Topics 10.1 and 10.2
Paper 1 style questions are multiple choice. You are not permitted to use a calculator or the data book for these questions, but you should use a periodic table.
A periodic table pop-up is available on the left hand menu.
Which compound is not in the same homologous series as the others?
Homologous series of compounds have the same general formula. Their formulae differ in successive sequence by CH2. They also have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. They show a gradation in physical properties.
CH4, C3H8 and C5H12 are all alkanes, with general formula CnH2n+2.
C4H8 (CnH2n) is an alkene and is therefore the correct answer.
Which functional group is circled in the molecule?
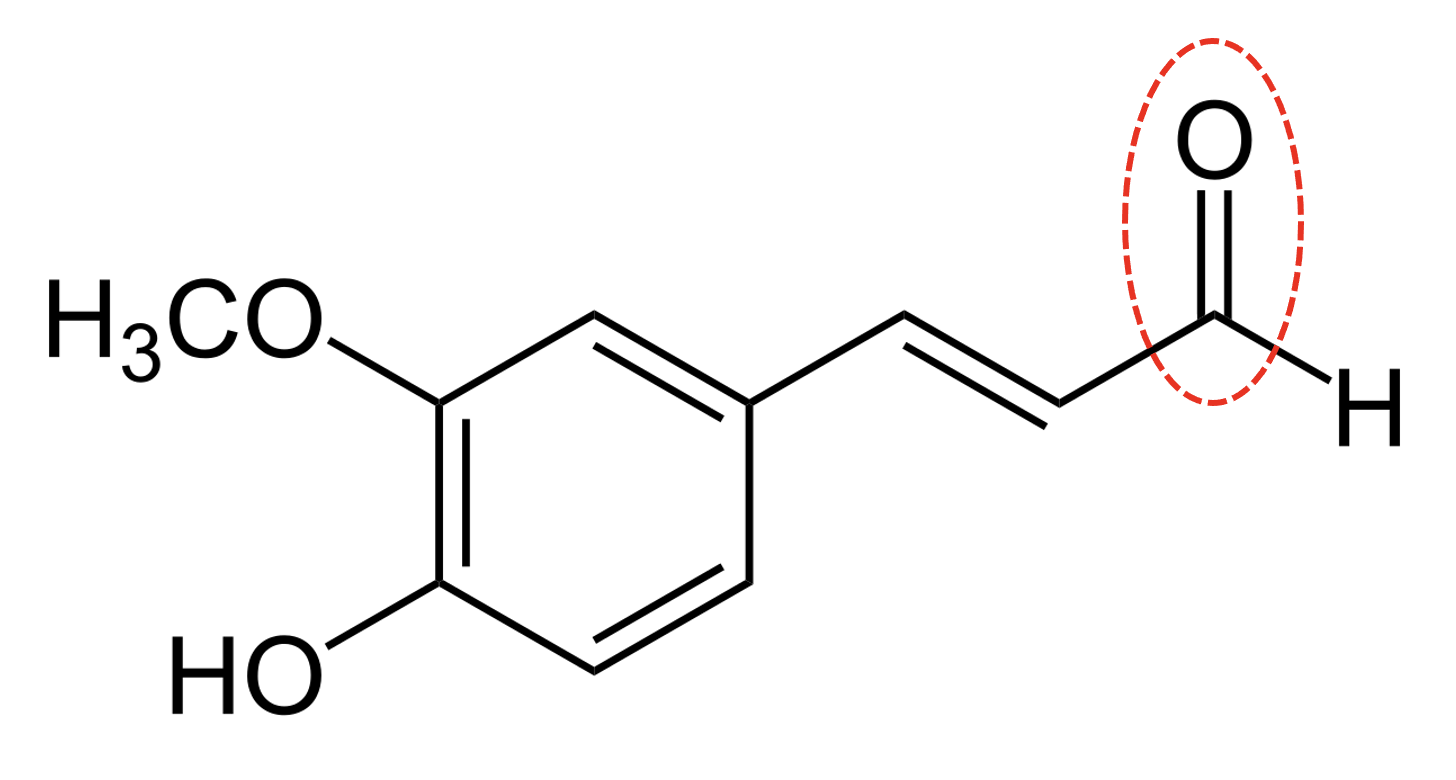
It is important to thoroughly learn all of the functional groups and the classes of compounds by heart, and to be confident in interpreting or drawing displayed formulae from structural or skeletal formula.
