Ionic Lattices
- The ions form a lattice structure which is an evenly distributed crystalline structure
- Ions in a lattice are arranged in a regular repeating pattern so that positive charges cancel out negative charges
- Therefore the final lattice is overall electrically neutral
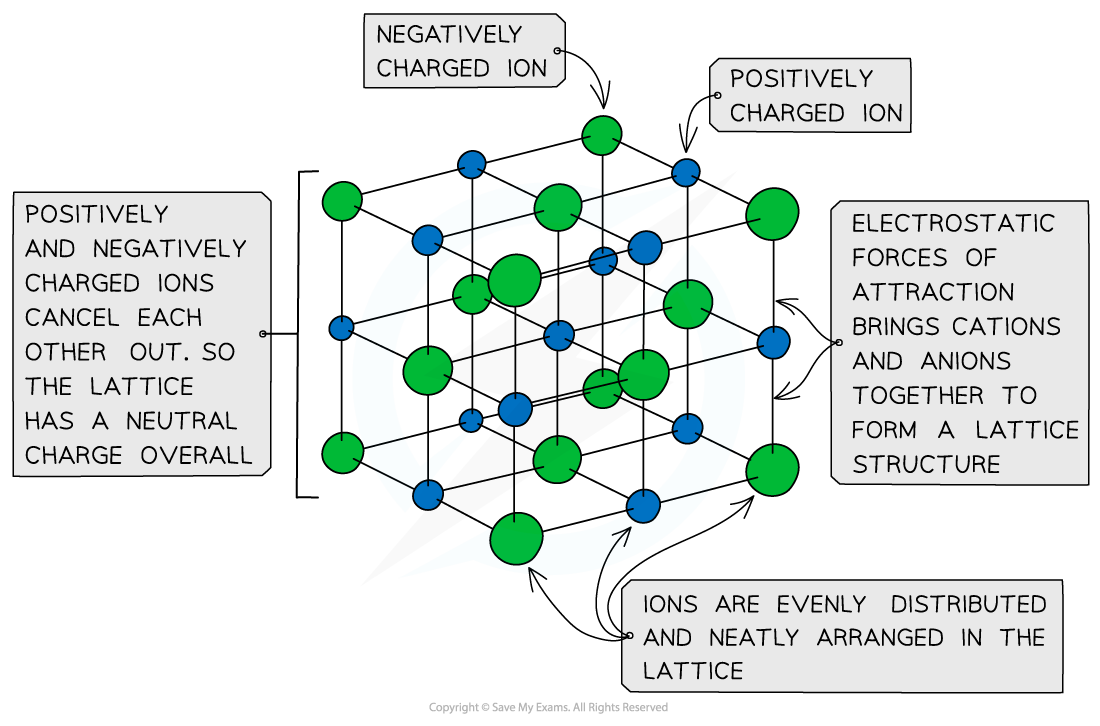
Ionic solids are arranged in lattice structures
Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Different types of structure and bonding have different effects on the physical properties of substances such as their melting and boiling points, electrical conductivity and solubility
Ionic bonding & giant ionic lattice structures
- Ionic compounds are strong
- The strong electrostatic forces in ionic compounds keep the ions strongly together
- They are brittle as ionic crystals can split apart
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points
- The strong electrostatic forces between the ions in the lattice act in all directions and keep them strongly together
- Melting and boiling points increase with charge density of the ions due to the greater electrostatic attraction of charges
- Mg2+O2- has a higher melting point than Na+Cl-
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water as they can form ion - dipole bonds
- Ionic compounds only conduct electricity when molten or in solution
- When molten or in solution, the ions can freely move around and conduct electricity
