can be used by society
- Generating energy reliably requires the use of a range of different energy resources
- A renewable energy resource is defined as
An energy source that is replenished at a faster rate than the rate at which it is being used
- As a result of this, renewable energy resources cannot run out
- Renewable resources include:
- Solar energy
- Wind
- Bio-fuel
- Hydroelectricity
- Geothermal
- Tidal
- Bio-fuels
- Non-renewable energy resources are those that cannot replenish faster than they are used
- Non-renewable resources include:
- Petrol (gasoline)
- Diesel
- Coal
- Natural gas
- Nuclear fission
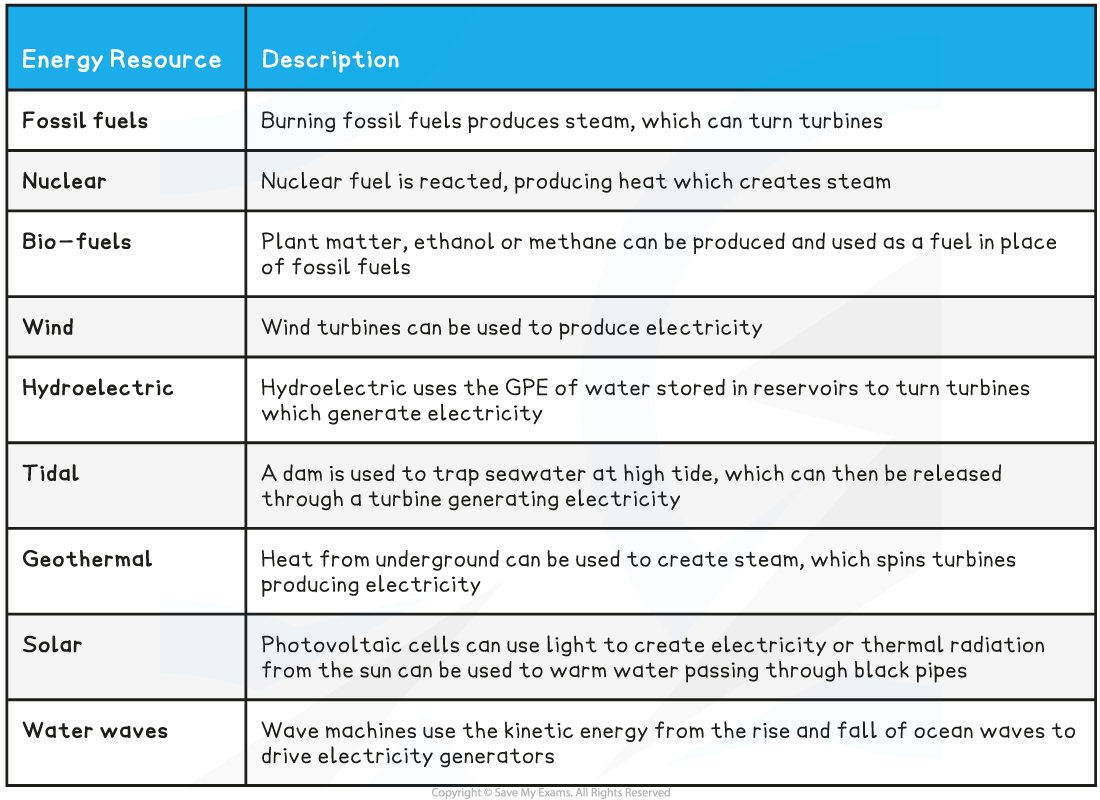
Energy Resources Table
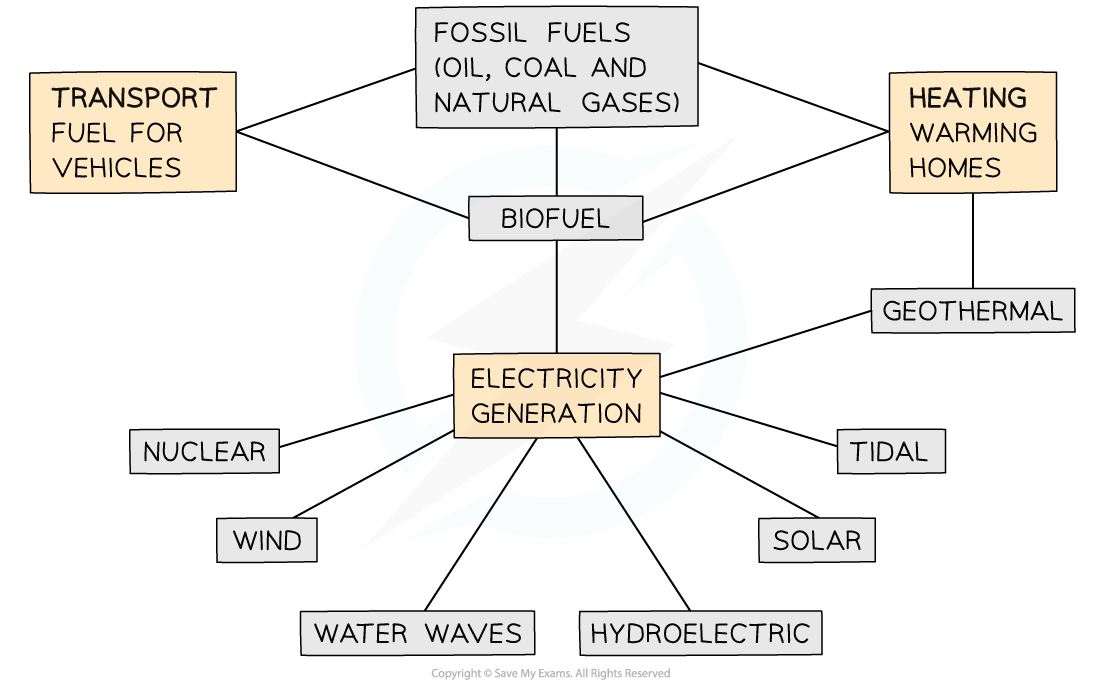
Uses of Energy Resources
- The three main uses of energy resources include:
- Transport
- Electricity generation
- Heating
Types of energy resources
Transport
- The majority of vehicles in the world are powered by petroleum products such as petrol, diesel and kerosene
- These resources all originate from crude oil, which is a fossil fuel
- A growing number of vehicles are now being powered by electricity
- The advantage of this is that while the vehicle is being driven, it produces zero carbon emissions
- The disadvantage is that when the vehicle is being charged, it is connected to the National Grid, which currently uses a combination of renewable and non-renewable energy sources
- Vehicles can also be powered by biofuel
