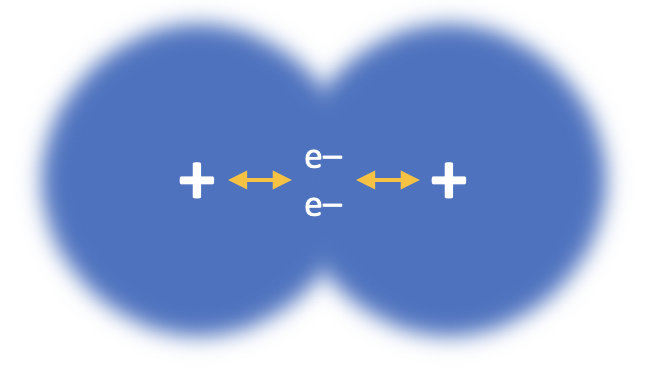
 Our model of covalent bonding is based on the Bohr model of the atom. We often think of a covalent bond as a shared pair of electrons (which it is) but be aware of the full definition that needs to be learned: A covalent bond is the electrostatic attraction between two nuclei and a pair of shared electrons.
Our model of covalent bonding is based on the Bohr model of the atom. We often think of a covalent bond as a shared pair of electrons (which it is) but be aware of the full definition that needs to be learned: A covalent bond is the electrostatic attraction between two nuclei and a pair of shared electrons.
Ensure you are confident using the terms below and learn the asterisked* definitions
a covalent bond*, bond polarity/dipole*, electronegativity*, electrostatic attraction, bonding pair, lone (non-bonding) pair
What is a covalent bond?
The correct answer is the electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared pairs of electrons. The other explanations represent different types of bonding (ionic, metallic and intermolecular).
How many electrons in total are shared between nitrogen atoms in an N2 molecule?
The bond between the two nitrogen atoms is a triple bond (N≡N). Each bond consists of a pair of electrons, thus 3 × 2 = 6 electrons is the correct answer.
The number of bonds that non-metals atoms are likely to form can be predicted by their valency, and corresponds to the number of electrons needed for a full valence shell.
| Group number - old (new system) | IV (14) | V (15) | VI (16) | VII (17) |
| Electrons in outer (Bohr) shell | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Valency | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Example | C | N | O | Cl |
Metals tend not to form covalent bonds. Hydrogen has a valency of 1.
Ethane, ethene and ethyne have single, double and triple bonds respectively between the carbon atoms:
C–C ; C=C ; C≡C
Which is the shortest and which is the strongest of the bonds?
The shorter the bond, the stonger the bond, since the electrostatic attraction between the shared electrons and the nuclei becomes greater the closer they are. Triple bonds are stronger and shorter than double bonds which are stronger and shorter than single bonds due to the greater number of electrons in the bond.
Thus: C≡C is the shortest and the strongest, is the correct answer.
Which is the best definition of electronegativity?
A measure of...
Electronegativity is defined as '...the relative ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond'.
Which of the following bonds is the most polar?
F–O ; O–C ; O–N; N–C
Polarity of a bond can be estimated by looking at the difference in electronegativity of the elements of the atoms involved. Electronegativity values can be found in the data book:
| C | N | O | F |
| 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 4.0 |
The C–O bond with a 0.8 difference is the most polar.
When you don't have a data book, remember that electronegativity increases moving right and upwards across the periodic table. All of the bonds given are made up of elements next to each other in the periodic table except for the C–O bond, which has greater separation and is therefore likely to be the most polar.
Which representation shows the correct dipoles for the bonds in a molecule of an alcohol (hydroxyl functional group)?
Polarity of a bond can be estimated by looking at the difference in electronegativity of the elements of the atoms involved. Electronegativity values can be found in the data book:
| C | O | H |
| 2.6 | 3.4 | 2.2 |
When you don't have a data book, remember that electronegativity increases moving right and upwards across the periodic table. Hydrogen is an exception; remember that it has an electronegativity very similar to, but slightly less than carbon.
Here the oxygen atom is more electronegative than both carbon and hydrogen, so will carry the δ– charge; both C and H will carry a δ+ charge as they are less electronegative than O.
Paper 1
Core (SL&HL): Bonding and Structure core (SL and HL) paper 1 questions
AHL (HL only): Bonding and Structure AHL (HL only) paper 1 questions
Paper 2
Core (SL&HL): Bonding & Structure core (SL & HL) paper 2 questions
AHL (HL only): Bonding & Structure AHL (HL only) paper 2 questions
How much of Covalent bonding have you understood?








 Twitter
Twitter  Facebook
Facebook  LinkedIn
LinkedIn