Electric fields exist in the space around charged particles. The strength of an electric field depends on the position occupied within that space.
(a)
Define what is meant by the strength of an electric field.
Assess your score
View Answer
An electron e - and a positron e + occupy two positions in space.
(b)
Sketch on the image the resultant electric field in the region between the electron and the positron.
Assess your score
View Answer
(c)
The distance between the electron and the positron is 150 cm.
(i)
Calculate the magnitude of the electrostatic force between the electron and the positron.
[2]
(ii) State the direction of the electrostatic force on the electron.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
A positive test charge is placed exactly midway between the electron and the positron.
(d)
Outline the subsequent motion of the positive test charge.
Assess your score
View Answer
Next Question
An integrated circuit uses thin strips of gold and silicon as connectors and resistors respectively.
A strip of gold, of cross-sectional area 2.0 × 10–6 m2 has a charge carrier density of 7.0 × 1028 m–3 and a current of 8.5 mA.
(a)
Calculate the charge carrier drift speed for gold.
Assess your score
View Answer
An approximate value for the charge carrier drift speed for a sample of silicon of the same dimensions, carrying the same current, would be 0.20 m s–1 .
(b)
Compare this value with the one you obtained in part (a) for gold and explain the reason for the difference between the two drift speeds.
Assess your score
View Answer
In another integrated circuit a current of 2.0 A flows through a resistor for 90 minutes.
(c) Determine the number of electrons that pass a point in the resistor this time.
Assess your score
View Answer
The current in part (c) flows across a potential difference of 12 V.
(d)
Using your answer to part (c), calculate the total energy transferred in the integrated circuit.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
A parallel-plate capacitor is an electrical component that stores electric charge.
It is set up by connecting two metal plates to a power supply.
(a)
Label:
(i) the positively charged metal plate with the letter A
[1]
(ii) the negatively charged metal plate with the letter B
[1]
(iii) the electric field lines between the plates.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
State, for each of the scenarios below, whether the electric field strength between the metal plates increases, decreases, or stays constant:
(i)
a positive test charge moving from one plate to the other.
[1]
(ii)
a positive test charge moving between the plates along a line parallel to each other.
[1]
Assess your score
View Answer
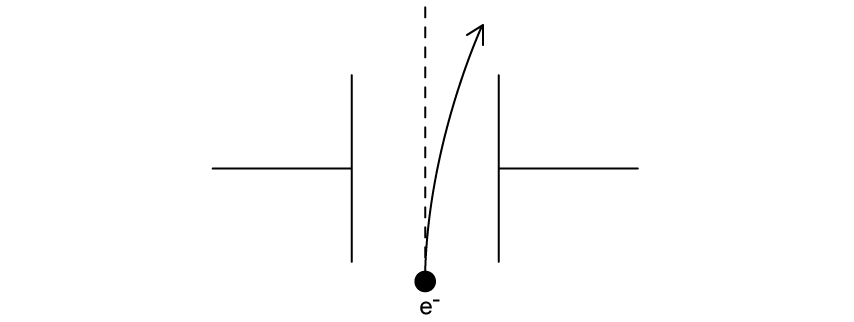
A free electron finds itself incident in the space between the metal plates and is deflected as it moves between them.
(c)
The magnitude of the electric field strength is 200 N C–1 . Calculate the magnitude of the electron’s acceleration in the space between the plates.
Assess your score
View Answer
(d)
Explain the shape of the path shown in part (c).
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
a)
State Coulomb’s law in words.
Assess your score
View Answer
In simple models of the hydrogen atom, an electron is in a circular orbit around the proton.
The magnitude of the force between the proton and the electron is 5.8 × 10–9 N.
(b)
Calculate:
(i) the orbital radius of the electron.
[2]
(ii)
the magnitude of the electric field strength due to the proton at any point in the electron’s orbit.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
The gravitational field strength g due to the proton at any point in the electron’s orbit is given by the equation:
g = G
where is the proton mass, r is the orbital radius and G is the gravitational constant.
(c)
Show that the ratio of the gravitational field strength to the electric field strength due to the proton at any point in the electron’s orbit is of the order 10–28 .
Assess your score
View Answer
Ionisation is the process of removing an outer shell electron from an atom, so it is transferred from its orbit to a point where the potential is zero.
The potential difference between the electron’s orbit in a hydrogen atom and this point is about 3.4 V.
(d)
Calculate the gain in potential energy of an orbiting electron in a hydrogen atom if it is ionised.
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question Next Question
When a copper wire is exposed to an electric field, a current is detected in it.
(a)
Explain, with reference to charge carriers, why there is a current detected in the wire.
Assess your score
View Answer
(b)
Calculate the drift speed of the charge carriers in the copper wire if a potential difference of 4.0 V is applied to it.
The following data are available for the wire:
density of free electrons = 8.5 × 1028 m–3
resistance = 25 Ω
diameter = 0.8 mm
Assess your score
View Answer
A defect is discovered in the wire. This causes the cross-sectional area to increase by 42% at a point X along its length.
(c)
Calculate the new drift speed of charge carriers in the copper wire at point X if the same potential difference is applied as that in part (b).
Explain how you arrived at your answer.
Assess your score
View Answer
When the applied potential difference is removed, the current in the copper wire falls to zero. However, individual charge carriers move within the wire at thermal speeds which are often orders of magnitude above drift speeds.
(d)
(i)
Suggest a reason why charge carriers can attain such large speeds with no potential difference applied.
[1]
(ii)
Explain why the current remains zero.
[2]
Assess your score
View Answer
Previous Question