Question 1
Velocity is a vector quantity, so can be represented by a vector arrow. Which quantity is represented by the length of its vector arrow?
Speed
Magnitude
Acceleration
Distance
Velocity is a vector quantity, so can be represented by a vector arrow. Which quantity is represented by the length of its vector arrow?
Speed
Magnitude
Acceleration
Distance
Which of the following represents correct vector and scalar quantities?
|
|
vectors |
scalars |
|
A. |
Electric charge |
Weight |
|
B. |
Impulse |
Current |
|
C. |
Temperature |
Pressure |
|
D. |
Time |
Work done |
Which of the following represents the correct values of the x-component and y-component of the vector -F ?
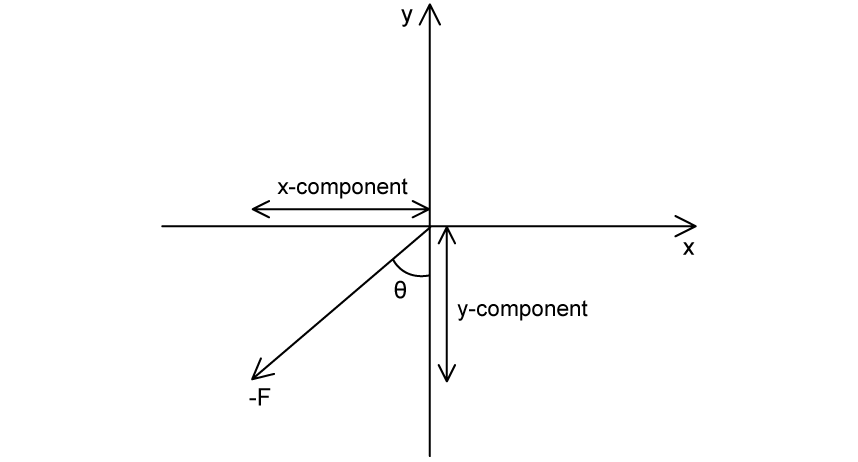
|
|
x-component |
y-component |
|
A. |
–F sin θ |
–F cos θ |
|
B. |
–F cos θ |
–F tan θ |
|
C. |
F sin θ |
–F cos θ |
|
D. |
–F cos θ |
–F sin θ |
The magnitude of a is 15 N and that of b is 30 N.
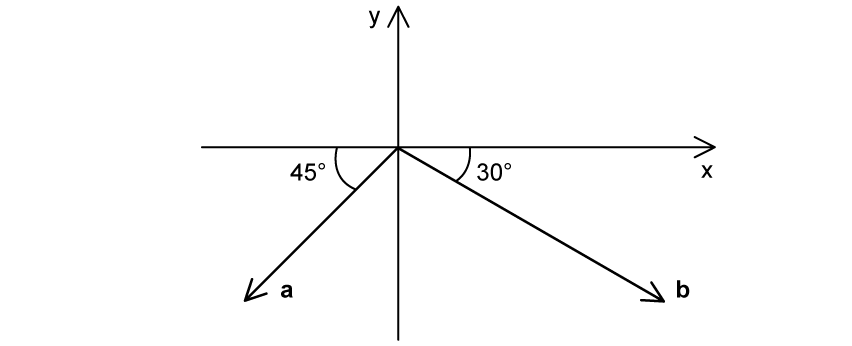
Which of the following represents the correct resultant horizontal and vertical components of the vectors in the diagram?
|
|
Horizontal Component |
Vertical Component |
|
A. |
15 |
15 – 7.5 |
|
B. |
15 |
–15 – 7.5 |
|
C. |
15 |
–15 – 7.5 |
|
D. |
–15 – 7.5 |
15 – 7.5 |
You may use the fact that:
cos(30) = and cos(45) =
sin(30) = and sin(45) =
The diagram shows vector p.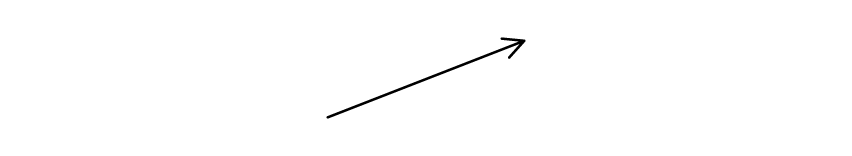
In which of the following diagrams is vector p multiplied by a scalar represented?
