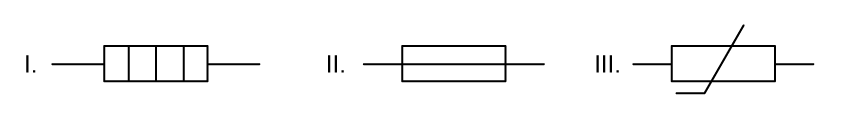
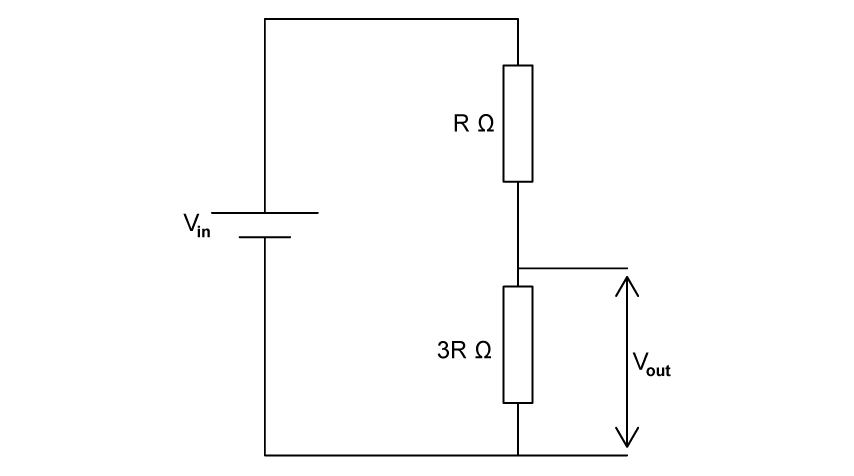Select the row which correctly identifies the three circuit symbols shown below.
I. II. III.
A. heating element
potentiometer
variable resistor
B. heating element
fuse
thermistor
C. resistor
ammeter
variable resistor
D. voltmeter
fuse
thermistor
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Next Question
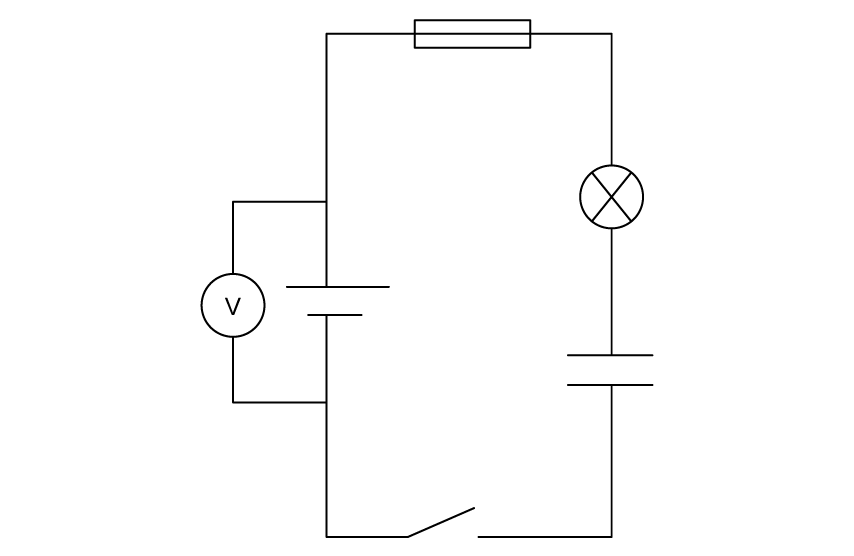
Identify two features of the circuit shown.
A. a bulb is in series with a fixed resistor
current can be measured through the cell
B. a bulb is protected by a fuse
current can be measured through the bulb
C. a bulb is protected by a fuse
voltage can be measured across the cell
D. a capacitor is in series with a fuse
voltage can be measured across the bulb
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Electrons moving through a metal wire transfer some of their electric potential energy to the positive ions of the metal. Which two changes are caused by this energy transfer?
