Forming Ions
- As a general rule, metals are on the left of the Periodic Table and non-metals are on the right-hand side
- Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from a metallic element to a non-metallic element
- Transferring electrons usually leaves the metal and the non-metal with a full outer shell
- Metals lose electrons from their valence shell forming positively charged cations
- Non-metal atoms gain electrons forming negatively charged anions
- Once the atoms become ions, their electronic configurations are the same as a noble gas.
- A sodium ion (Na+) has the same electronic configuration as neon: [2,8]
- A chloride ion (Cl-) also has the same electronic configuration as argon: [2,8,8]
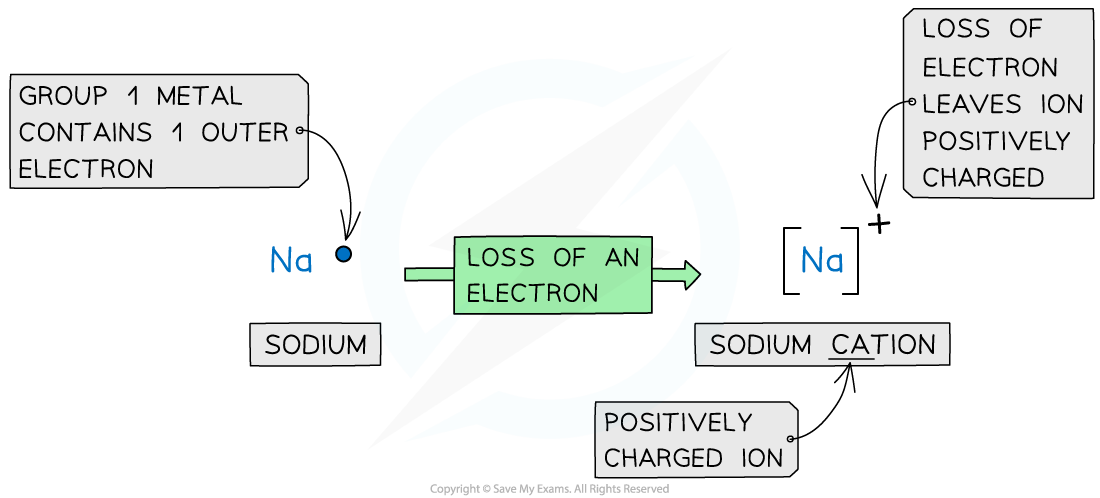
Forming cations by the removal of electrons from metals
