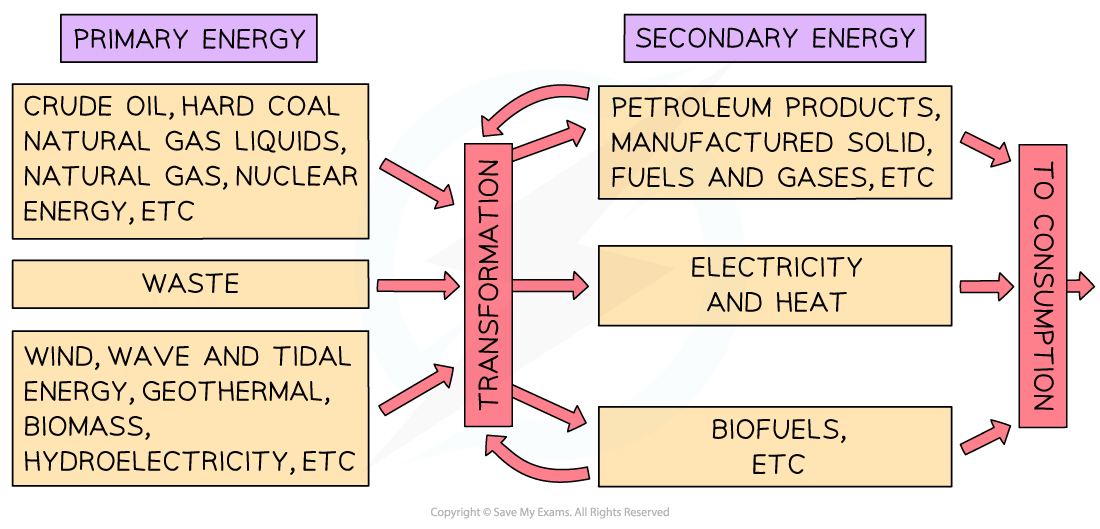
Primary Energy Sources
- Primary energy sources are found in nature and have some stored energy capacity
- To be a primary energy source, there must be:
- No processing or refining
- Stored energy must occur naturally in the source
- The definition of a primary energy source is:
Energy sources found in the natural environment
- Examples of primary energy sources include fuels such as:
- oil
- kerosene
- coal
- Nuclear material for fission
- Primary energy sources can also be renewables such as:
- Geothermal
- Heat from the Earth's crust
- Hydroelectric
- Energy stored in water higher than a set of turbines
- Solar power
- Radiation energy from the Sun
- Wind power
- Kinetic energy contained within the wind
- Tidal power
- Kinetic energy contained within the tides
- Geothermal
- In each example listed above, the primary energy source is the focus of the collection
- Once processing or conversion of energy from one form to another occurs, then it is no longer a primary energy source
Secondary Energy Sources
- Secondary energy sources come from the use or processing of primary energy sources
- Often the secondary energy source is electricity
- It can also be petrol, biofuel and heat
- The definition of a secondary energy resource is:
Useful transformations of the primary resources into energy
- Examples include:
- Stored gravitational energy from water is converted into electricity in a hydroelectric plant.
- Oil is refined to produce petrol that can be used to power a car
- Coal is burnt to produce heat on a fire
- The table below shows examples of primary and secondary energy sources as they are used to produce useful energy