- The advantage of biofuel is that it is a renewable resource
- However, the claim that biofuels are carbon-neutral is largely controversial
Electricity Generation
- Electricity plays a bigger role in people's lives than ever before
- With almost 8 billion people in the world, this means the demand for electricity is extremely high
- To keep up with this demand, a combination of all the energy resources available is needed
- On the downside, the majority (84%) of the world's energy is still produced by non-renewable, carbon-emitting sources
- This has an enormous negative impact on the environment
- Currently, scientists are working hard to develop more and more efficient ways to produce electricity using more carbon-neutral energy resources
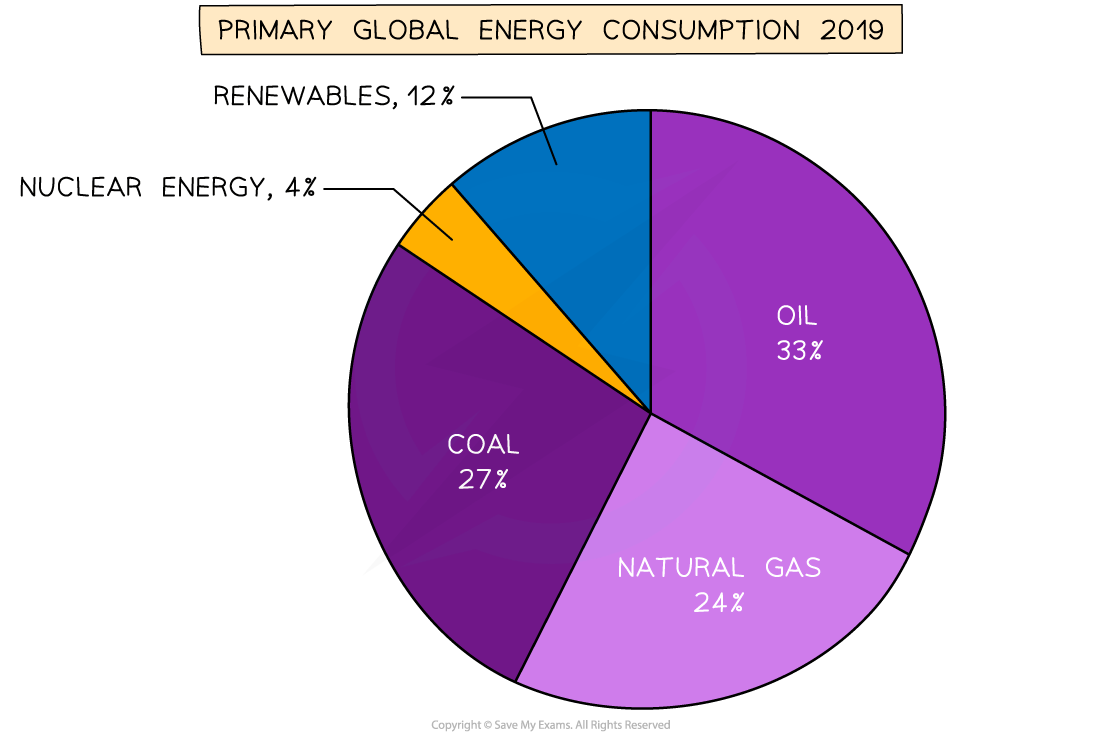
Pie chart of global energy consumption
Heating
- Most homes in cold countries are fitted with central heating systems
- These utilize natural gas in order to heat up water which can be pumped around radiators throughout the home
- Unfortunately, gas is a non-renewable energy resource
- In geologically active countries, such as Iceland, they are fortunate to be able to heat their homes using geothermal energy
Photovoltaic Cells & Solar Heating Panels
Solar Heating Panels
- Solar heating panels are used to heat tap water (for washing and showers) using the thermal energy of the Sun
- Solar heating panels can contain a water or glycol-water mixture which is pumped around to heat cold water from the main water supply