- In the solid state they’re in a fixed position and unable to move around
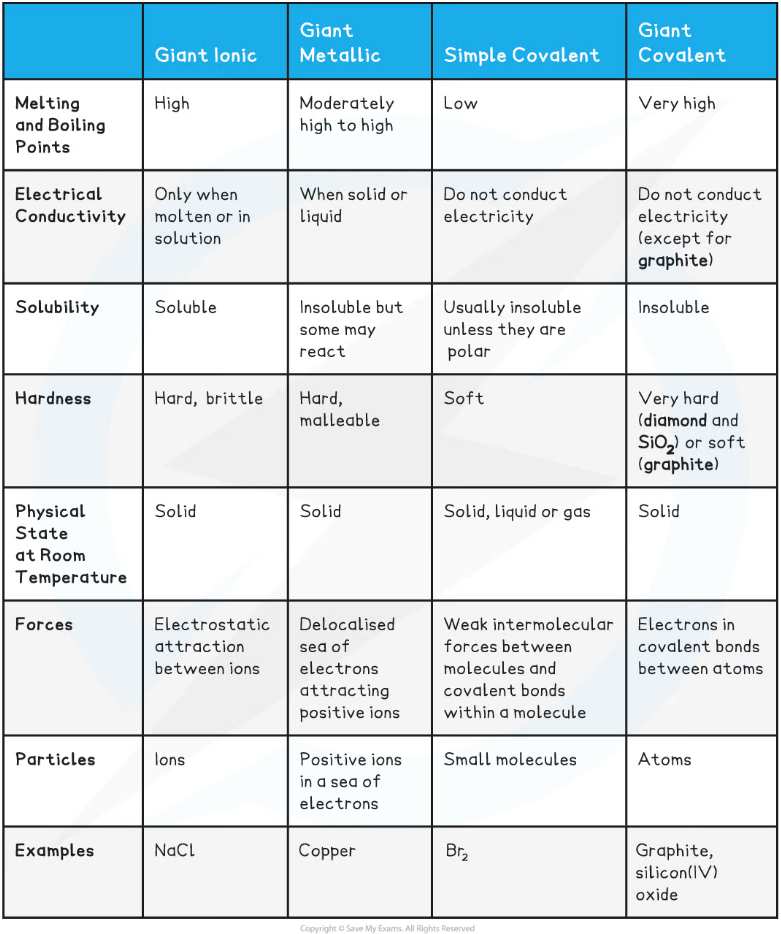
Characteristics of Giant Ionic Lattices compared to other Structures
Worked Example
The table below shows the physical properties of substances X, Y and Z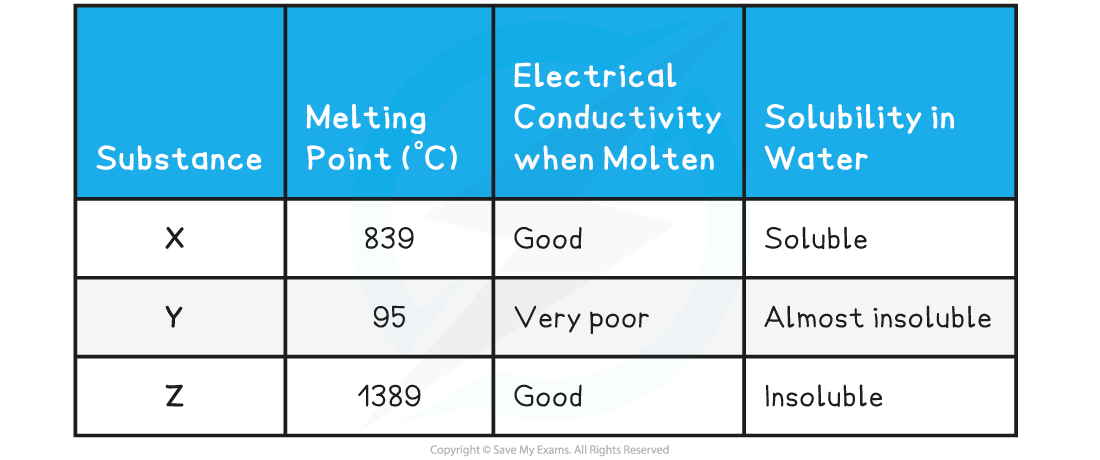
Which one of the following statements about X and Y is completely true?
Statement 1: X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a giant molecular structure, Z is a metal
Statement 2: X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant molecular structure
Statement 3: X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant ionic structure
Statement 4: X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z is a metal
Answer:
The correct answer is Statement 4
- The relatively high melting point, solubility in water and electrical conductivity when molten suggest that X is an giant ionic structure
- The low melting point of Y suggests that little energy is needed to break the lattice which corresponds to a simple molecular structure. This is further supported by the low electrical conductivity and almost insoluble in water
- Compound Z has a very high melting point which is characteristic of either metallic or giant molecular lattices, however since it conducts electricity, compound Z must be a giant metallic lattice
