Photosynthesis Defined
- Simple, inorganic compounds are converted into complex organic ones by photosynthesis
- The energy required is provided by light
- Photosynthesis occurs in autotrophic organisms such as plants, algae and cyanobacteria
- H2O and CO2 are the raw materials
- Photosynthesis is a form of energy conversion, from light energy to chemical energy, stored in biomass
- Energy is stored within the bonds of these organic compounds
- Photosynthesis can be thought of as the exact reverse of respiration
- Respiration is the process by which energy is released from organic molecules in living cells
- The overall chemical equation for photosynthesis is as follows:
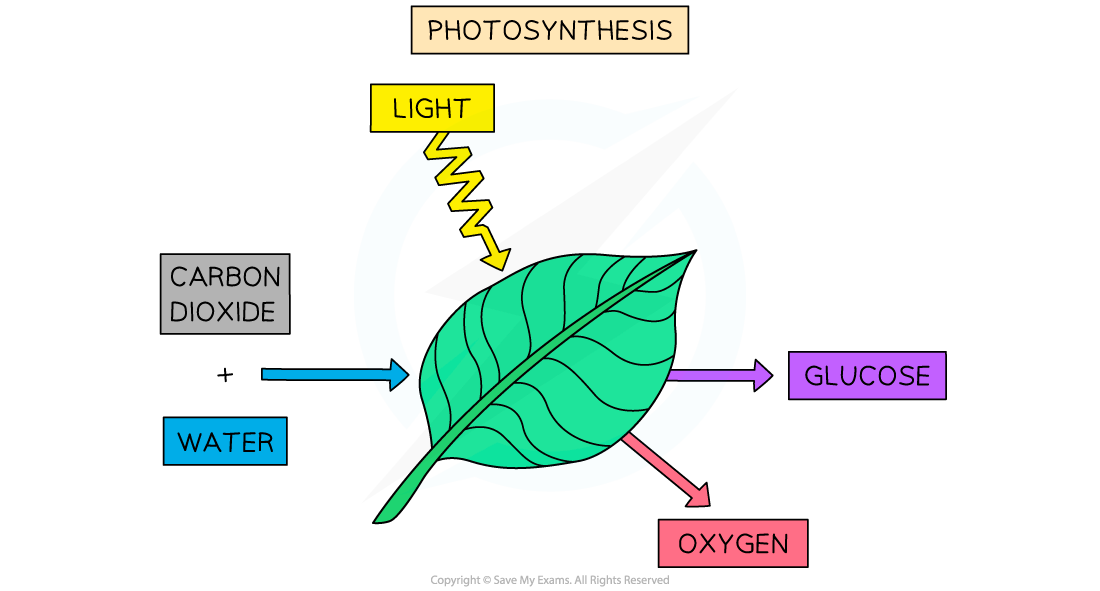
The basic equation of photosynthesis as it takes place in a leaf

The chemical equation for photosynthesis
Exam Tip
Remember, energy is never created or destroyed; it is only ever converted from one form to another!
Visible Light Wavelengths
- Chloroplasts contain pigments in order to absorb light
- Pigments are coloured, which means they absorb some wavelengths (or colours) of the white light that the Sun radiates
- The remaining light is reflected, giving the pigment its colour
- Chloroplasts contain several different photosynthetic pigments, so that they can absorb multiple different wavelengths of light
- The main photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll
- Violet light has the shortest wavelength of light in the visible spectrum (around 400nm)
- Red light has the longest wavelength of light in the visible spectrum (around 700nm)
- Green light has a wavelength in the middle of this range (around 550nm)
- The absorption of light varies with wavelength, as does the rate of photosynthesis that a plant can carry out
- When plants are exposed to light of a specific wavelength, the rate of photosynthesis can be measured as well as the absorbance (the % of the light that is absorbed by the plants)
- There are peaks in both plots at the blue and red ends of the spectrum, where photosynthesis can occur
- There are troughs in both plots for green light, which is not absorbed and so cannot provide energy for photosynthesis
