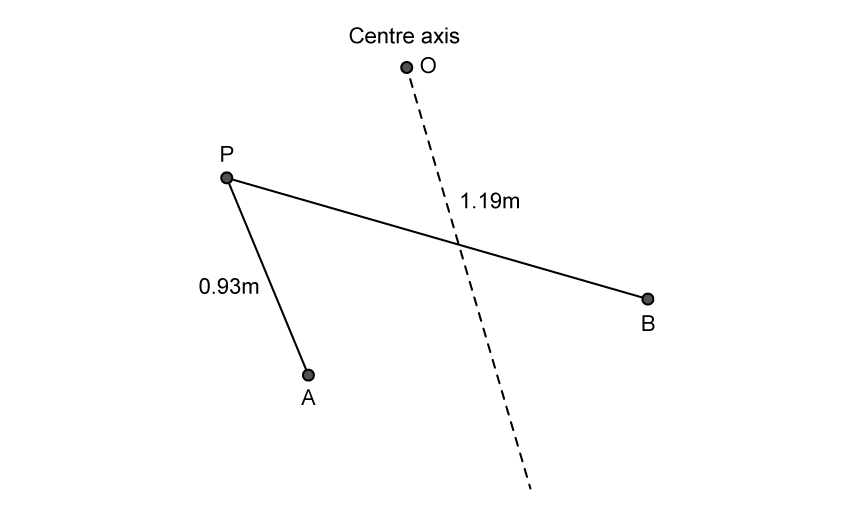
Question 1a
When electromagnetic waves are reflected from a shiny surface, such as a road sign, they often become polarised.
Question 1b
Changes in phase can occur when electromagnetic waves are reflected from a surface.
If an electromagnetic wave is reflected at the boundary between a medium with a higher refractive index than the medium it is travelling in, the oscillating electric field undergoes a phase change of π radians.
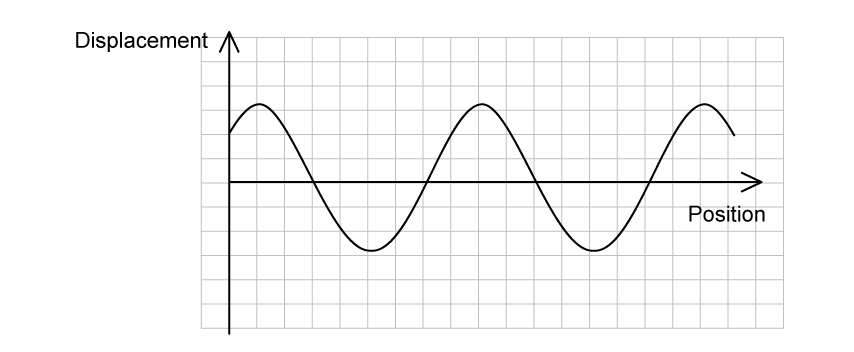
Light is incident on an air-water boundary. A displacement-position sketch of the amplitude of the incident electric field is shown. The origin represents the boundary.
Question 1c
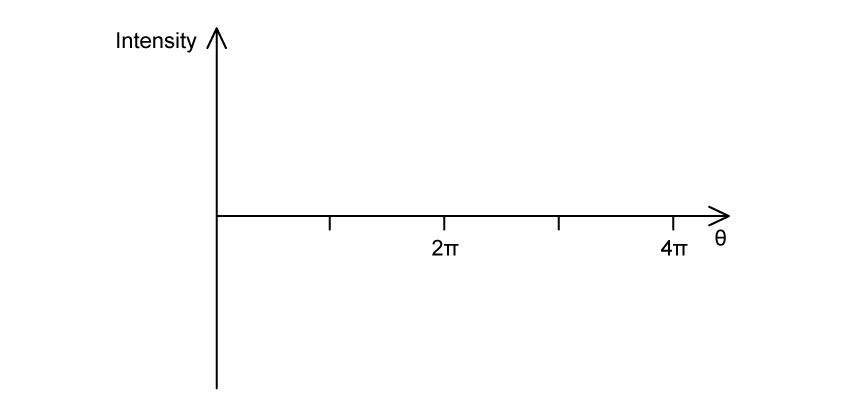
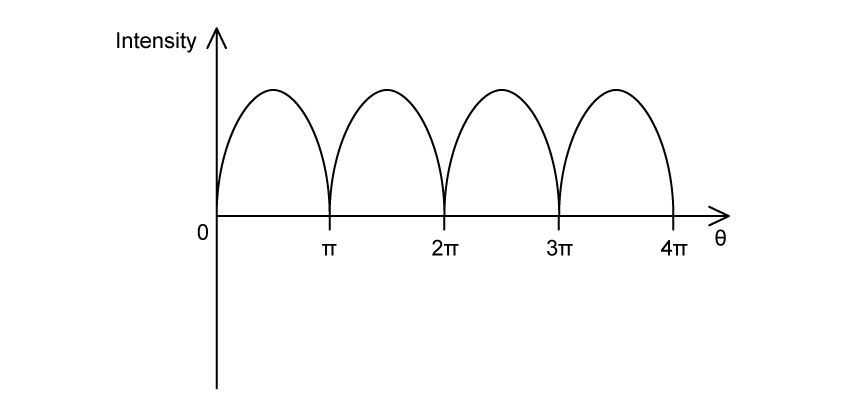
Three polaroid filters P1, P2 and P3 are aligned as follows:
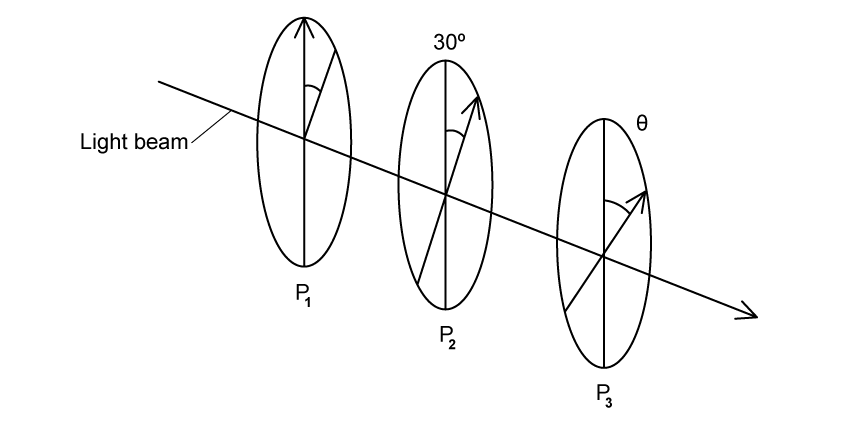
Unpolarised light is incident on P1 and subsequently passes through each of the three polaroid filters. P1 and P2 are in fixed positions, but P3 can be rotated to any angle θ to P1.
Question 1d
| Wave | Polarised or unpolarised | Reason |
| Light from the sun | ||
| Compression waves caused by an earthquake | Unpolarised | Longitudinal waves cannot be polarised |
| Electromagnetic waves emitted from a dipole aerial | ||
| Ultrasonic waves from an echo sounder |
[3]