- The pumped fluid becomes hot within the solar panel and transfers this heat within a hot water storage cylinder
- A solar panel heating system is usually combined with a boiler to produce hot water at all times
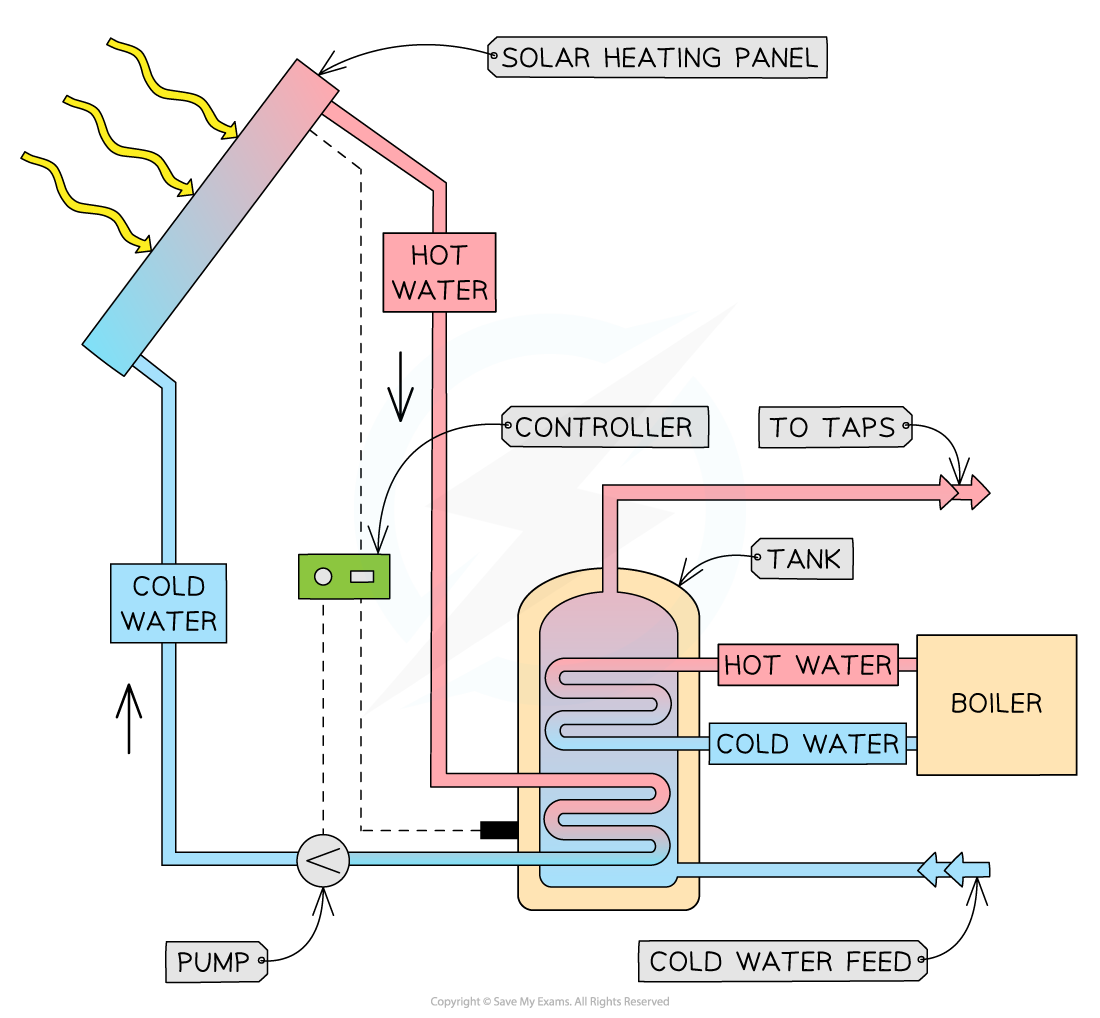
A solar heating panel system in a home
Photovoltaic Cells
- Photovoltaic (PV) cells are able to convert light from the Sun directly into electricity
- PV cells contain a single crystal of semiconductor that has been doped to have one side be a p-type semiconductor and the opposite side is an n-type semiconductor
- p-type and n-type relate their names to the majority of charge carriers within them
- negative electrons for the n-type semiconductor
- positive 'holes' which is the absence of electrons in the p-type semiconductor
- Photovoltaic cells generate electricity as follows:
- Light from the sun incident on the PV cell creates a photoelectric effect on the electrode at the surface
- The reflect-proof film prevents the light from being reflected back into the air
- Typically, the charge carriers in the semiconductor are in equilibrium, but when radiation is incident upon the PV cell, it enables electrons to move from the n-type layer to the p-type layer
- The movement of the electrons generates an electrical current
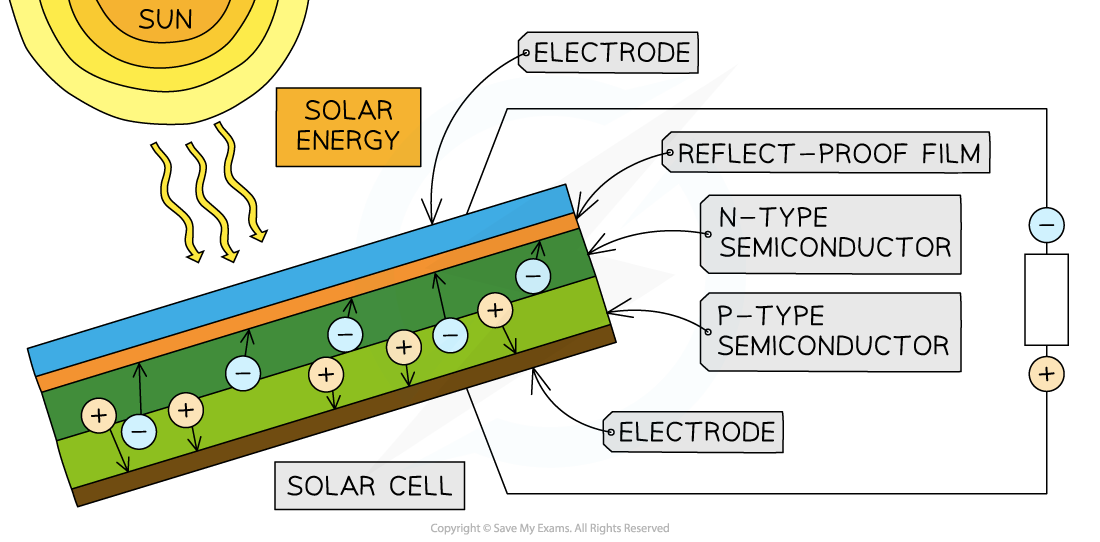
A simple diagram of a PV cell
- A solar panel system is made up of many PV cells in series and parallel within the panel to increase electrical generation
