Question 1
What is the current reading on the ideal ammeter shown?
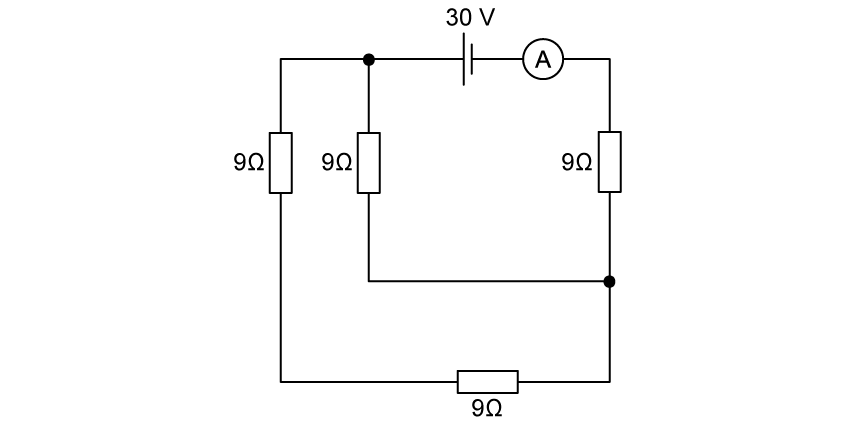
1.0 A
2.0 A
3.3 A
6.6 A
What is the current reading on the ideal ammeter shown?

1.0 A
2.0 A
3.3 A
6.6 A
What is the current reading on the ideal ammeter shown?
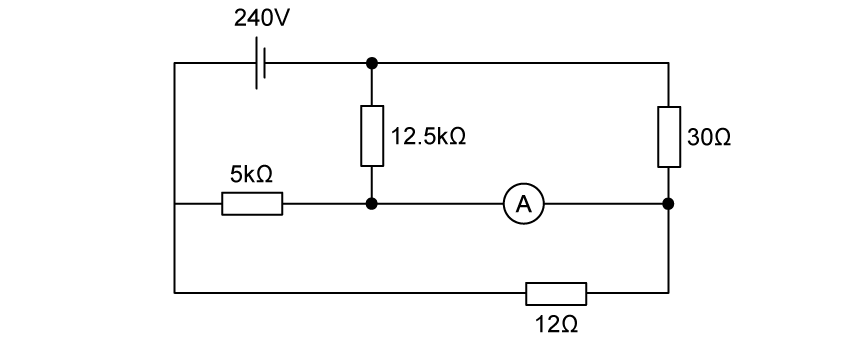
0 A
0.12 mA
12 A
26.7 A
A student is investigating the properties of cells made using lemons. They find that their lemon cell has an emf of 1.0 V and internal resistance 5000 Ω. The student wonders what the least number of lemons they would need to light a bulb with a rating of 5.0 W and 8.0 V.
What is the best estimate of the least number of lemons?
9
3000
15 000
30 000
The diagram shows a cubical wire framework made from rigid, uniform copper wire. The sides are all of the same length.
Point A is at a potential of 6.0 V and point H has potential 0.0 V. The current of 12.0 A enters at A and leaves at H. Side AB has resistance of 2.0 Ω.
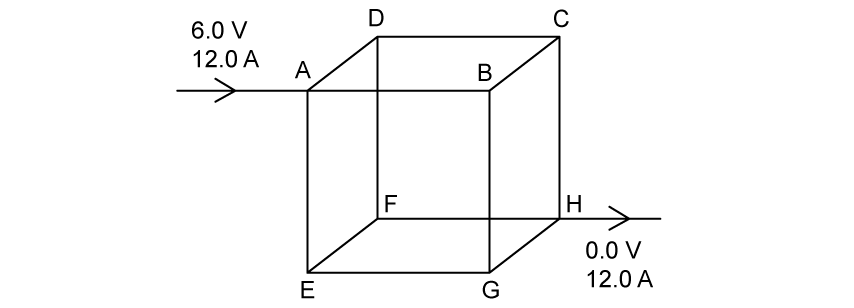
Which line correctly identifies the current in BC, the potential at F and the total resistance of the network?
| current in side BC / A | potential at F / V | total resistance / Ω | |
| A. | 2 | 2 | 0.33 |
| B. | 2 | 2 | 1.67 |
| C. | 4 | 4 | 0.33 |
| D. | 4 | 6 | 1.67 |
The circuit shown includes three identical cylindrical resistors, with dimensions such that the cross-sectional area is 5 mm2, the length is 20 cm and the resistance is R Ω.
When the switch is closed, the total resistance of the circuit is 5 kΩ.
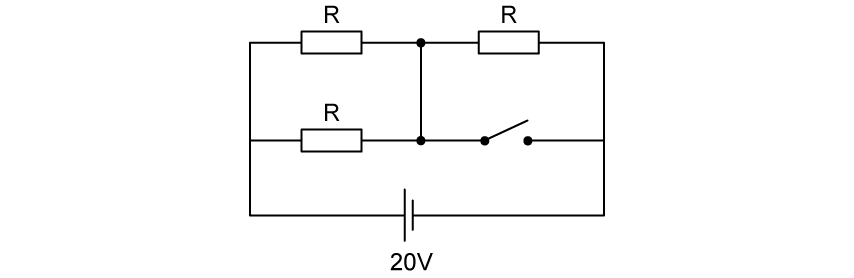
What is the resistivity of the material that the resistors are made from?
0.08 Ω m
0.25 Ω m
8.0 Ω m
25 Ω m
The readings on both ammeters are zero. What are the values of X and Y?
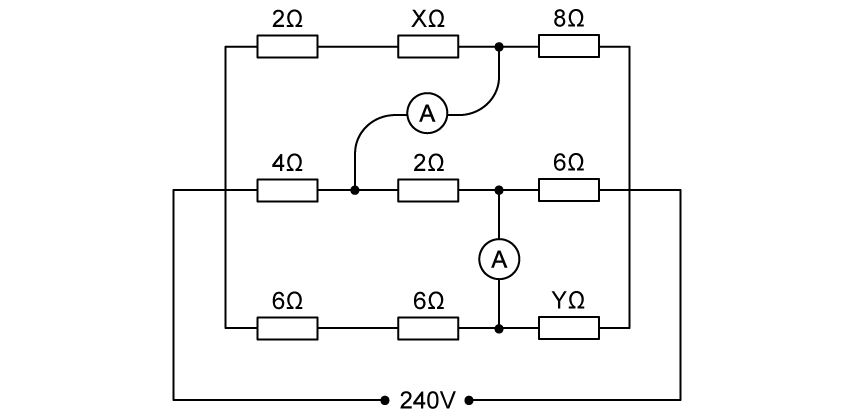
| X / Ω | Y / Ω | |
| A. | 2 | 12 |
| B. | 2 | 6 |
| C. | 4 | 12 |
| D. | 4 | 6 |
A strain gauge is a device which measure force. An applied tension on a thin wire of known resistance changes the length and cross-sectional area so that the value of the resistance is changed in a predictable way (assuming that volume remains constant).
When the length of the wire is increased by 5 % what will be the effect on the resistance?
− 5 %
+ 5 %
− 10 %
+ 10 %
Two rods have the same length, and the same resistance. One rod is made from copper and the other from aluminium.
Copper is three times as dense as aluminium but has half the value of resistivity.
A student wants to know the ratio of:
Which option is the correct answer?
The identical resistors marked (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) are connected as shown. The battery which has negligible internal resistance supplies a total power of 20 W.
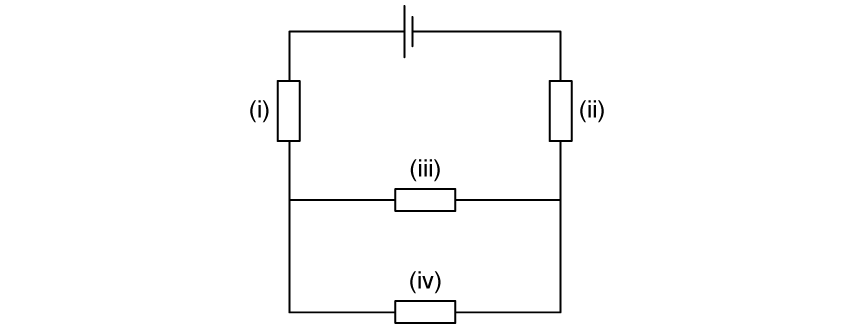
What is the power dissipated in resistor (iv)?
2.0 W
3.0 W
4.0 W
6.0 W
A circuit contains five identical resistors and four identical voltmeters. The reading on voltmeter V1 is 8.0 V and the reading on voltmeter V2 is 1.0 V. What are the readings on V3 and V4?
|
reading on voltmeter V3 / V |
reading on voltmeter V4 / V |
|
|
A. |
1.5 |
1.0 |
|
B. |
3.0 |
2.0 |
|
C. |
4.5 |
3.0 |
|
D. |
6.0 |
4.0 |