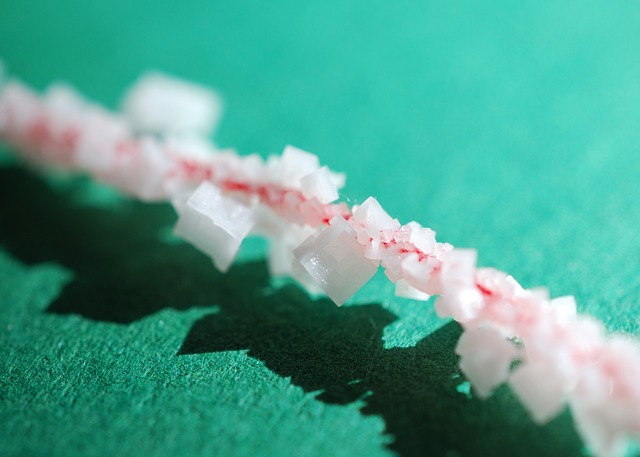
 Chemical bonding - lasting attraction between particles - is electrostatic in nature (attraction between positive and negative) although the character of the bonding depends on the chemical species involved. Chemical structure is the (microscopic) spatial arrangement of particles, often in repeating patterns, that gives a substance particular macroscopic (large scale) properties.
Chemical bonding - lasting attraction between particles - is electrostatic in nature (attraction between positive and negative) although the character of the bonding depends on the chemical species involved. Chemical structure is the (microscopic) spatial arrangement of particles, often in repeating patterns, that gives a substance particular macroscopic (large scale) properties.
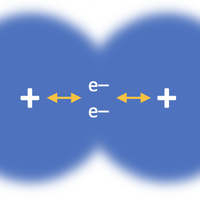
Covalent bonding
Topic 4.2 Covalent bonds form between non-metal atoms.
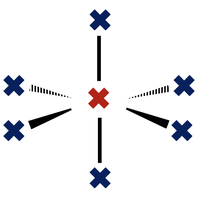
Covalent structure
Topic 4.3 Covalent compounds can be molecules (of various shapes) or giant structures.
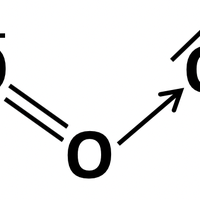
Further covalent bonding and structure
Topic 14.1 Extending our understanding of covalent bonds and structures.
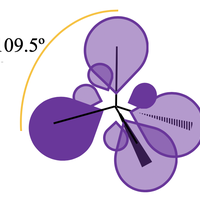
Hybridization
Topic 14.2 Hybridization, an adjustment to our bonding model, is more straightforward that it at first appears.
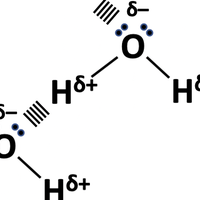
Intermolecular forces
Topic 4.4 Exploring the forces that exist between molecules.
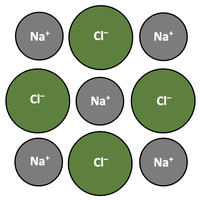
Ionic bonding and structure
Topic 4.1 Ionic compounds form between metals and non-metals.
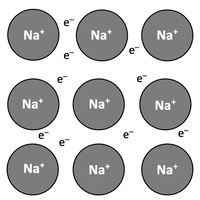
Metallic bonding
Topic 4.5 Metallic bonding and structure gives metals particular properties.


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn