(a)
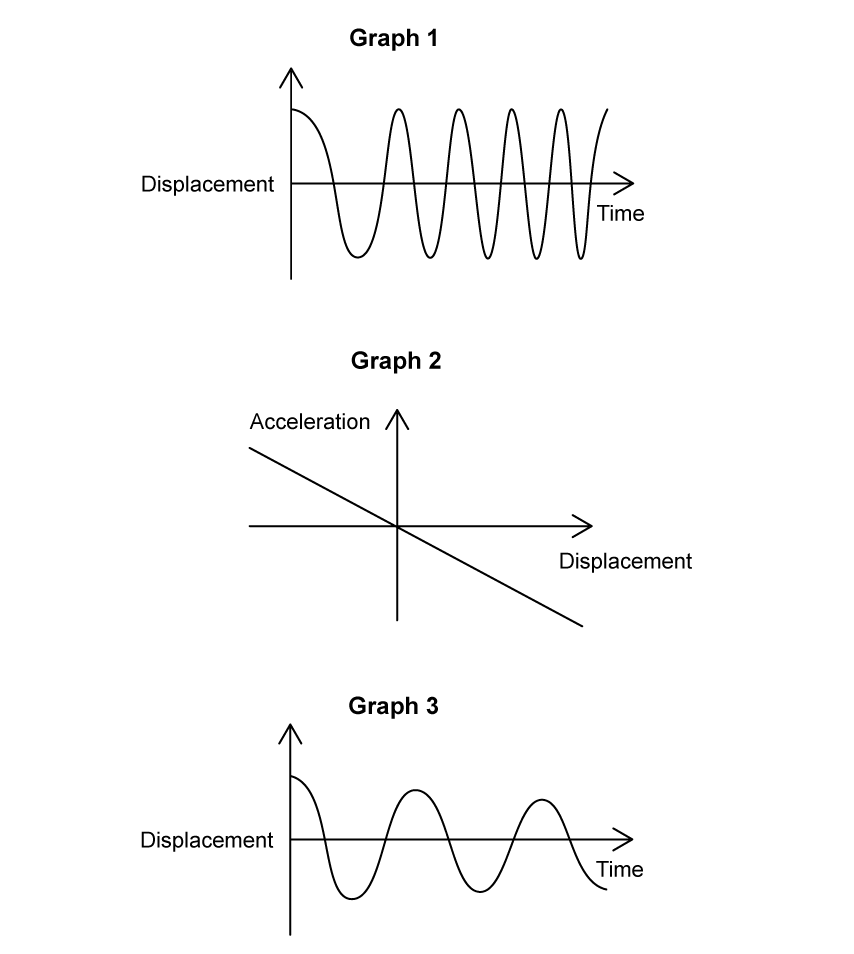
State and explain whether the motion of the objects in graphs I, II and III are simple harmonic oscillations
[6]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Explain why, in practice, a freely oscillating pendulum cannot maintain a constant amplitude.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
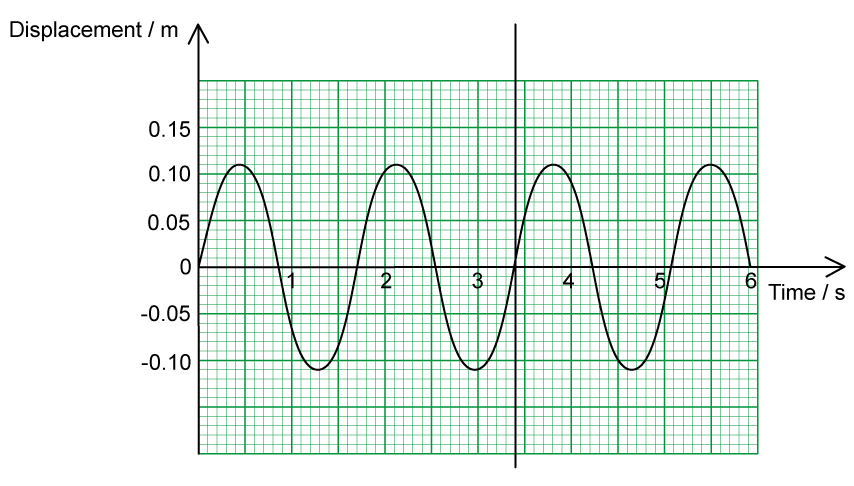
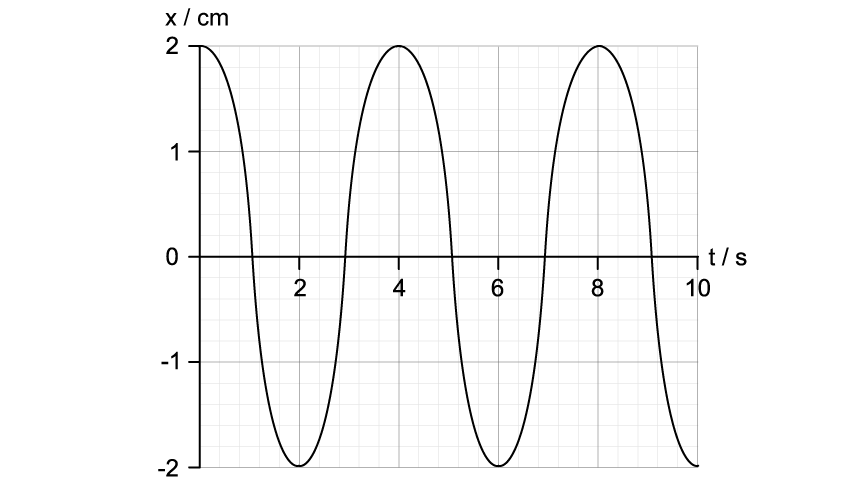
The motion of an object undergoing SHM is shown in the graph below.
(c)
For this oscillator, determine:
(i)
The amplitude, A.
[1]
(iii)
The frequency, f.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Using the graph from part (c), state a time in seconds when the object performing SHM has:
(i)
Maximum positive velocity.
[1]
(ii)
Maximum negative acceleration.
[1]
(iii)
Maximum potential energy.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A ball of mass 44 g on a 25 cm string oscillating in simple harmonic motion obeys the following equation:
a = −ω 2 x
(a)
Demonstrate mathematically that the graph of this equation is a downward sloping straight line that goes through the origin.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
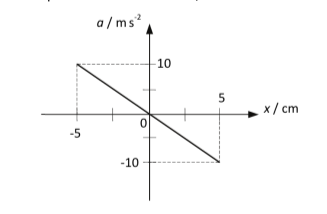
The graph below shows the acceleration, a , as a function of displacement, x , of the ball on the string.
The angular speed, ω , in rad s−1 , is related to the frequency, f , of the oscillation by the following equation:
(b)
For the ball on the string, determine the period, T , of the oscillation.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
The ball is held in position X and then let go. The ball oscillates in simple harmonic motion.
(c)
Explain the change in acceleration as the ball on the string moves through half an oscillation from position X.
You can assume the ball is moving at position X.
[4]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Describe the energy transfers occurring as the ball on the string completes half an oscillation from position X.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
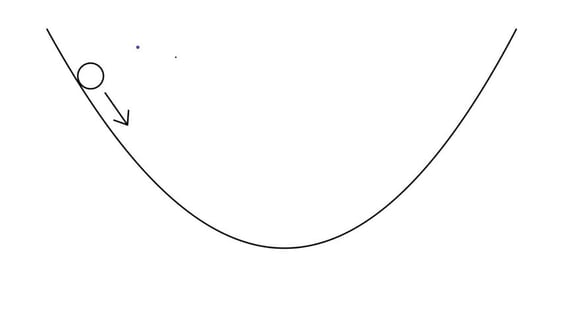
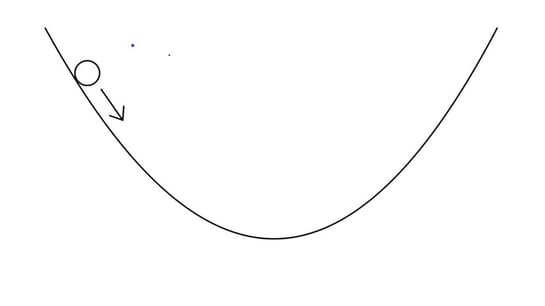
A smooth glass marble is held at the edge of a bowl and released. The marble rolls up and down the sides of the bowl with simple harmonic motion.
The magnitude of the restoring force which returns the marble to equilibrium is given by:
Where is the displacement at a given time, and is the radius of the bowl.
(a)
Outline why the oscillations can be described as simple harmonic motion.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Describe the energy changes during the simple harmonic motion of the marble.
Assess your score
View Answer
As the marble is released it has potential energy of 15 μJ. The mass of the marble is 3 g.
(c)
Calculate the velocity of the marble at the equilibrium position.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Sketch a graph to represent the kinetic, potential and total energy of the motion of the marble, assuming no energy is dissipated as heat. Clearly label any important values on the graph.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question