Question 1
When an object oscillates in simple harmonic motion, a restoring force acts toward the equilibrium position.
Which graph shows the restoring force, F, as a function of displacement, x?
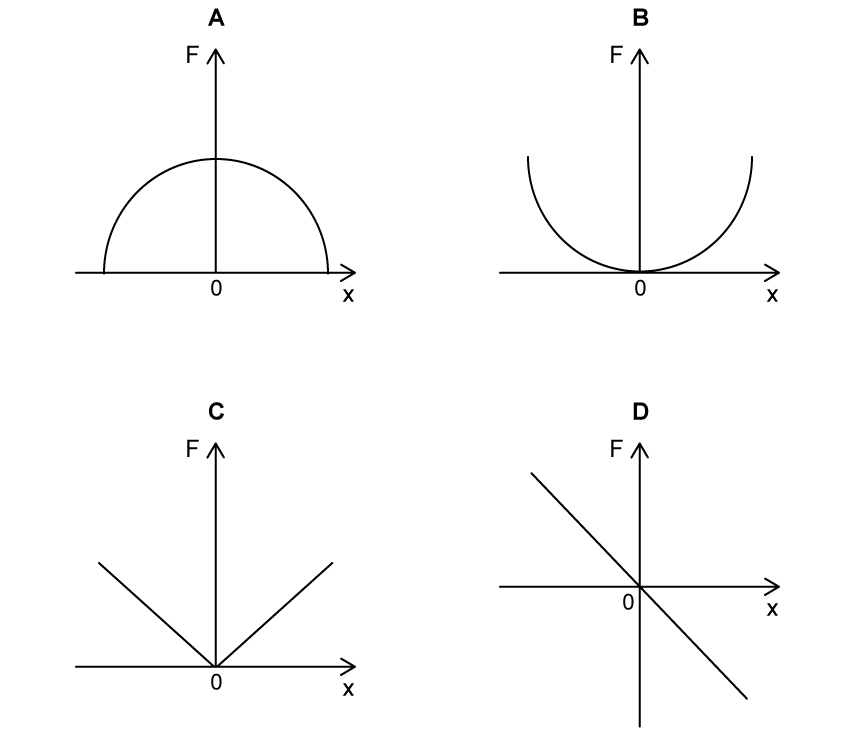
When an object oscillates in simple harmonic motion, a restoring force acts toward the equilibrium position.
Which graph shows the restoring force, F, as a function of displacement, x?

The graph below shows the displacement as a function of time for a particle in SHM.
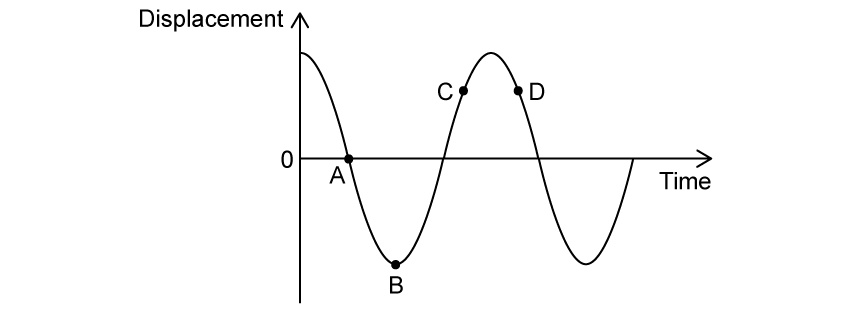
At certain points in the oscillation, the acceleration and velocity act in opposite directions.
Which letter indicates such a point?
A mass is attached to a spring from above and the spring is secured to a clamp. The mass is pulled down and released resulting in a simple harmonic oscillation.
Which one of the following statements is true?
The tension, T, in the spring is at a minimum as the mass passes through the equilibrium position
The total potential energy, EP, in the system is at a maximum when the mass is at the highest point of its oscillation
The acceleration, a, of the mass is at a maximum as it passes through the equilibrium position
The kinetic energy, EK, is at a minimum when the mass is at the lowest point in its oscillation
A pendulum bob on a string oscillates in SHM with a frequency, f.
