Question 1
What is the correct relationship between the gravitational force and the distance between two point masses?
What is the correct relationship between the gravitational force and the distance between two point masses?
The force, F between two point masses is 10 N. The distance, r between the two masses is doubled.
What is the new force between the two masses?
2.5 N
5 N
20 N
100 N
The gravitational force, FG as shown on the diagram, keeps the Earth orbiting the Sun in a circular orbit.

What type of force is FG?
Electrostatic force
Centripetal force
Centrifugal force
Contact force
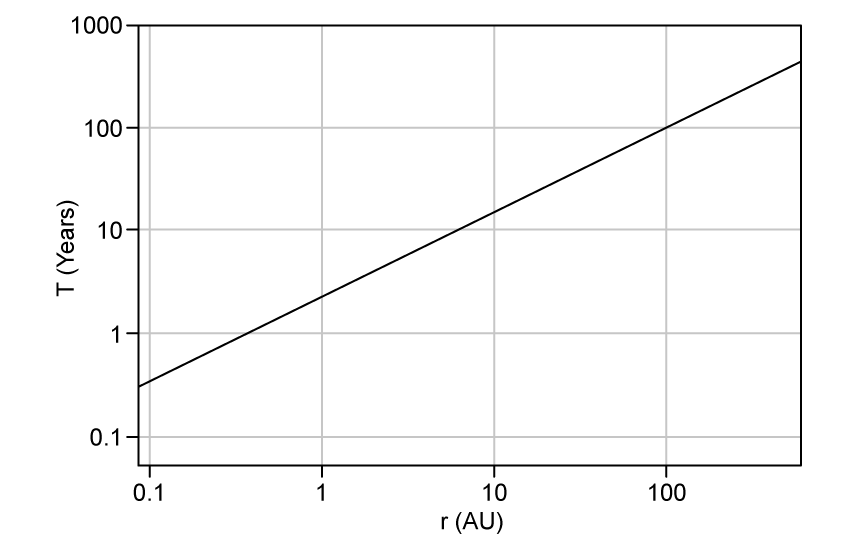
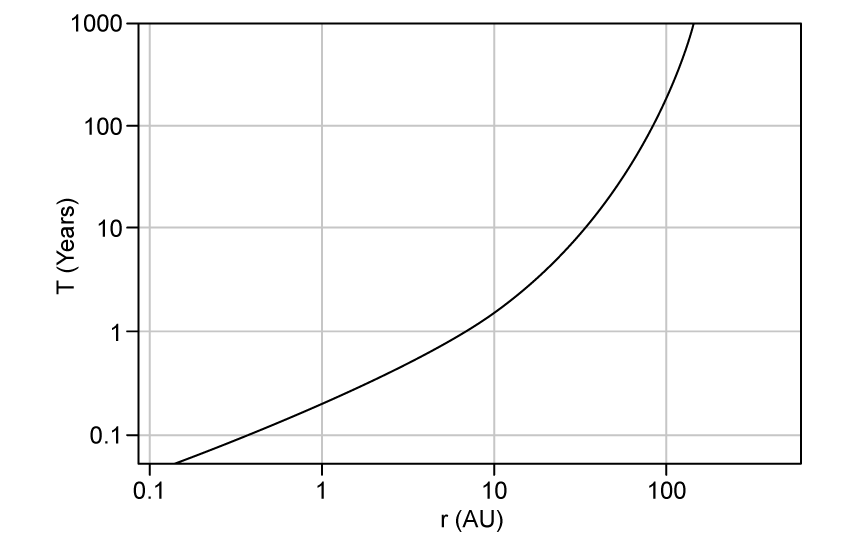
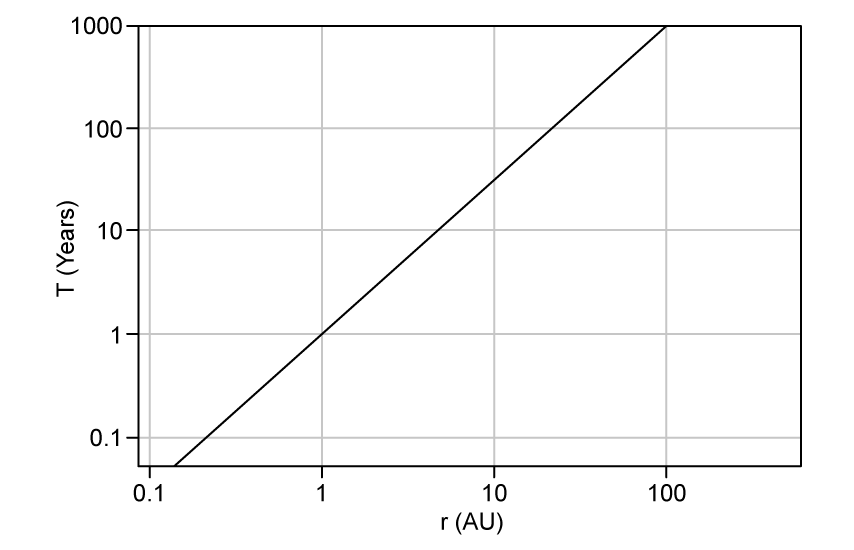
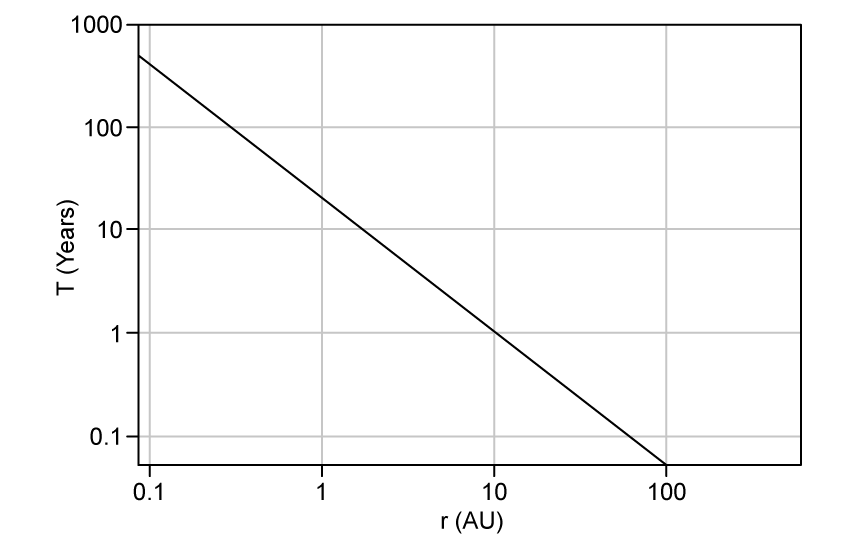
Which expression best describes the relationship between the orbital time period, T and the orbital radius, r?
Which of the following is not an equation which can be used to calculate g, the gravitational field strength?
Which of the following statements about gravitational force is true?
Gravitational force has a finite range
A greater gravitational force is exerted on objects with larger mass
On planets with a large value of g, the gravitational force per unit mass is smaller than on planets with a smaller value of g
An object's mass changes depending on the gravitational field strength at that point
An alien of mass 100 kg lives on a planet with a gravitational field strength of 50 N kg−1.
What is the weight of the alien on this planet?
5000 N
1000 N
0.05 N
100 N
A commercial low-orbit space flight carries a passenger of mass 70 kg.
What is the approximate gravitational force of attraction between the Earth and the passenger?
0 N
7 N
700 N
7000 N
A planet has twice the radius of the Earth and 4 times the mass. Assume the planet is spherical and of uniform density.
If the magnitude of the gravitational field strength on Earth is g, what is the magnitude of the gravitational field strength on the surface of the planet?
4g
8g
2g
g
Which graph, plotted on logarithmic axes, shows Kepler's Third Law for the planets in our Solar System?