 This section requires a sound knowledge of the rest of the acids and bases topics, that is Theories and properties of acids and bases, along with pH, strong and weak acids and acid deposition, and also Calculations involving acids and bases. Ensure you are confident with those topics before you begin your revision here.
This section requires a sound knowledge of the rest of the acids and bases topics, that is Theories and properties of acids and bases, along with pH, strong and weak acids and acid deposition, and also Calculations involving acids and bases. Ensure you are confident with those topics before you begin your revision here.
Ensure you are confident using the terms below and learn the asterisked* definitions
Lewis acid*, Lewis base*, A dative (coordinate) bond*, Equivalence point, Half equivalence point, Salt hydrolysis, Buffer solution*
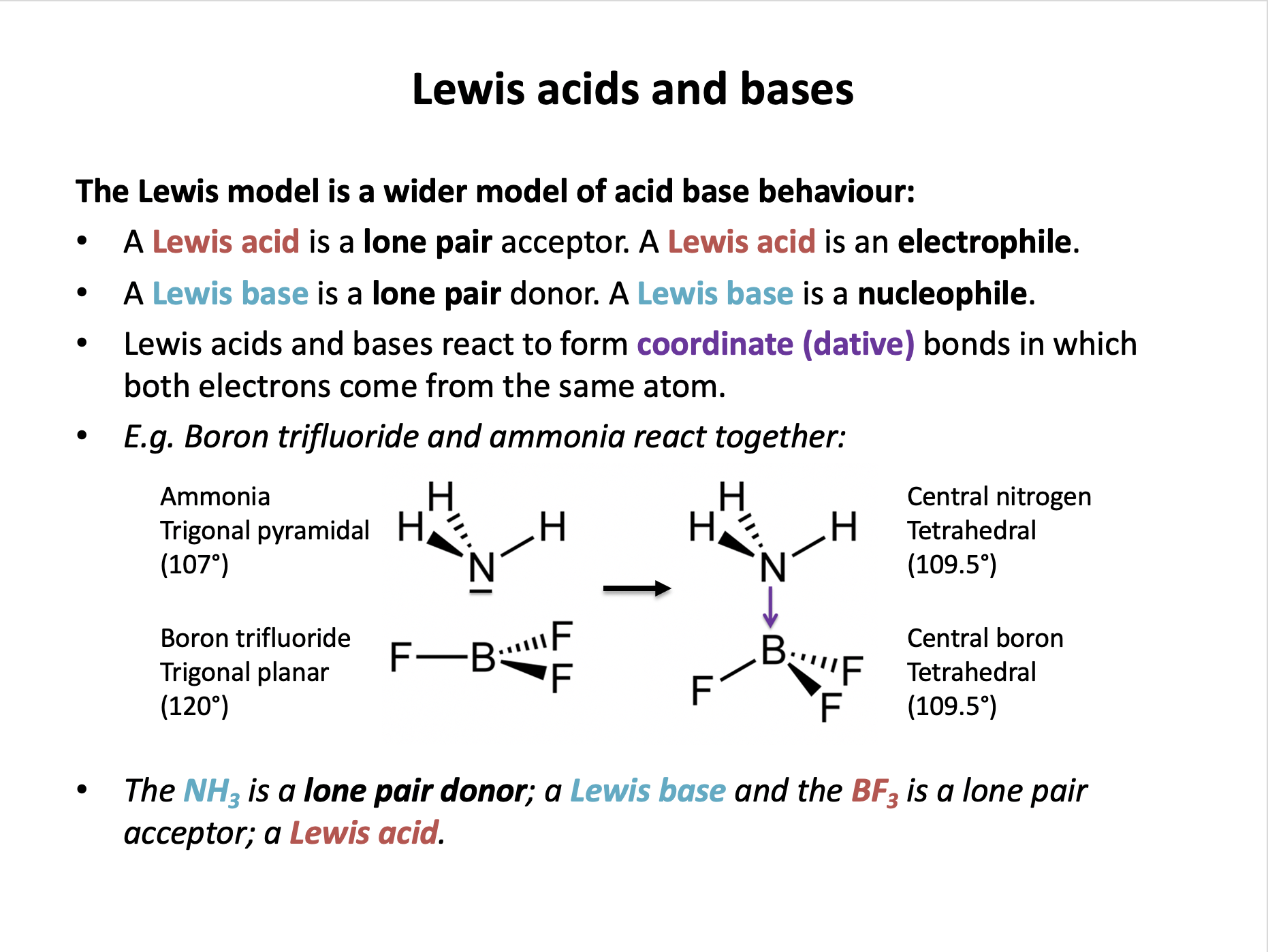
Why can ammonia be described as a Lewis base?