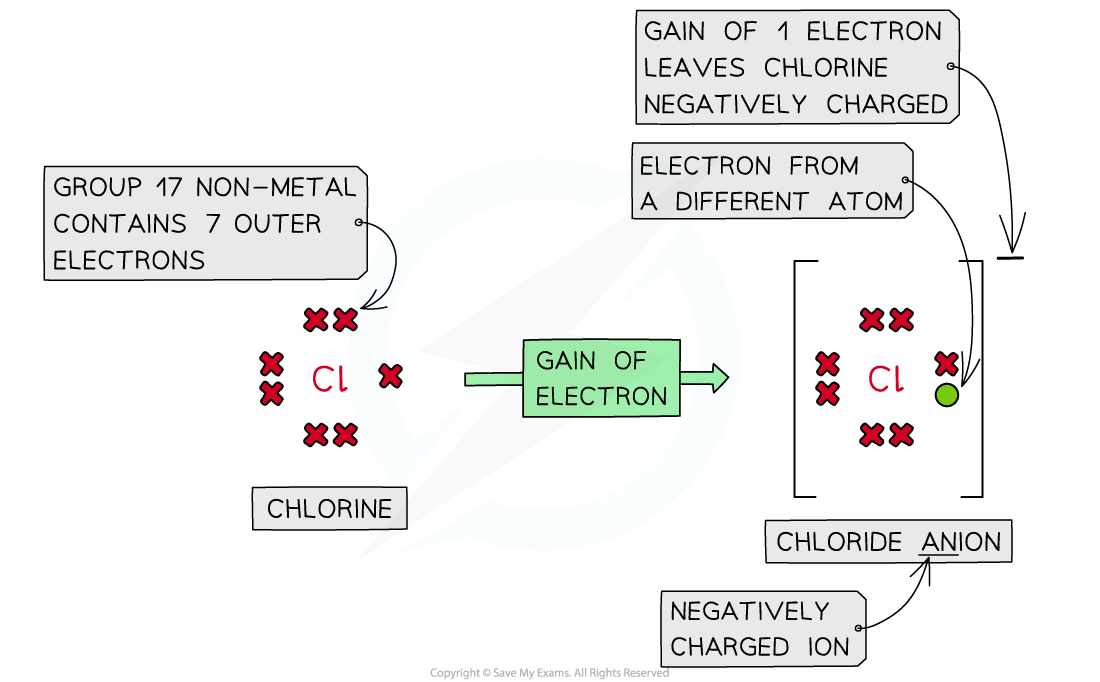
Forming anions by the addition of electrons to nonmetals
- Cations and anions are oppositely charged and therefore attracted to each other
- Electrostatic attractions are formed between the oppositely charged ions to form ionic compounds
- This form of attraction is very strong and requires a lot of energy to overcome
- This causes high melting points in ionic compounds
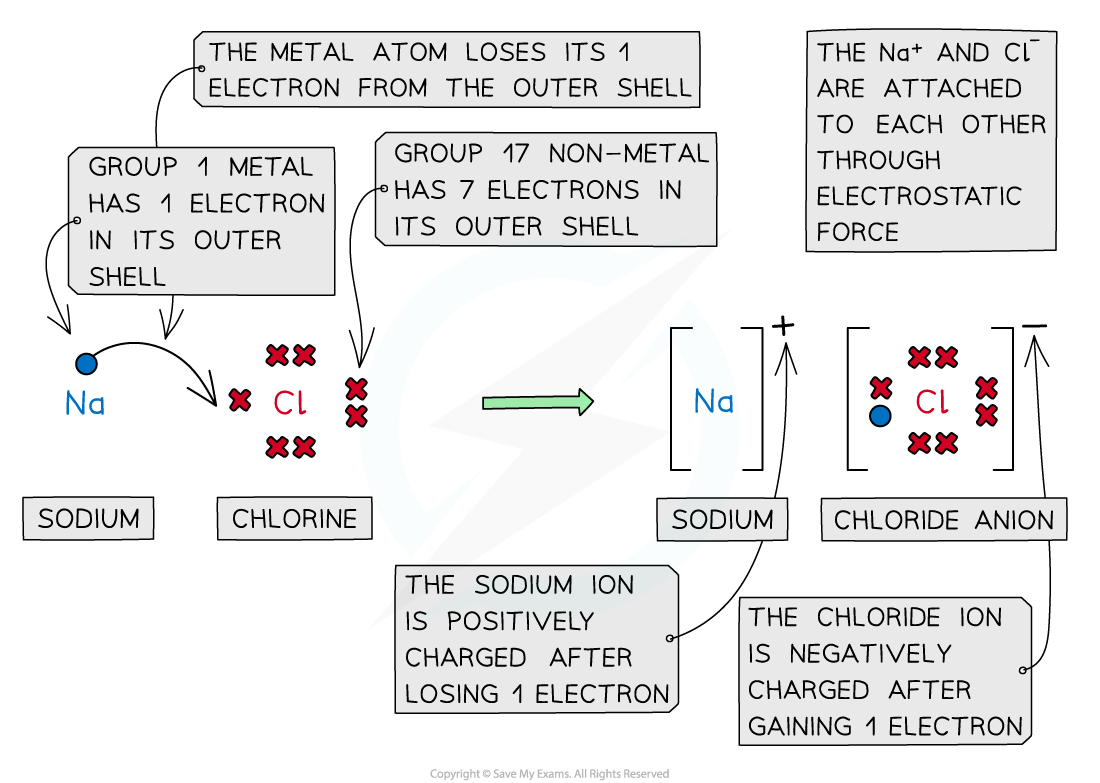
Cations and anions bond together using strong electrostatic forces, which require a lot of energy to overcome
Exam Tip
Metals usually lose all electrons from their outer valence shell to become cations.You can make use of the groups on the periodic table to work out how many electrons an atom is likely to lose or gain by looking at the group an atom belongs to.