Kinetic energy of the lattice Resistance of the metal wire
A. decreases
decreases
B. decreases
increases
C. increases
decreases
D. increases
increases
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
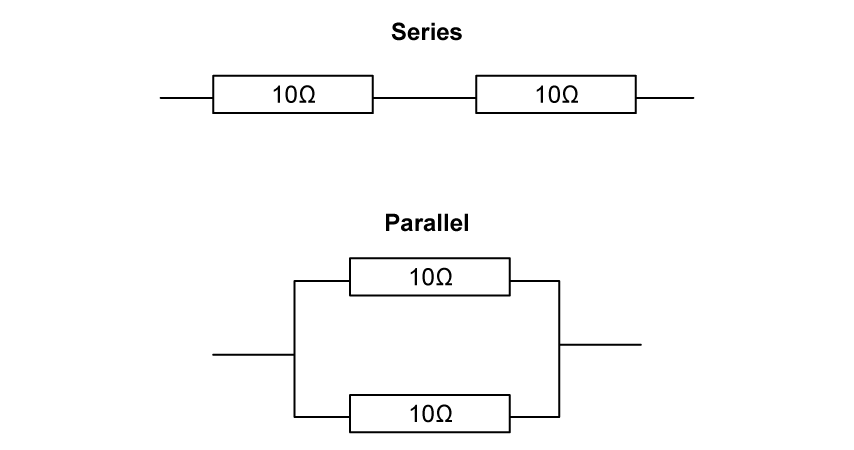
Two identical 10 Ω resistors are connected first in series, and then in parallel, as shown.
Determine the correct combined resistance of each arrangement.
Series Parallel
A. 5 Ω
20 Ω
B. 10 Ω
20 Ω
C. 20 Ω
10 Ω
D. 20 Ω
5 Ω
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
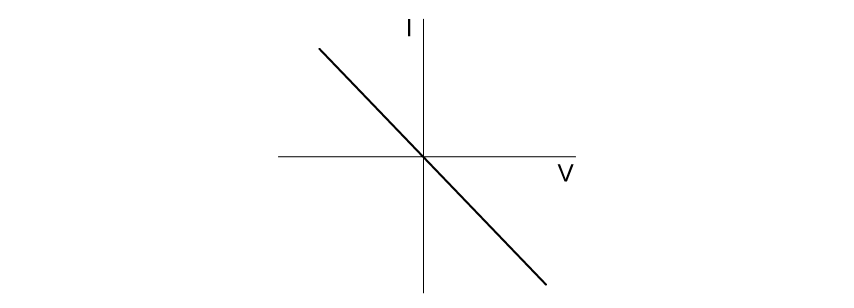
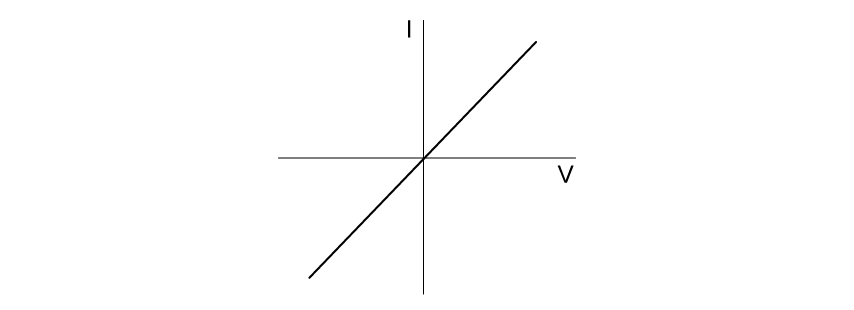
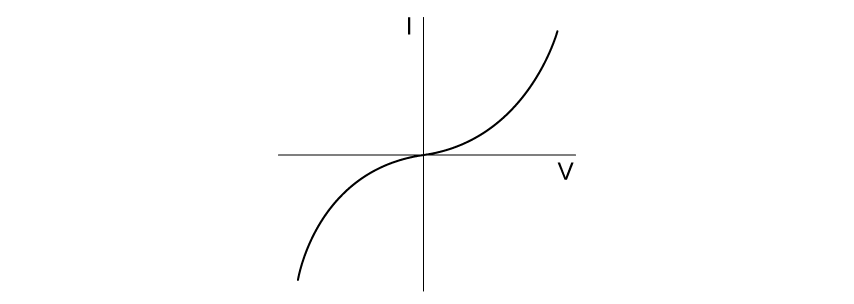
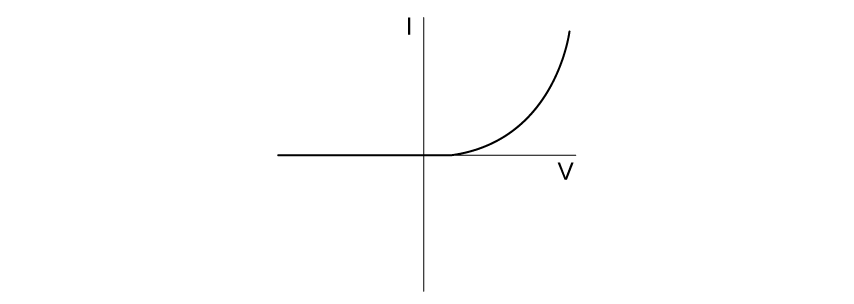
Select the graph which best describes the I-V characteristic of an ohmic resistor.