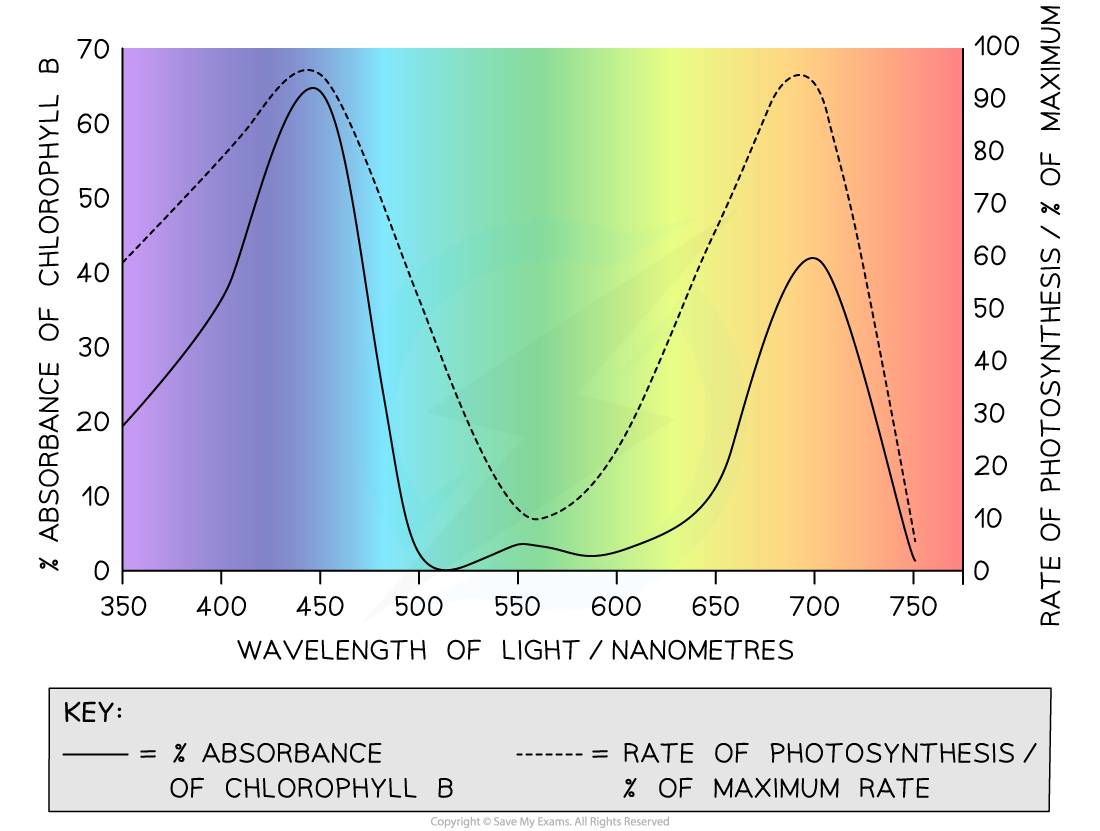
The effect of visible light wavelength on the % absorbance of chlorophyll b and the rate of photosynthesis
Exam Tip
You don't have to memorise the wavelengths of different colours of light, but you need to know that visible light has a wavelength of between 400 and 700 nanometres (nm).
Chlorophyll
- Plant cells contain chloroplasts which are the site of photosynthesis
- The main photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll
- Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light most effectively and reflects green light more than other colours
- Chlorophyll appears green because it absorbs red and blue light
- The green light is reflected away and so leaves appear green to the eye
- This explains why the majority of plants are green (with variations in the shades of green that we can see)
- Red and blue light provides the energy needed for photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll exists in two main forms, a and b
- There are two groups of pigments: primary pigments known as chlorophylls and accessory pigments known as carotenoids
- Chlorophylls absorb wavelengths in the blue-violet and red regions of the light spectrum
- Carotenoids absorb wavelengths of light mainly in the blue-violet region of the spectrum
- The combination of pigments maximises the amount of white light energy that can be captured
Exam Tip
Remember – chlorophyll is not the only photosynthetic pigment, others exist to maximise light energy absorption.
Photolysis of Water
- Oxygen is produced in photosynthesis from the photolysis of water
- Photo - means 'with light'
- Lysis - means 'breaking apart'
- Water is broken apart using light energy; this is called photolysis
- This releases electrons (e-), protons (H+) and the waste product, oxygen gas
2H2O → 4e- + 4H+ + O2
- Whilst oxygen is a waste product, the electrons and protons play a crucial role in the further reactions of photosynthesis
- Though oxygen is a waste product, in practice, a plant will use some of the oxygen it produces in photosynthesis for its own respiration (during the day)
