Skills: Analysing DNA Methylation Patterns
Methylation of DNA
- Methyl groups (-CH3) can be directly added to DNA to change the activity of a gene
- DNA methylation commonly involves the direct addition of a methyl group to cytosine bases which can influence gene expression
- Methylation of DNA suppresses the transcription of the affected gene by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors
- Cells use this mechanism to lock genes in the ‘off’ position
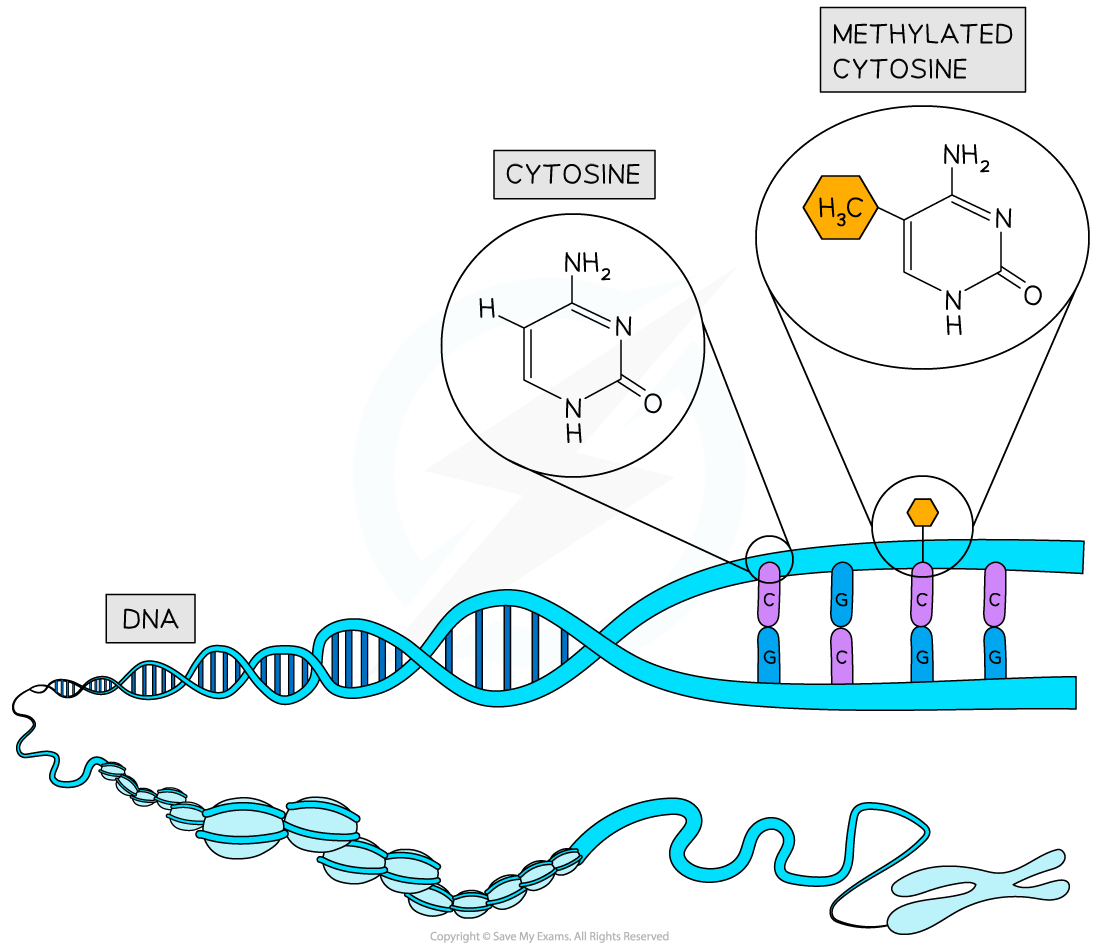
DNA methylation involves the addition of a methyl group to a cytosine nucleotide
Analysing DNA Methylation Patterns
- DNA methylation varies throughout a lifetime and can be affected by environmental, lifestyle or age-related factors