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
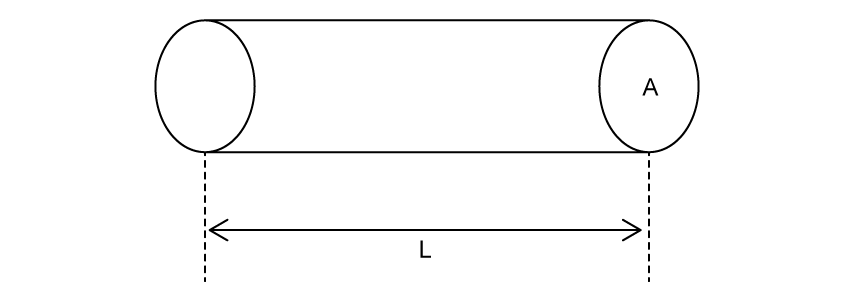
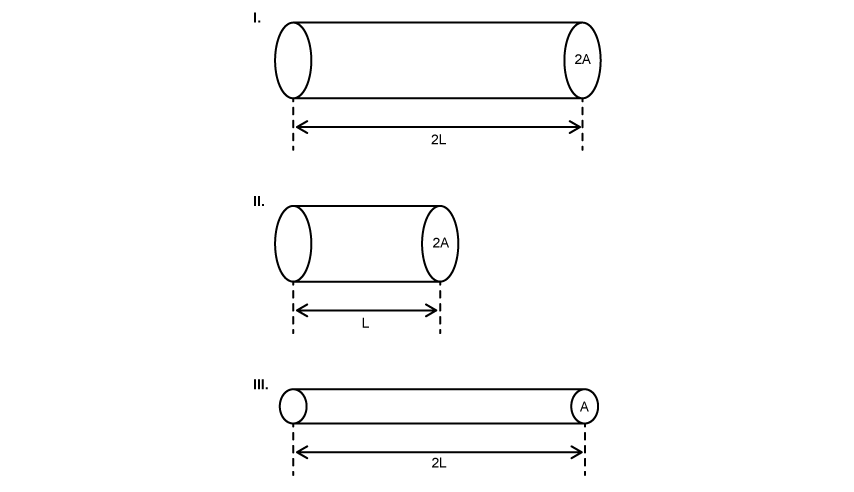
A wire with resistivity ρ , length L and cross-sectional area A has resistance R .
Which of the wire, made from the same material, will also have resistance R?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Which of the following statements are benefits of using parallel circuits when connecting components in homes and vehicles?
A single power source supplies all lights and appliances with the same potential difference
The current is the same in all branches so only one type of fuse is needed
If one bulb breaks, the appliances in other branches continue to work
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
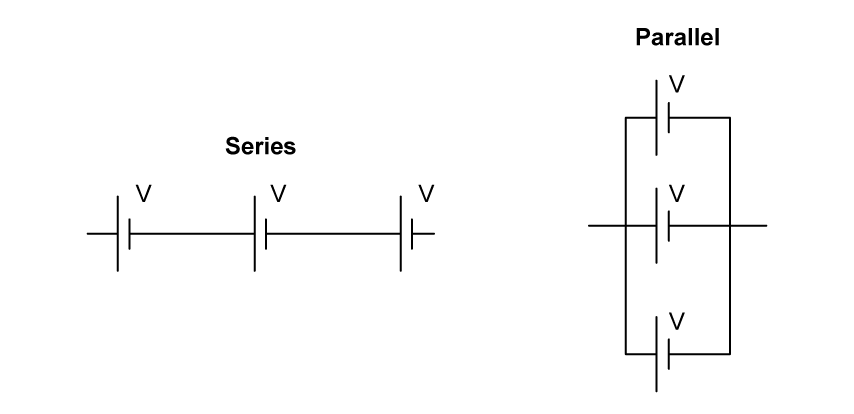
A student is provided with three identical cells, each having a potential difference of V .
For the two arrangements shown, what is the total potential difference across the array?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A particular quantity X is an important factor when calculating for electrical circuits. X can be found using several different equations, as shown.
Which option identifies X ?
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
Potential divider circuits are used to control outputs that are often changed, such as volume and brightness. For the potential divider circuit shown, identify the output voltage, Vout in terms of the input voltage, Vin .
Choose your answer A B C D
View Answer
Previous Question