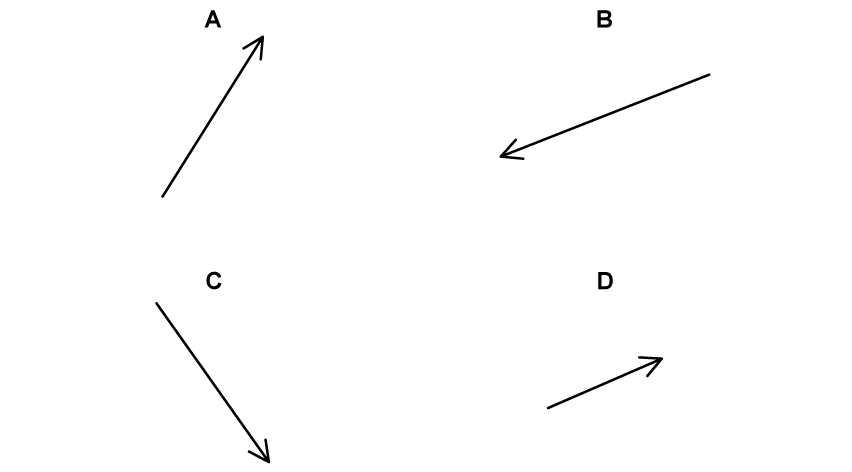
1 and 4
2 only
2 and 4
1 only
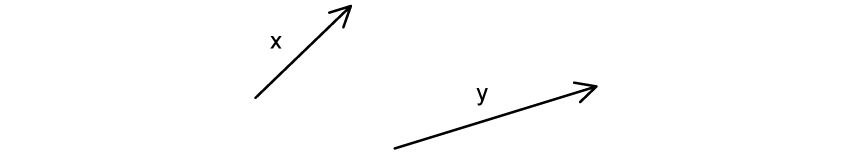
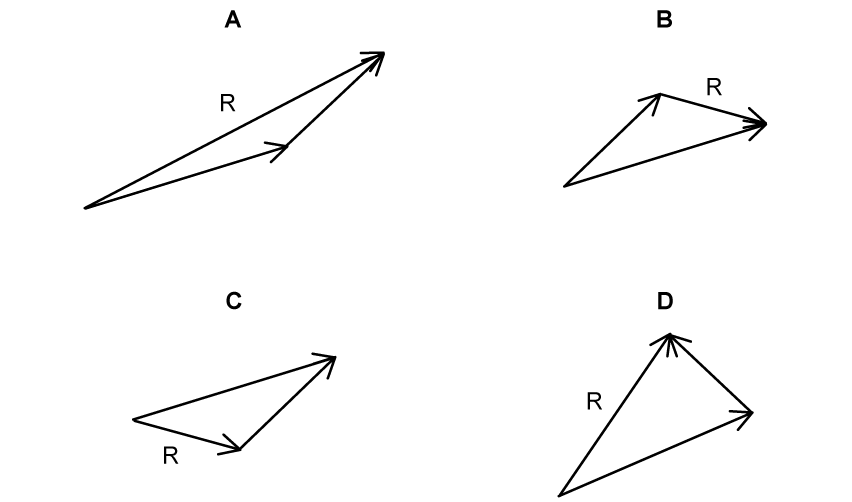
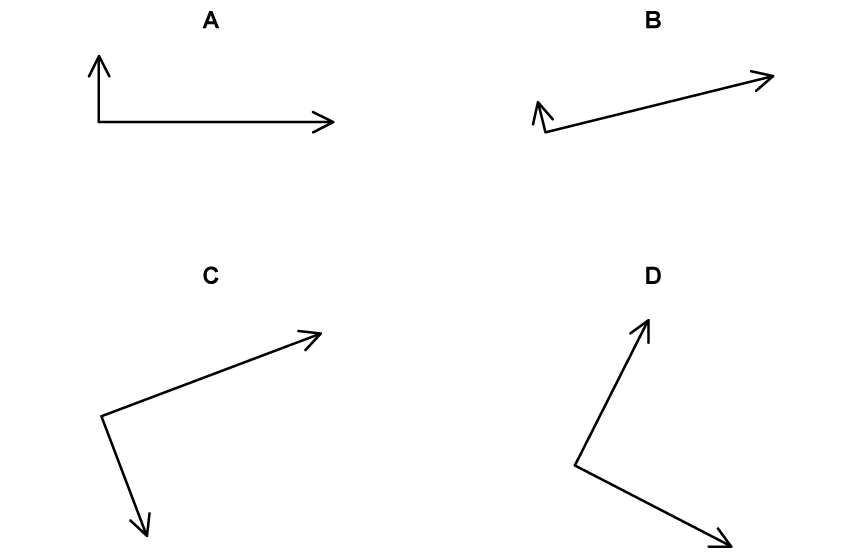
In which of the following diagrams is