The functional group circled is C=O, which is a carbonyl group.
Carbonyl is therefore the correct answer.
Which compound has the lowest boiling point?
All the compounds have molecular formula C6H14 and are alkanes. Alkanes with greater branching tend to have lower molecular surface area so tend to form fewer London dispersion forces and therefore have lower boiling points.
CH3C(CH3)2CH2CH3 has the greatest amount of branching (two branched methyl groups) so will have the lowest boliing point and is therefore the correct answer.
Which compounds react to form CH3COOCH(CH3)2?
This is an esterification reaction. Esters are named by the 'alcohol part' first then the 'acid part', that is firstly the carbon chain section that is directly attached to the oxygen atom by a single bond, then the carbon chain section that includes the C=O.
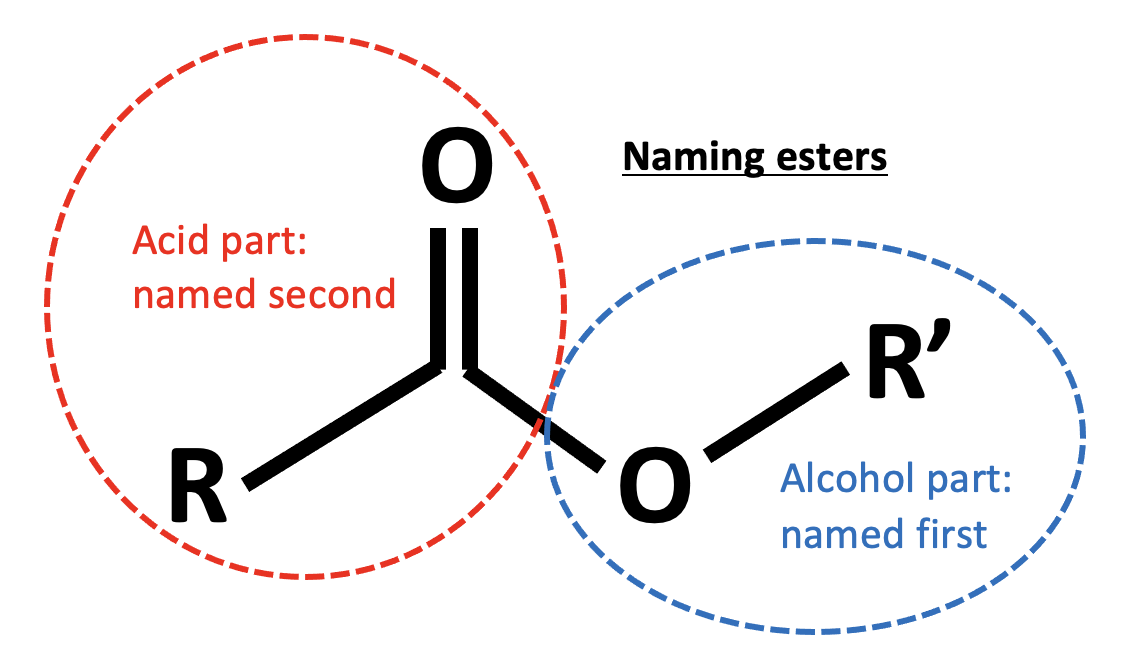
This ester, CH3COOCH(CH3)2 is 2-propyl ethanoate. The 'alcohol part' is from propan-2-ol (the oxygen is attached to the middle carbon in the chain of three) and the 'acid part' is from ethanoic acid.
Therefore the correct answer is Ethanoic acid and propan-2-ol.
What are the possible names of a molecule with molecular formula C3H8O?
1: Methoxy ethane
2: Propan-1-ol
3: Propanal
Methoxy ethane (CH3OC2H5) and propan-1-ol (CH3CH2CH2OH) both have molecular formula C3H8O.
Propanal (CH3CH2CHO) has molecular formula C3H6O.
Therefore 1 and 2 only in the correct answer.
What is the product of the reaction between but-2-ene and steam?