- Typical efficiencies of commercially available PV cell-based solar panels are around 20%
Advantages and disadvantages
- Advantages of using solar power include:
- Unlimited supply of energy
- Clean to produce the electricity
- Freely available everywhere
- Cheap maintenance
- No fuel is required for energy
- Disadvantages of using solar power include:
- Impacted by poor weather
- Limited efficiency
- Only available during the day
- Requires large investment upfront
- Needs large areas
Worked Example
A small community has solar panels which have an efficiency of 23%. They have arranged 103 m2 of solar panels to catch the sunlight incident upon them which has an intensity value of: 1.36 x 103 W m-2. Estimate the approximate power these solar panels will produce in 1 hour.
Step 1: List known values
-
- Solar panel area: 103 m2
- The average intensity of the Sun: 1.36 × 103 W m-2
- Solar panel efficiency: 23%
Step 2: Identify relationship needed
-
- The final answer required is power in Watts
- Therefore the quantities must be multiplied together
Power = Area × Average Intensity × Efficiency
Step 3: Perform the multiplication
Power = 103 × 1.36 × 103 × 0.23 = 3.2 × 104 W
Step 4: State the final answer
-
- The approximate power the solar panels will produce in 1 hour is: 3.2 × 104 W
Exam Tip
An in-depth understanding of how Photovoltaic cells works is not necessary for IB DP Physics, however a basic understanding of the process can be useful for tackling relevant questions.