the addition of vectors x and y represented?
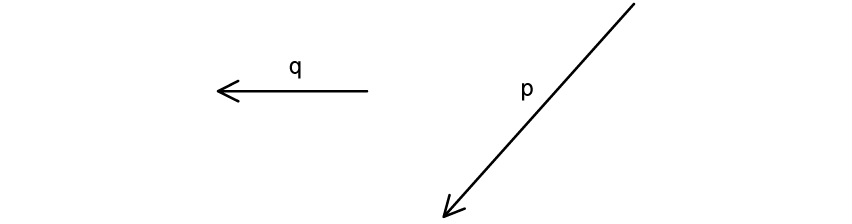
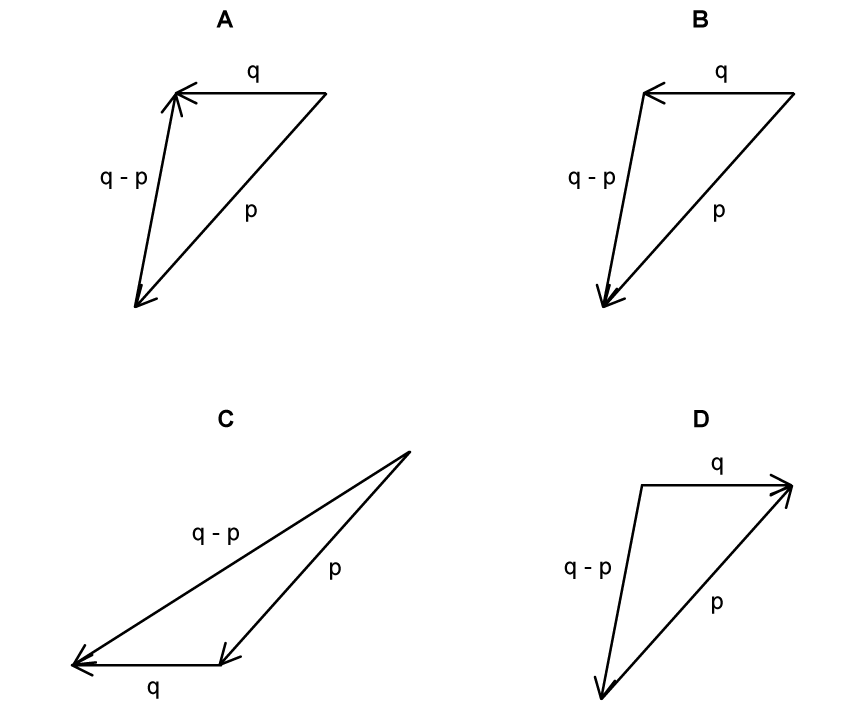
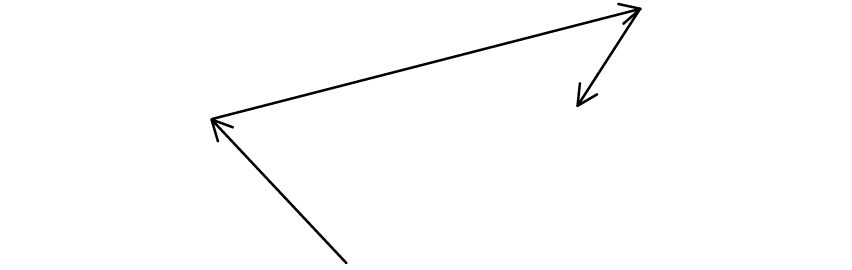
In which of the following diagrams is q – p represented correctly?