A Lewis base is a substance that can donate a pair of electrons to a lewis acid, forming a co-ordinate (dative) bond.
The other statements about ammonia are ture but do not explain why it can behave as a Lewis base. (Bronsted-Lowry bases can accept H+ ions.)
The correct answer is therefore It can donate a pair of electrons to form a co-ordinate bond.
Which of the following could correctly be described as an electrophile?
An electrophile is a substance which can accept a lone pair of electrons, which is an identical description to that of a Lewis acid.
Likewise, a nucleophile is equivalent to a Lewis base as it can donate a lone pair of electrons.
Lewis acid is therefore the correct answer.
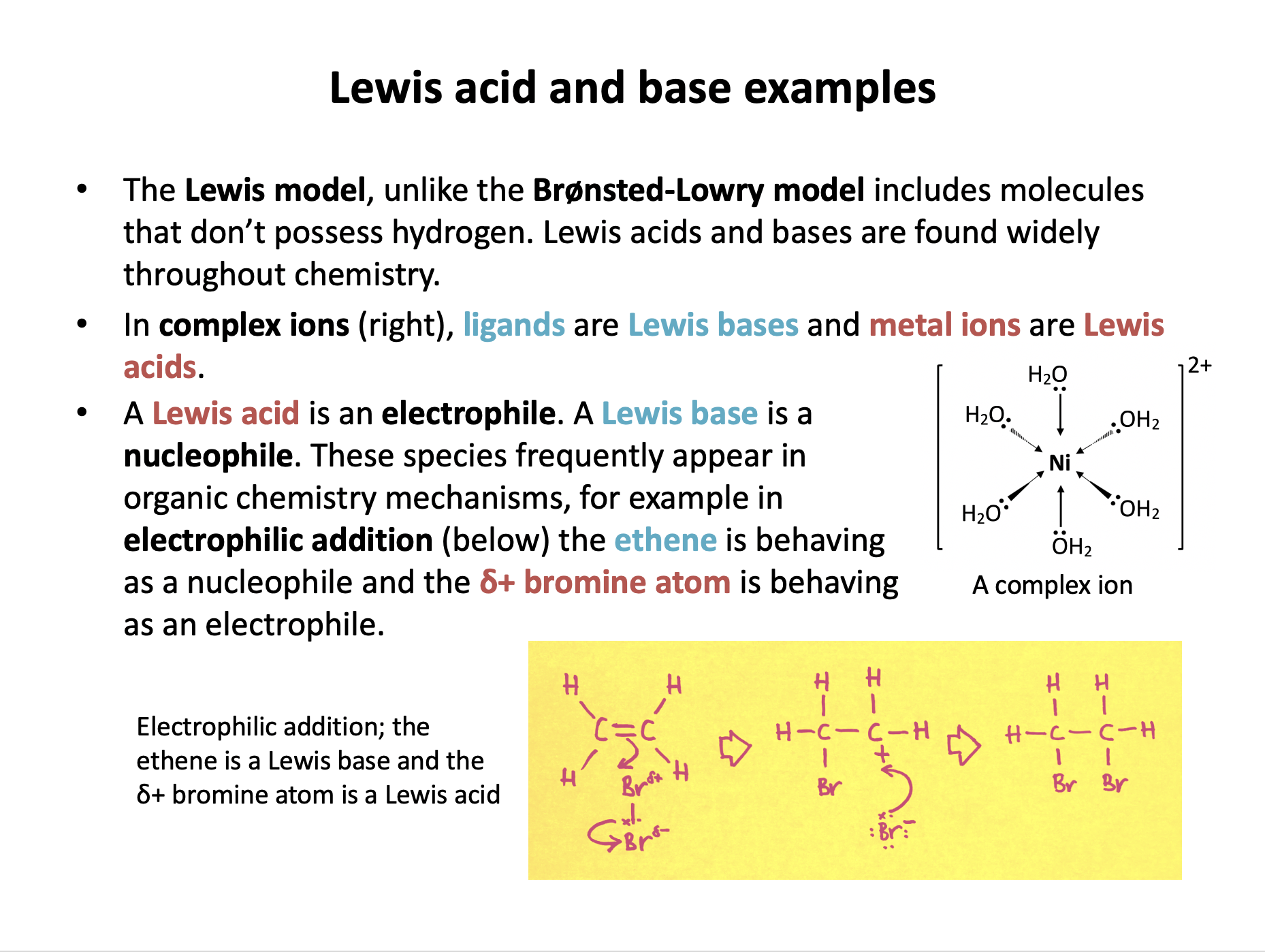
When copper(II) ions dissolve in aqueous solution, the hexaaquacopper(II) complex ion, [Cu(H2O)6]2+ is formed.