- Changes in DNA methylation are observed in genetic diseases like cancer
- DNA methylation can be used as a biomarker to identify cancer related genes
- This could help develop therapeutics to improve early diagnosis of disease
- Numerous methods are available to identify which cytosine bases have been methylated
- Analysis of methylation patterns between a disease and non-disease state can help identify disease marker genes
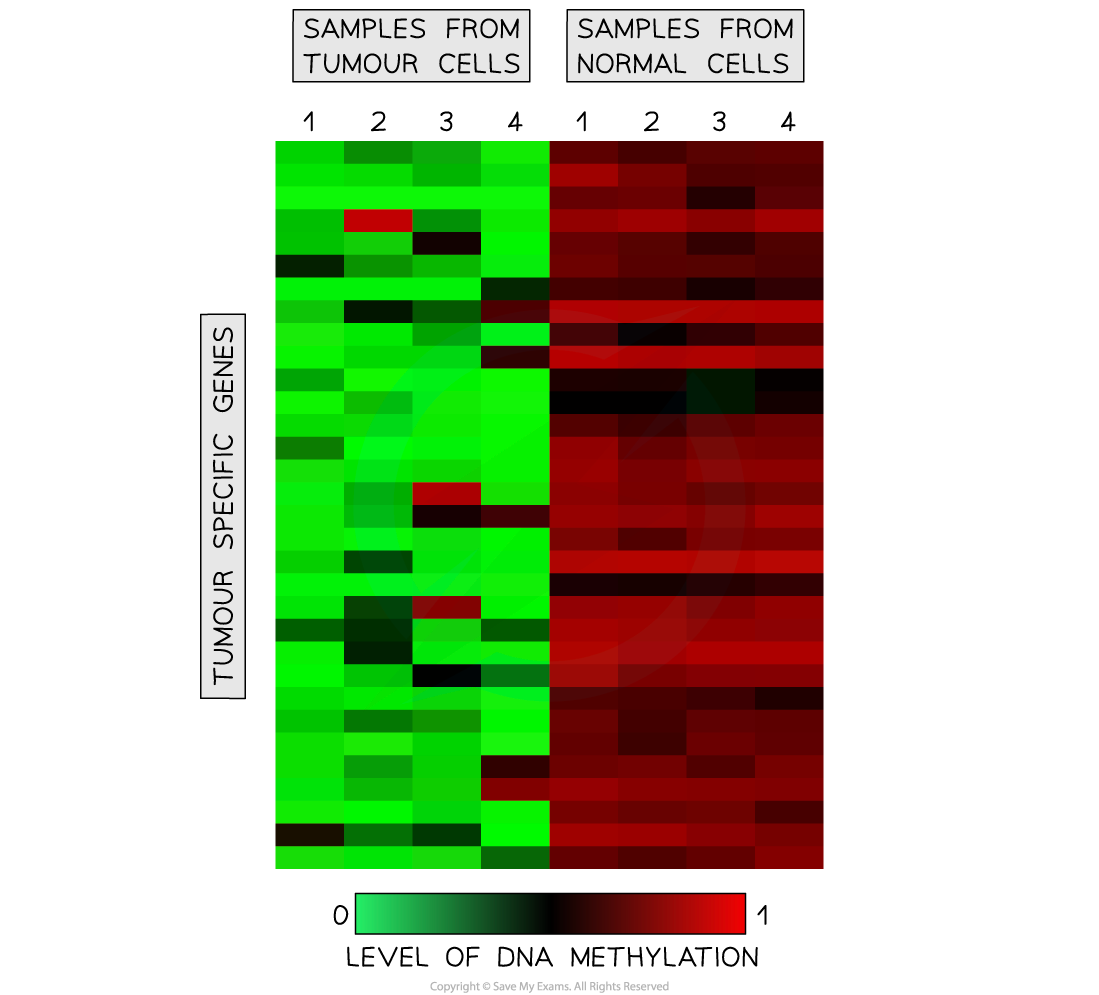
DNA Methylation analysis showing reduced methylation of tumour-specific genes in cancerous cells. Reduced methylation results in genes always being ‘switched on’ which can lead to cancer