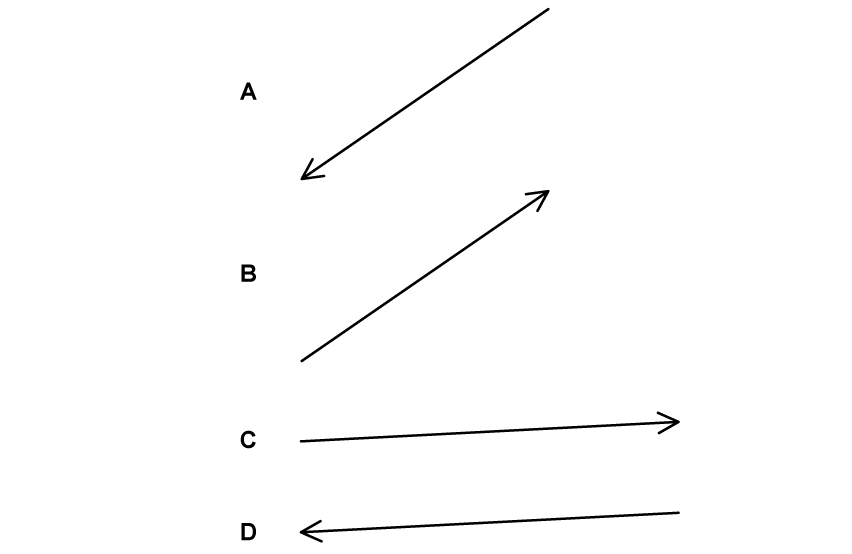
The arrow represents the vector R.

Which diagram does not represent R as two perpendicular components?
Three forces act on a body as shown.
Which fourth force is required so that the resultant force is zero?
A rectangular object sits at rest on a plane inclined at angle to the horizontal.
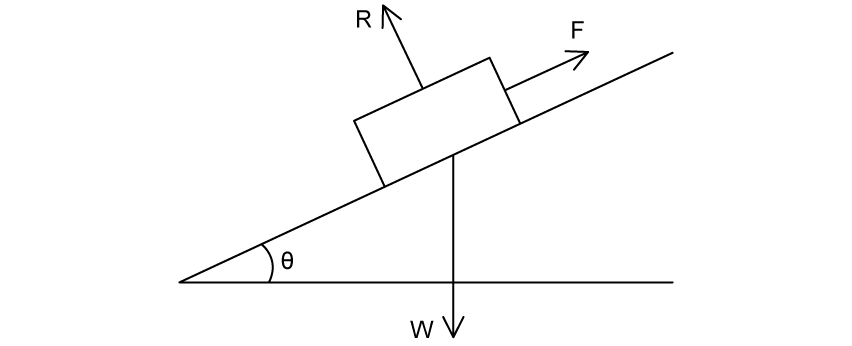
R is the normal force, W is the weight and F is friction.
Which row correctly labels R and F in terms of mass m and acceleration due to gravity g.
|
|
R |
F |
|
A. |
mg |
mg |
|
B. |
mg cos θ |
0 |
|
C. |
mg sin θ |
mg cos θ |
|
D. |
mg cos θ |
mg sin θ |