Which of the following correctly describes the Cu2+ ion in this process?
A ligand in a complex ion donates a pair of electrons to the central metal ion. The ligand is behaving as a Lewis base (nucleophile) as it is donating a pair of electrons. The central metal ion is behaving as a Lewis acid (electrophile) as it is accepting a pair of electrons. Coordinate (dative) bonds form.
The Cu2+ ion is the central metal ion in this complex.
Therefore the correct answer is A Lewis acid.
Ethene reacts with hydrogen bromide in an addition reaction to produce bromoethane.
Which of the following correctly describes the ethene molecule in this process?
Alkenes react with halogens and hydrogen halides in an electrophilic addition reaction.
The C=C double-bond of the ethene behaves as a Lewis base (a nucleophile) and donates a pair of electrons to the δ+hydrogen atom of the hydrogen bromide. The δ+hydrogen atom of the hydrogen bromide is behaving as a Lewis acid (an electrophile), and accepting a pair of electrons, hence the name of the mechanism - electrophilic addition.
Therefore the correct answer is A Lewis base.
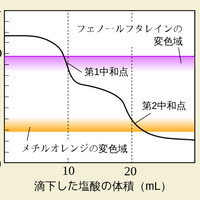
The graph below represents a pH titration curve. Which of the following combinations of acid and base could generate this curve?
The shapes of the four pH titration curves need to be learned.
The low starting pH and high finishing pH and the long steep inflection in the curve indicate that this is a strong acid, strong base pH curve.
Strong acid and strong base is the correct answer.
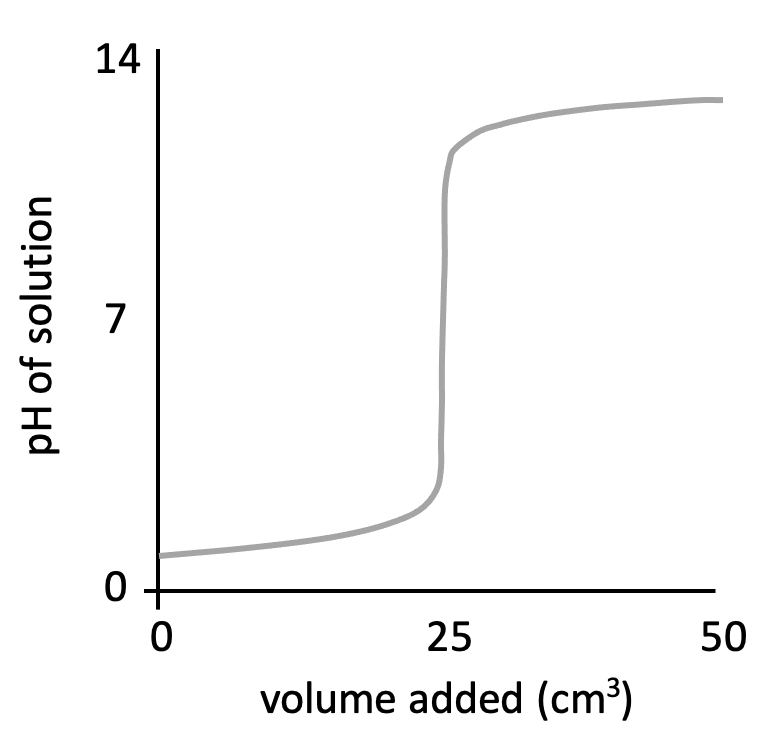
The graph below represents a pH titration curve. Which of the following combinations of acid and base could generate this curve?
The shapes of the four pH titration curves need to be learned.
The low starting pH, finishing pH of ∼11, and the steep inflection in the curve below pH 7 indicate that this is a strong acid, weak base pH curve.
Hydrochloric acid and methylamine solution is therefore the correct answer.
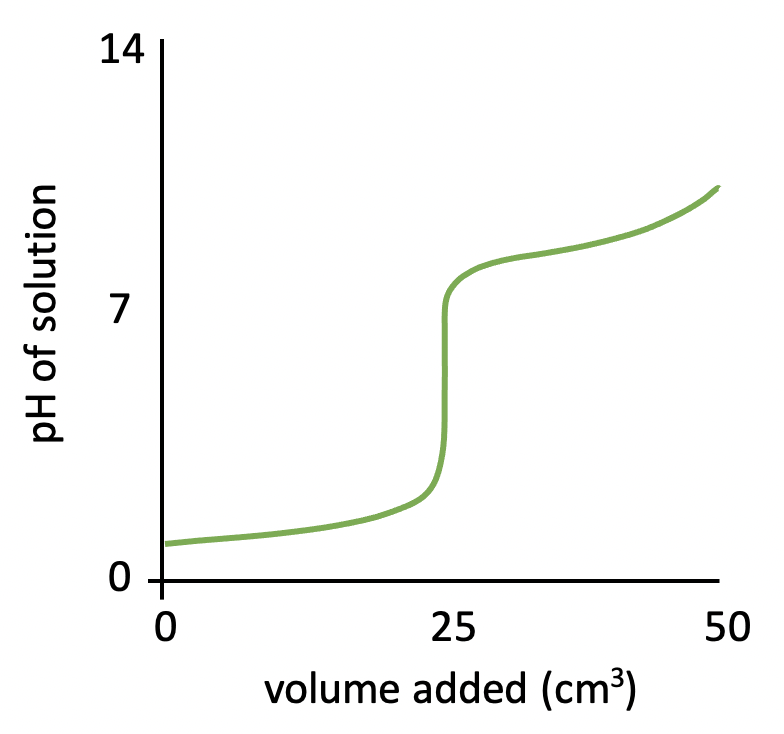
The graph below represents a pH titration curve. Which of the following statements about the curve are correct?
1: The pH curve could have been produced by titration of ethanoic acid with ammonia solution.
2: The equivalence point is at approximately pH 9.
3: Phenolphthalein indicator could be used for this titration.
The shapes of the four pH titration curves need to be learned.
The starting pH (∼3), high finishing pH and the steep inflection in the curve above pH 7 indicate that this is a weak acid, strong base pH curve. Therefore the curve could not have been produced by titration of ethanoic acid with ammonia solution, since they are both weak.
The equivalence point is the point at which the moles of acid = moles of base, and for a weak acid and strong base pH curve, this is typically around pH 9.
The indicator used must change colour within the pH range that corresponds to the steep infection in the curve. The data book indicates that phenolphthalein's pH range is 8.3-10.0, which does correspond to the steep inflection between pH 7 and 11.
2 and 3 only is therefore the correct answer.
Which of the following will form a buffer solution?
1: 20cm3 of 0.1 mol dm−3 ethanoic acid and 20cm3 of 0.1 mol dm−3 sodium ethanoate
2: 20cm3 of 0.1 mol dm−3 ethanoic acid and 10cm3 of 0.1 mol dm−3 sodium hydroxide
A buffer solution is the solution of a weak acid and salt of the weak acid (or weak base and salt) that resists/opposes changes in pH upon addition of small amounts of acid or base.
A combination of ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate (in any reasonable quantities) will therefore form a buffer solution.
A combination of an excess of ethanoic acid with sodium hydroxide will also form a buffer solution, since all of the sodium hydroxide will be neutralised and will produce sodium ethanoate.
Mixture 2 does have an excess of ethanoic acid (reaction mole ratio is 1:1) so will form a buffer solution.
1 and 2 is therefore the correct answer.
Which of the following statements about a buffer solution made up of ammonia solution and ammonium chloride solution are correct?
1: The initial pH of the buffer will be greater than 7.
2: Upon the addition of a small quantity of acid, ammonia will react with water to produce hydroxide ions.
3: Upon the addition of a large quantity of concentrated alkali the pH will significantly increase.
A buffer solution is the solution of a weak acid and salt of the weak acid (or weak base and salt) that resists/opposes changes in pH upon addition of small amounts of acid or base.
The buffer solution here has the following equilibrium:
NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH−
The solution will have a pH greater than 7, since it is an alkali buffer.
Addition of a small quantity of acid will react with the OH− (H+ + OH− → H2O) and the equilibrium will shift to the right to replace the lost OH−; so the ammonia is reacting with water to produce hydroxide ions.
Any buffer can only resist changes in pH for a small quantity of added acid or base, so addition of a large quantity of concentrated alkali will cause the pH to significantly increase.
1, 2 and 3 is therefore the correct answer.
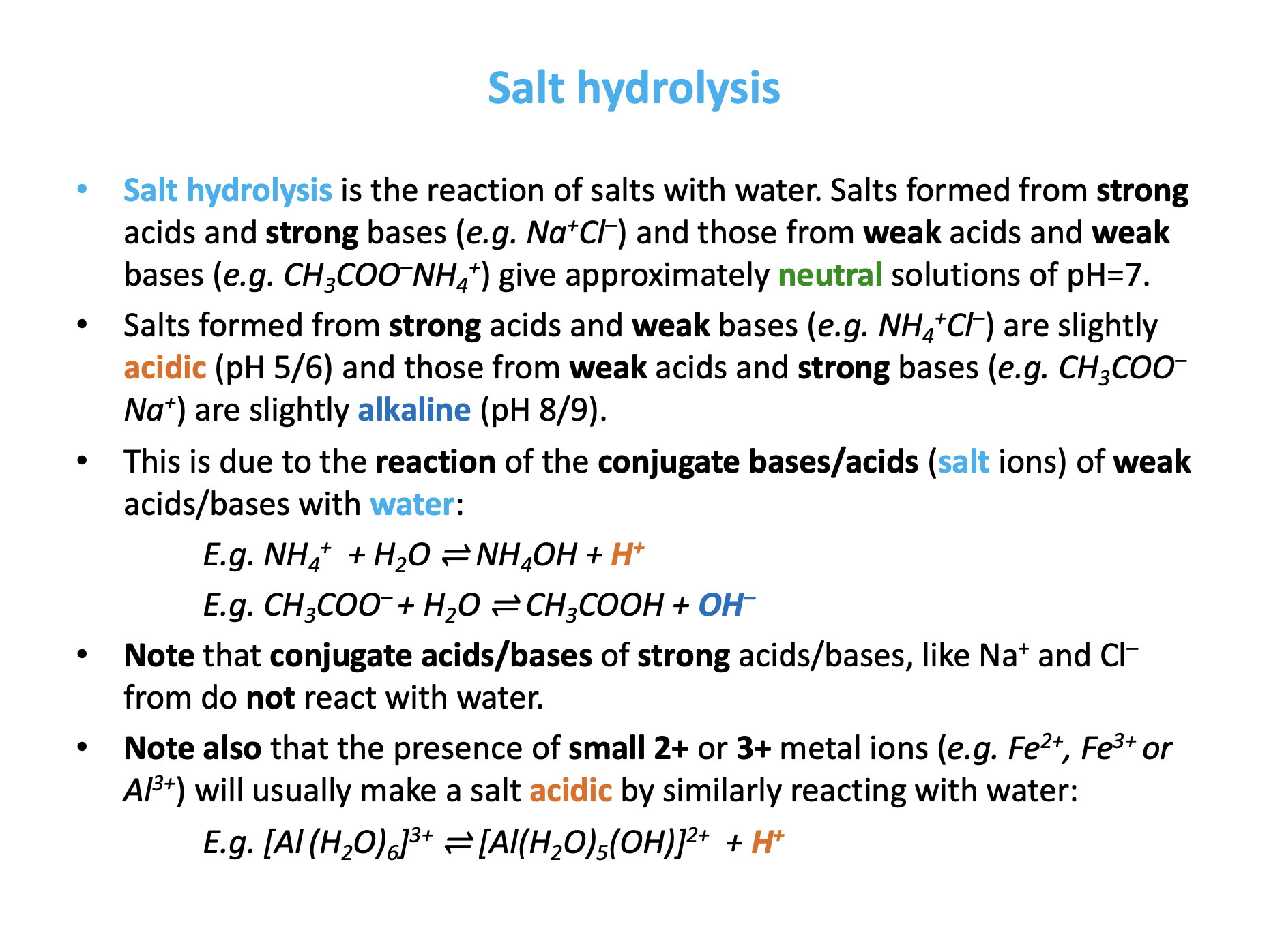
Which of the following will be the most acidic when dissolved in water?
KOH is a strong base so will not be acidic.
The other three options are all salts.
As a useful rule-of-thumb, salts formed from strong acids and strong bases (e.g. NaCl) and those from weak acids and weak bases give approximately neutral solutions of pH=7.
Salts formed from strong acids and weak bases (e.g. NH4Cl) are acidic and those from weak acids and strong bases (e.g. CH3COONa) are alkaline.
NH4Cl is therefore the correct answer.
Paper 1
Core (SL&HL): Acids and Bases core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions
AHL (HL only): Acids and Bases AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions
Paper 2
Core (SL&HL): Acids and Bases core (SL & HL) paper 2 questions
AHL (HL only): Acids and Bases AHL (HL only) paper 2 questions
How much of Lewis acids and bases, and pH curves have you understood?













 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn