Acid Deposition
What is acid deposition?
- Rain is naturally acidic because of dissolved CO2 which forms carbonic acid
H2O (l) + CO2 (g) ⇌ H2CO3 (aq)
- Carbonic acid is a weak acid and dissociates in the following equilibrium reaction giving a pH of 5.6
H2CO3 (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)
- For that reason acid rain is defined as rain with a pH of below 5.6
- Acid deposition includes all processes by which acidic components leave the atmosphere
- This could be gases or precipitates
- There are two types of deposition: wet acid deposition and dry acid deposition
- Wet acid deposition refers to rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog, mist and dew
- Dry acid deposition refers to acidic particles and gases that fall to the ground as dust and smoke
- Acid deposition is formed when nitrogen or sulfur oxides dissolve in water to form HNO3, HNO2, H2SO4 and H2SO3
Acid Deposition Equations
Formation of sulfur based acids
- Fossil fuels are often contaminated with small amounts of sulfur impurities
- When these contaminated fossil fuels are combusted, the sulfur in the fuels get oxidised to sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
- Sulfur dioxide may be further oxidised to sulfur trioxide
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3 (g)
- The sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide then dissolve in rainwater droplets to form sulfurous acid and sulfuric acid
SO2(g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
SO3 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO4 (aq)
- These acids are components of acid rain which has several damaging impacts on the environment
Formation of acid rain by nitrogen oxides
- The temperature in an internal combustion engine can reach over 2000 °C
- Here, nitrogen and oxygen, which at normal temperatures don’t react, combine to form nitrogen monoxide:
N2 (g)+ O2 (g) ⇌ 2NO (g)
- Nitrogen monoxide reacts further forming nitrogen dioxide:
2NO (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g)
- Nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with rain water to form a mixture of nitrous and nitric acids, which contribute to acid rain:
2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO2 (aq) + HNO3 (aq)
- Lightning strikes can also trigger the formation of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxides in air
- Nitrogen dioxide gas reacts with rain water and more oxygen to form nitric acid
4NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)→ 4HNO3 (aq)
- When the clouds rise, the temperature decreases, and the droplets get larger
- When the droplet containing these acids are heavy enough, they will fall down as acid rain
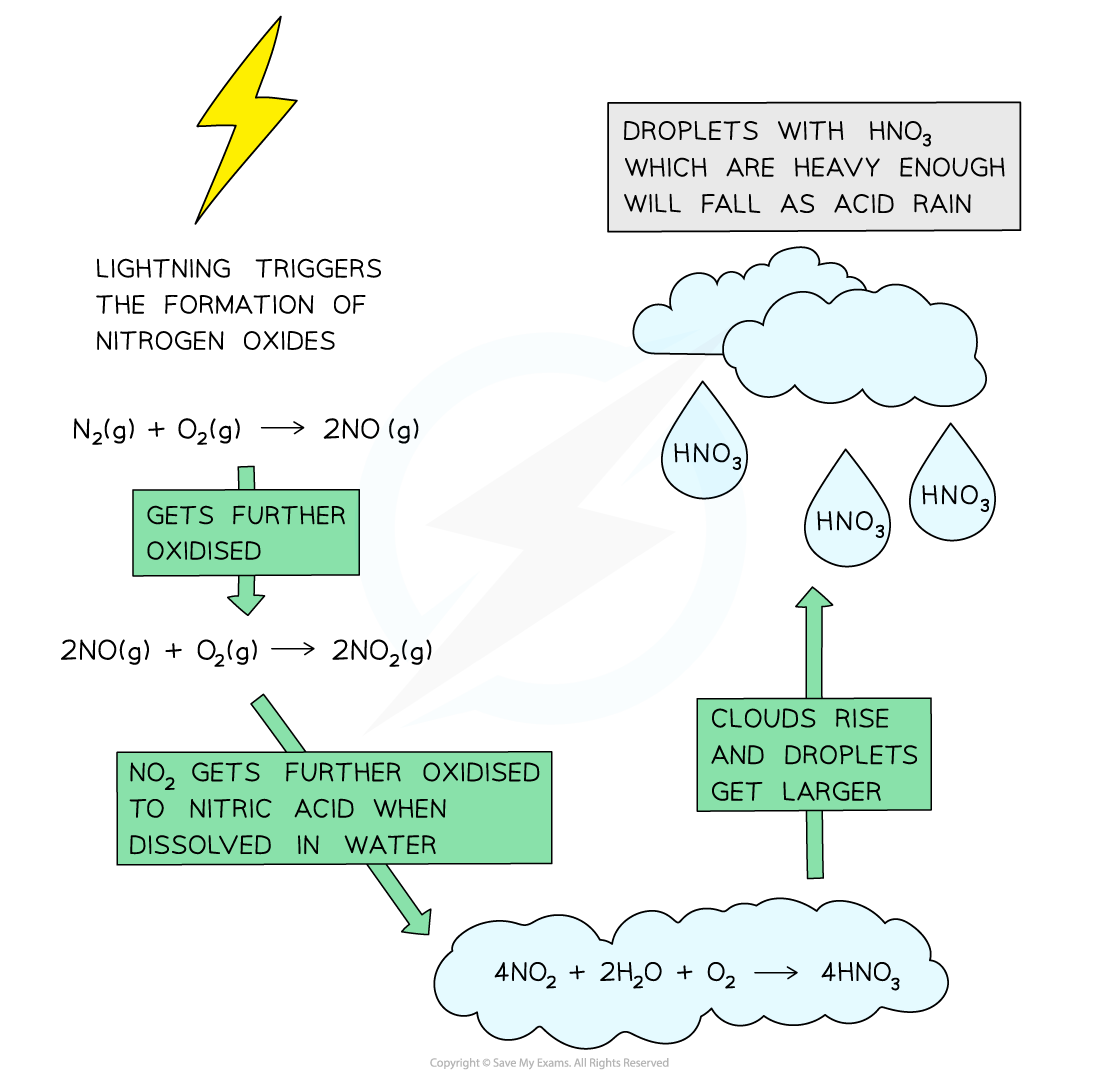
The diagram shows the formation of acid rain by the oxidation of nitrogen dioxide
