(a)
Describe what happens to the magnitude of a vector when it is
(i)
multiplied by an integer greater than 1.
[1]
(ii)
multiplied by a negative number.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
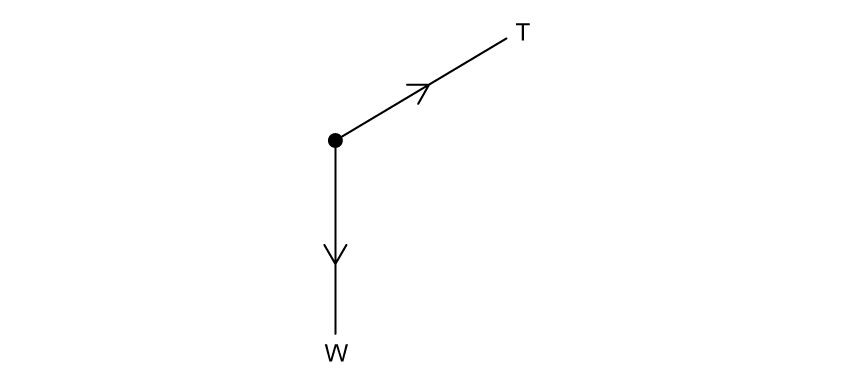
An incomplete free body force diagram for a painting hanging by special wires in equilibrium is shown.
Three forces act on the painting.
(b)
(i)
Complete the free body force diagram by sketching the additional force vector required for equilibrium.
[2]
(ii)
State the name of the force you have drawn.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
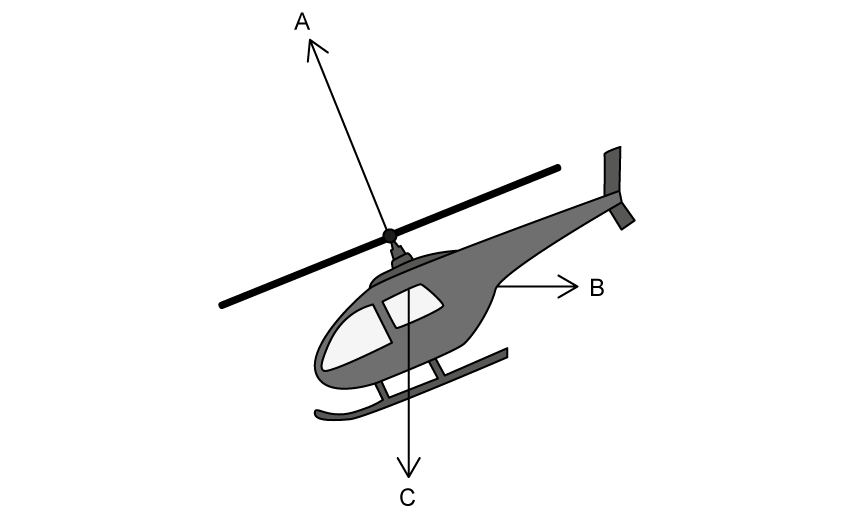
A helicopter is moving horizontally through the air. Three forces act on the helicopter, A, B and C.
(c)
State the name of each of the three forces A, B and C.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
State and explain the direction of horizontal motion for the helicopter shown in part (c).
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
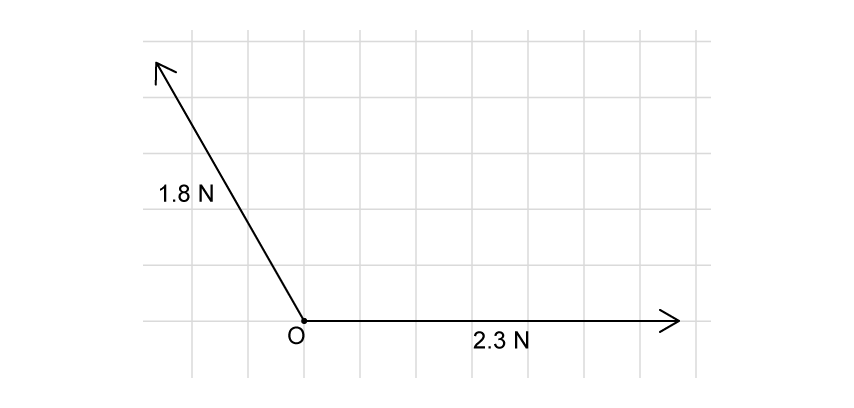
Two vectors act on an object at O. The length of each square on the grid is 1 cm.
(a)
Determine the scale used to draw the diagram, including an appropriate unit.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Complete the scale drawing by drawing an appropriate parallelogram on the grid in part (a) to show the resultant force on the object at O.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Hence, by measuring the resultant vector drawn in part (b), determine the amount of force it represents.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
The 1.8 N force now acts vertically upwards, such that the two forces acting on the object at O are perpendicular. Calculate the magnitude of the new resultant force acting on the object at O.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
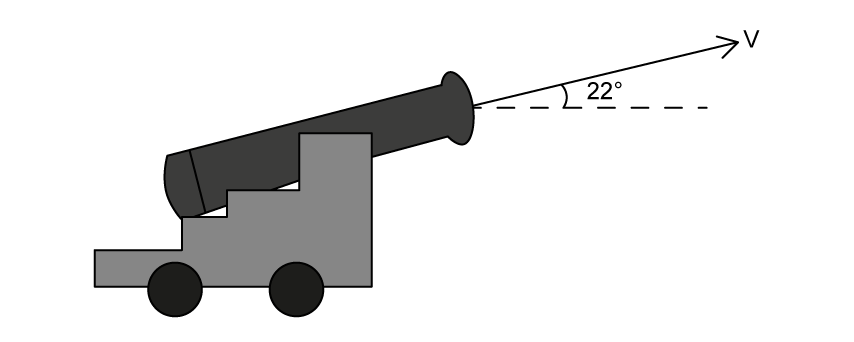
A small cannon is designed to fire projectiles at an angle of 22° to the horizontal with an initial velocity v .
(a)
Calculate the vertical component of velocity if its initial velocity v = 10 m s–1 .
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
State the direction of the horizontal component of velocity.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
State and explain why the horizontal component of velocity stays constant in the absence of air resistance.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The vertical component of the projectile's velocity decreases to zero.
(d)
(i)
State the point along the projectile's journey at which its vertical component of velocity is zero.
[1]
(ii)
Explain why the projectile's vertical component of velocity decreases to zero.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question