The period, T, of a simple pendulum is related to the length of the string, l, and the acceleration of free fall, g, by the following equation:
What would the ratio be of the original frequency to the new frequency if the length of the string was increased by a factor of 4?
4
A simple pendulum oscillates in SHM.
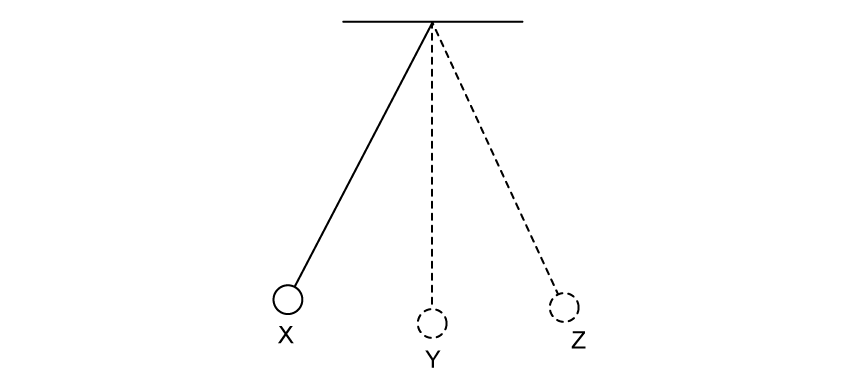
Which row correctly describes the force, F, acceleration, a, and velocity, v, at position Y?
|
Force |
Acceleration |
Velocity |
|
|
A. |
zero |
zero |
max |
|
B. |
max |
max |
zero |
|
C. |
max | zero | max |
|
D. |
zero |
max |
zero |
The total energy, ET, of a mass-spring system in SHM is related to the mass, m, angular speed, ω, and the amplitude, A, by the following equation:
What is the ratio of the original amplitude to the new amplitude if the mass is reduced by a factor of 4 and the angular speed is halved?
1
4
A mass spring system is set up so that the mass glides on a frictionless surface between two springs on a horizontal bench. The mass-spring system performs SHM
Which of the following statements is true?
As the mass oscillates about the equilibrium position, the kinetic energy of the mass is zero when the displacement from equilibrium is zero
As the mass oscillates about the equilibrium position, the kinetic energy of the mass is zero when the restoring force acting on the mass is zero
As the mass oscillates about the equilibrium position, the potential energy of the spring is at a maximum when the kinetic energy of the mass is zero
As the mass oscillates about the equilibrium position, the potential energy of the mass is at a maximum when the acceleration of the mass is zero
A mass-spring system has a period, T, mass, m, and a spring constant, k. These quantities are related by the following equation:
A new spring has a spring constant of 3 times the original value.
Using this new spring, which mass would cause the period, T, to decrease by a factor of 6?
8 m
12 m
The graph below shows the kinetic energy of a simple pendulum as a function of time. The time period of the pendulum is T.
What does the length of the line JK represent?
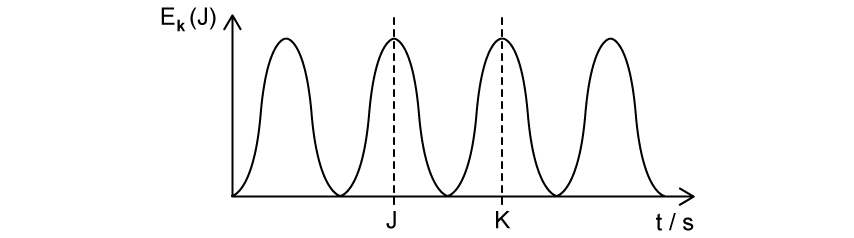
T
2T
The period, T, of a simple pendulum depends upon the length of the string, l, and the acceleration of free fall, g, as defined by the following equation:
If the length of the string was reduced by a factor of 5, what would be the resulting period of the new oscillator?
0.2T
0.45T
2T
8T