Cellular Respiration Defined
- Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP
- Respiration is a series of chemical reactions that happens in every cell
- Its purpose is to release energy in usable forms from the chemical energy stored in food e.g. glucose
- Respiration is a catabolic process
- Glucose is the main respiratory fuel used in cells
- Lipids and proteins can also be used
- Organic food substances contain a lot of chemical energy
- This energy cannot be released in one, uncontrolled step in cells, which would cause cell damage and tissue death
- Enzymes control the release of energy through a series of chemical reactions called a pathway
- This ends in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
- To make ATP, a phosphate group is linked to adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
- This process requires energy which comes from the breakdown of organic molecules
- The energy that is released is used for
- Fuelling anabolic processes
- Muscle contraction
- Fuelling active transport
- Moving molecules around the cell
- Generating heat to maintain body temperature in warm-blooded animals
Exam Tip
Respiration is often confused with breathing, but remember, respiration is a chemical process, breathing is a method of moving air in and out of the body
ATP
- ATP is a source of energy for cellular processes
- The energy can be released immediately, exactly when it is required
- All organisms require a constant supply of energy to maintain their cells and stay alive
- This energy is required:
- In anabolic reactions – synthesizing larger molecules from smaller molecules
- To move molecules across the cell membrane (active transport)
- To move substances and organelles within the cell
- In animals, energy is required:
- For muscle contraction – to coordinate movement at the whole-organism level
- In the conduction of nerve impulses, as well as many other cellular processes
- ADP and phosphate can then be re-converted to ATP during respiration
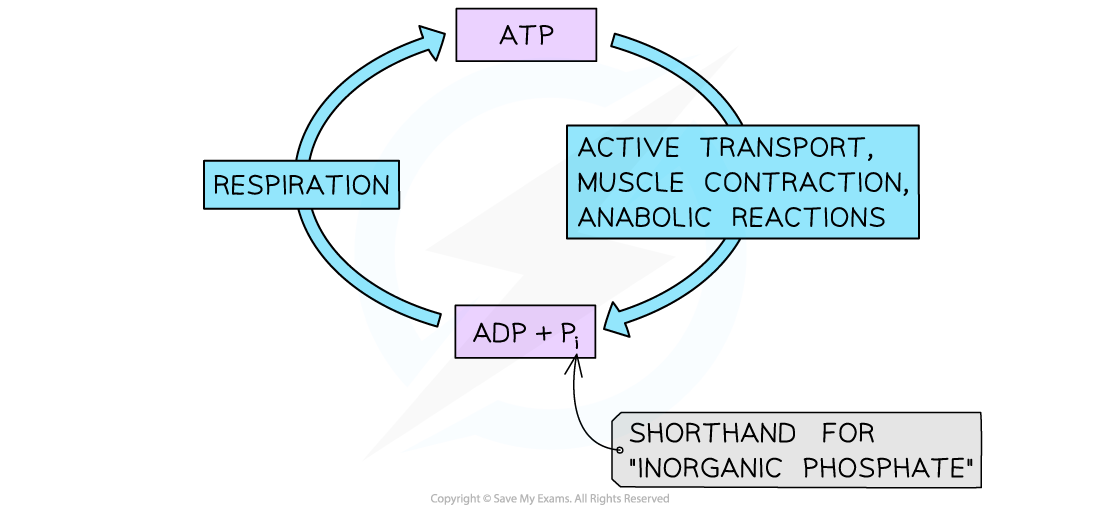
The constant cycling of ATP and ADP+Pi within a cell