H2O (steam) will add across the double bond of the but-2-ene forming the alcohol:
CH3CHCHCH3 + H2O → CH3CHOHCH2CH3
The hydroxy (−OH) group could attach to carbon 2 or to carbon 3 of the chain. However, as the molecule is symmetrical, attachment to carbon 2 or 3 leads to the same product, which is named according to the convention of using the lowest integers.
Therefore, Butan-2-ol is the correct answer.
Which compound could be formed when CH3CH2CH2CH2OH is heated with acidified potassium dichromate?
1: CH3CH2CH2COOH
2: CH3COCH2CH3
3: CH3CH2CH2CHO
Using acidified potassium dichromate, primary alcohols (butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) can be oxidised to aldehydes (butanal, CH3CH2CH2CHO) using distillation, or to carboxylic acids (butanoic acid, CH3CH2CH2COOH) using reflux.
Primary alcohols cannot be oxidised to ketones (butanone, CH3COCH2CH3). Ketones are produced from secondary alcohols.
Therefore 1 and 3 only is the correct answer.
Which monomer could create this polymer?
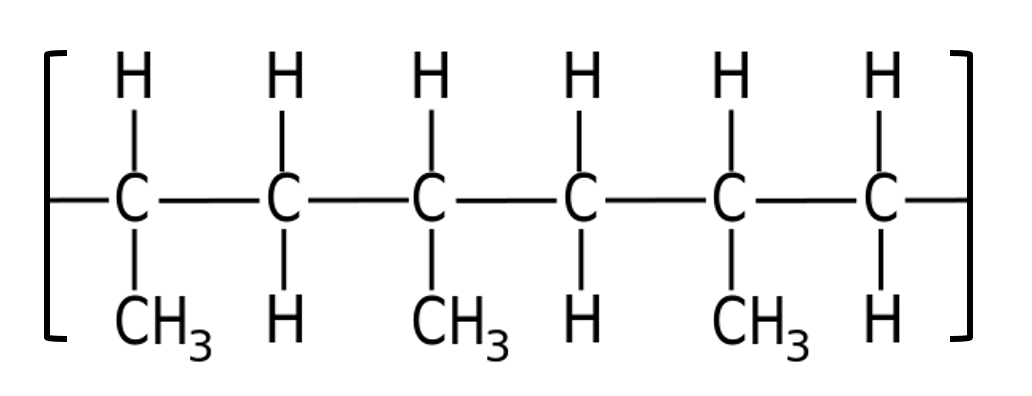
Identify the repeat unit:
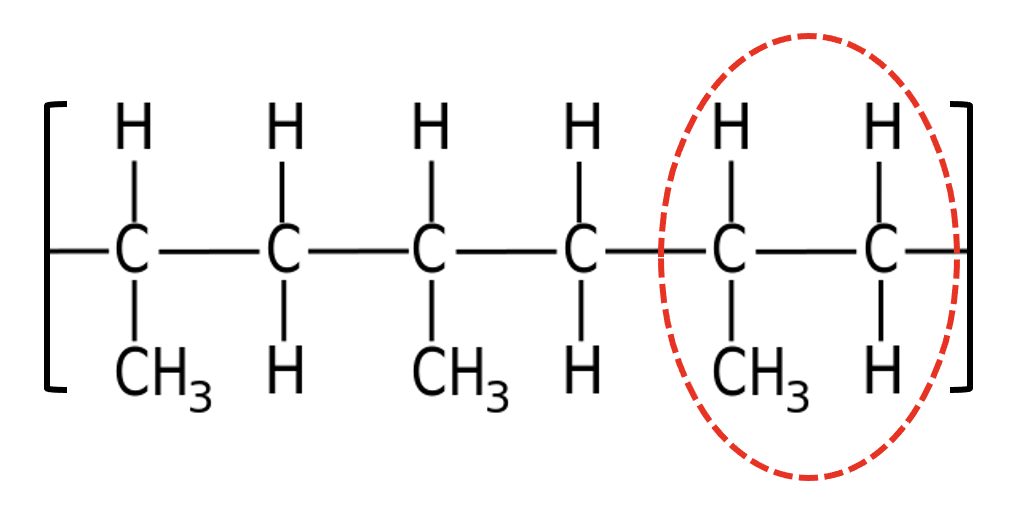
The repeat unit contains three carbons. The monomer must have a double carbon-carbon bond; the carbons in the polymer chain are linked through the double bonds. The alkene with three carbons must be propene.
