Standing waves are sometimes referred to as stationary waves.
(a)
State three conditions which are required for the formation of a standing wave.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Standing waves can be thought of as the opposite of progressive waves.
(b)
Use the text in the box to complete the sentences below, comparing the two types of wave.
constant transfer do not
store do different at different points
(i)
Standing waves ______ energy but progressive waves ______ energy.
[1]
(ii)
The amplitude of a standing wave is ______ , whereas the amplitude of a progressive wave is ______ .
[1]
(iii)
The crests of a standing wave ______ move along but simply oscillate up and down, while but the crests of a progressive wave ______ move along as the wave travels.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
A stationary wave is made up of nodes and anti-nodes. State the definitions of
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
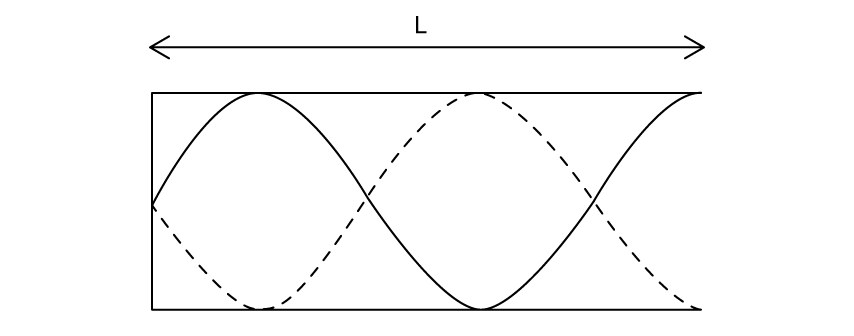
The length L shows 2.5 full wavelengths of a standing wave in a column of air.
(i)
Identify the points marked X and Y.
[2]
(i)
State the boundary conditions for the formation of this standing wave.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
Standing waves are formed when waves undergo superposition.
(a)
State the principle of superposition.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Name two types of waves which can undergo superposition.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
Distinguish between constructive interference and destructive interference.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
A standing wave representing the first harmonic is set up on a vibrating string.
(d)
State the number of nodes and anti-nodes which would appear on this wave.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A standing wave is set up in a column of air within a pipe of length L, which is open at one end.
(a)
Giving your answer as a fraction of L, determine the wavelength, λ.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
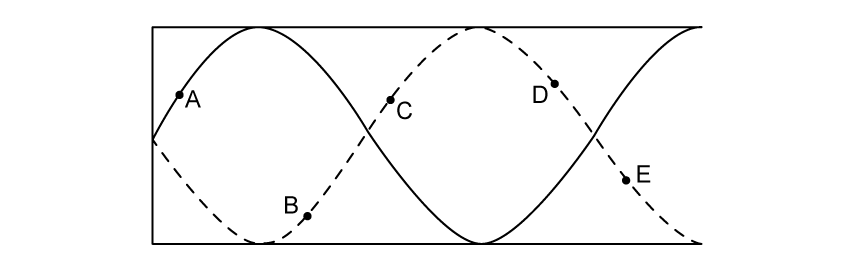
(b)
For the standing wave identify which points are in phase and which points are in anti-phase.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
The column of air is vibrated so that it oscillates at the third harmonic.
(c)
Sketch a diagram to show the shape of the wave produced in the pipe.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
The column of air oscillating at the seventh harmonic has length L and velocity, v.
(d)
In terms of L and v, determine the
(i)
Wavelength.
[1]
(ii)
Frequency.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
(a)
Describe three methods that can be used to identify that two points on a standing wave are in phase.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Describe the boundary conditions for a standing wave in a pipe of air which is open at one end and closed at the other.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
For a pipe that is open at both ends
(i)
Sketch the first harmonic.
[2]
(ii)
Write an expression for wavelength in terms of the length of the pipe, L.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
For a string which is fixed at both ends, sketch the third harmonic.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
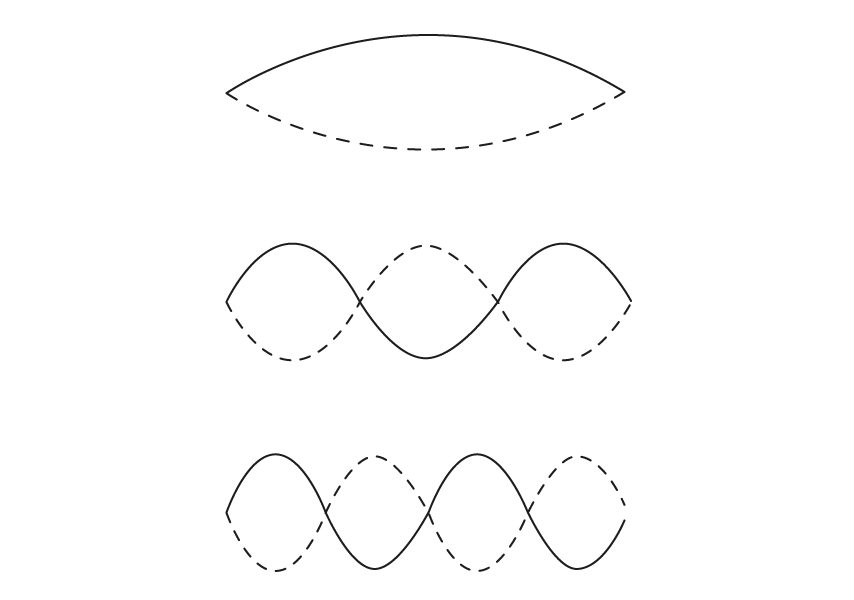
The diagram shows three possible harmonics on a string fixed at each end.
(a)
Identify the three harmonics.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
For the harmonic shown, identify an expression for the wavelength.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
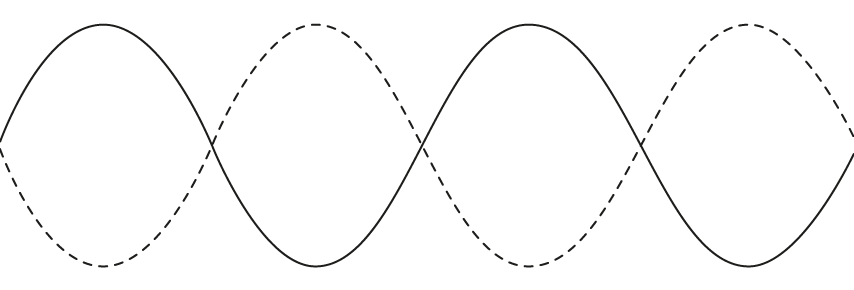
The diagram shows two waves which are travelling in phase.
(c)
Sketch the resultant wave, including labelling the axes with relevant quantities.
[3]
Assess your score
View Answer
Stationary waves are formed when two waves travelling on the same line superpose.
(d)
Identify two conditions which must be true for superposition to occur.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question