Propene is therefore the correct answer.
What is the name of this compound using IUPAC rules?
Grey atoms are carbon, white are hydrogen, and red are oxygen.
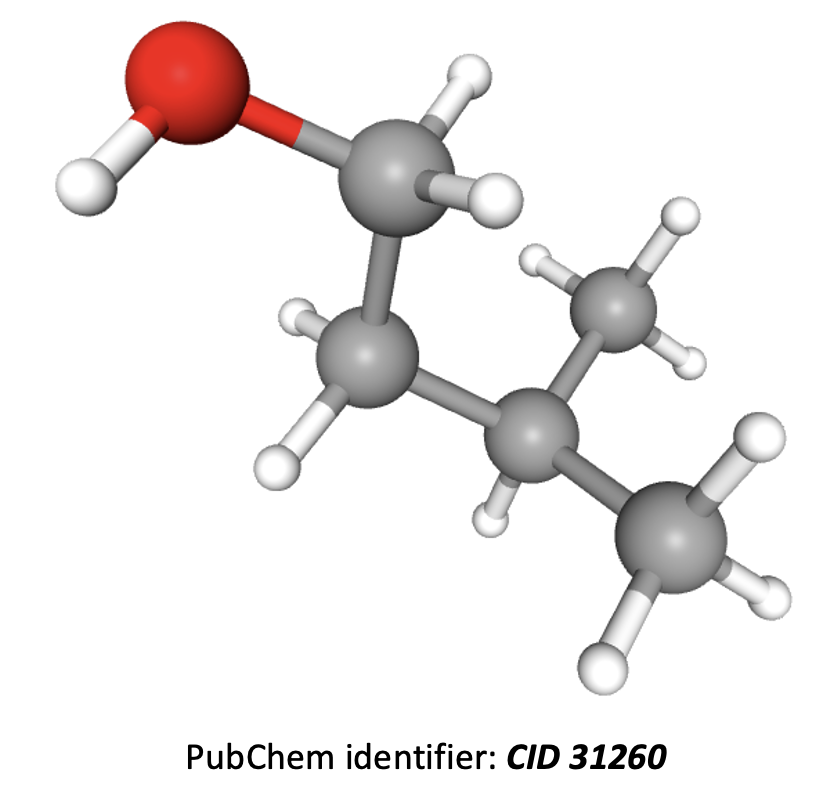
The longest carbon chain is 4 atoms, so the root of the name is butane. The molecule has a hydroxy (−OH) group on the end of the chain, and a methyl group is branched off the chain. The convention is for the name to have the lowest integers possible, so this molecule is 3-methylbutan-1-ol.
How many structural isomers of C6H14 exist?
Isomers have the same molecular formula but different structures.
C6H14 as a straight chain hydrocarbon is hexane (1st isomer)
It can be useful to think of reducing the longest chain length, and therefore adding branches, in a decreasing sequence:
5 carbons in a row with one (methyl) branch: 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane (2 isomers)
4 carbons in a row with two (methyl) branches: 2,3-dimethylbutane and 2,2-dimethylbutane (2 isomers)
Therefore 5 is the correct answer.
Which describes the reaction of propane and chlorine gas?
Alkanes (like propane) react with halogens (like chlorine) through a free radical mechanism requiring ultraviolet (UV) light. The UV light causes the halogen bond to break homolytically (The symmetrical breaking of a covalent bond so that one electron from the shared pair is left on each fragment, resulting in the formation of two free radicals).
Addition reactions, involving heterolytic bond breaking, occur between alkenes and halogens.
Mechanism: free radical, Bond fission: homolytic is therefore the correct answer.
Which structural formula represents a tertiary halogenoalkane?
A tertiary halogenoalkane has a halogen atom that is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to three other carbon atoms.
This is the case for CH3C(CH3)BrCH3
The other compounds are all secondary halogenoalkanes, in which the halogen is attached to a carbon atom that is attached to two other carbon atoms.
Therefore CH3C(CH3)BrCH3 is the correct answer.
How much of Organic chemistry core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions have you understood?


 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn