The Human Development Index (HDI)
- Economic development is the sustainable increase in living standards for a country, typically characterised by increases in life span, education levels, & income
- Composite indicators include indicators such as the Human Development Index (HDI), the Gender Inequality Index (GII), Inequality Adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI), and the Happy Planet index (HPI)
The Human Development Index (HDI)
- Developed by the United Nations, it is a combination of 3 indicators
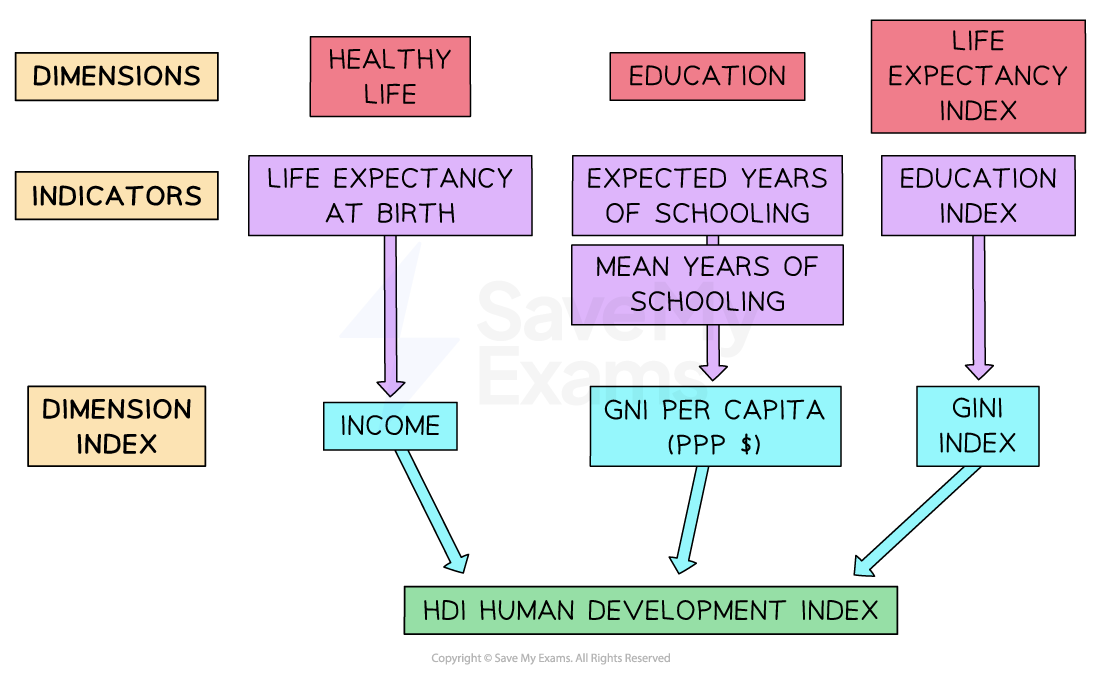
The components of the Human Development Index
- Health, as measured by the life expectancy at birth e.g.in 2019 it was 81.2 years in the UK
- Education, as measured by a combination of the mean years of schooling that 25 year old's have received, together with the expected years of schooling for a pre-school child
- Income, as measured by the real gross national income per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP)
- Each indicator is given equal weighting in the index
- The index ranks countries on a score between 0 & 1
- The closer to 1, the higher the level of economic development & the better the standard of living
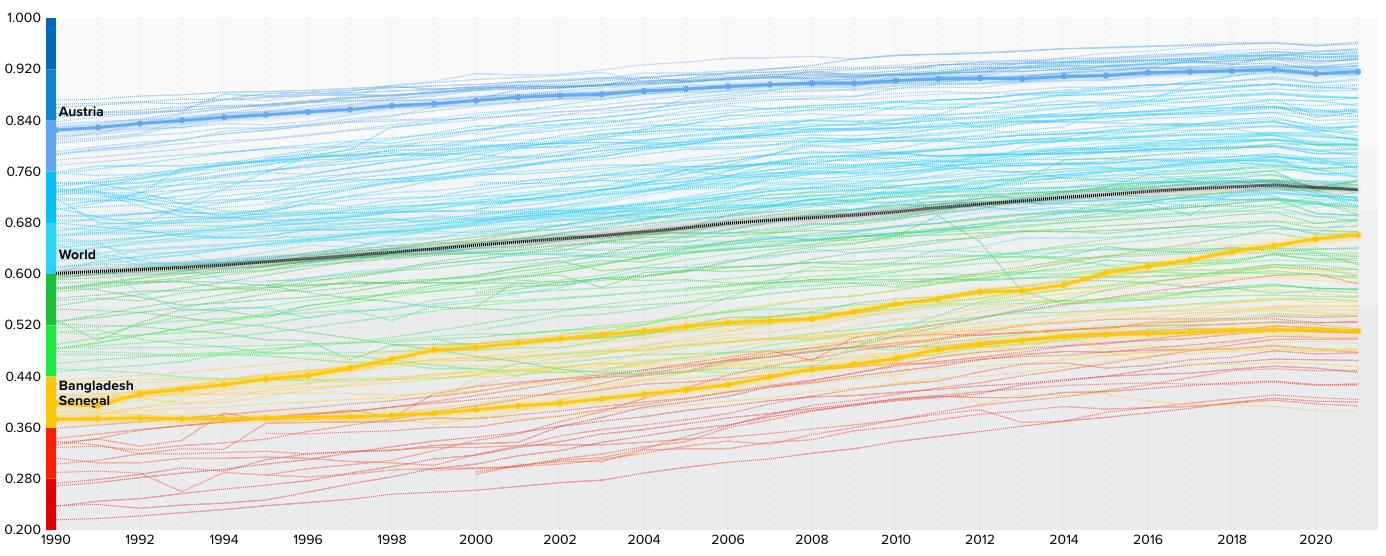
The Human Development Index scores from 1990 to 2021 (Source: UNDP Data Centre)
- A value of < 0.550 is considered low development e.g. Senegal was at 0.514 in 2021
- A value of 0.550-0.699 is considered medium development e.g.Bangladesh was at 0.667 in 2021
- A value of 0.700-0.799 is considered high development e.g Thailand was at 0.777 in 2021
- A value ≥ 0.800 is considered very high development e.g. Austria was at 0.918 in 2021
Inequality adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI)
- Created in 2010 to deal with the lack of information that the HDI provides on inequality
- The IHDI will be equal to the HDI value when there is no inequality, but falls below the HDI value as inequality rises
- This means that the IHDI measures the level of human development when inequality is accounted for
- The difference between the HDI and IHDI can be expressed as a percentage and represents the loss in potential human development due to inequality
- It provides greater insight into the differences in human development that exist in a country as opposed to the average human development
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
- The Gender Inequality Index (GII) measures gender inequality using three dimensions:
- Reproductive health
- Empowerment
- The labour market
- Countries are graded on a scale of 0→1
- The lower the value the better the inequality between men and women, and vice-versa
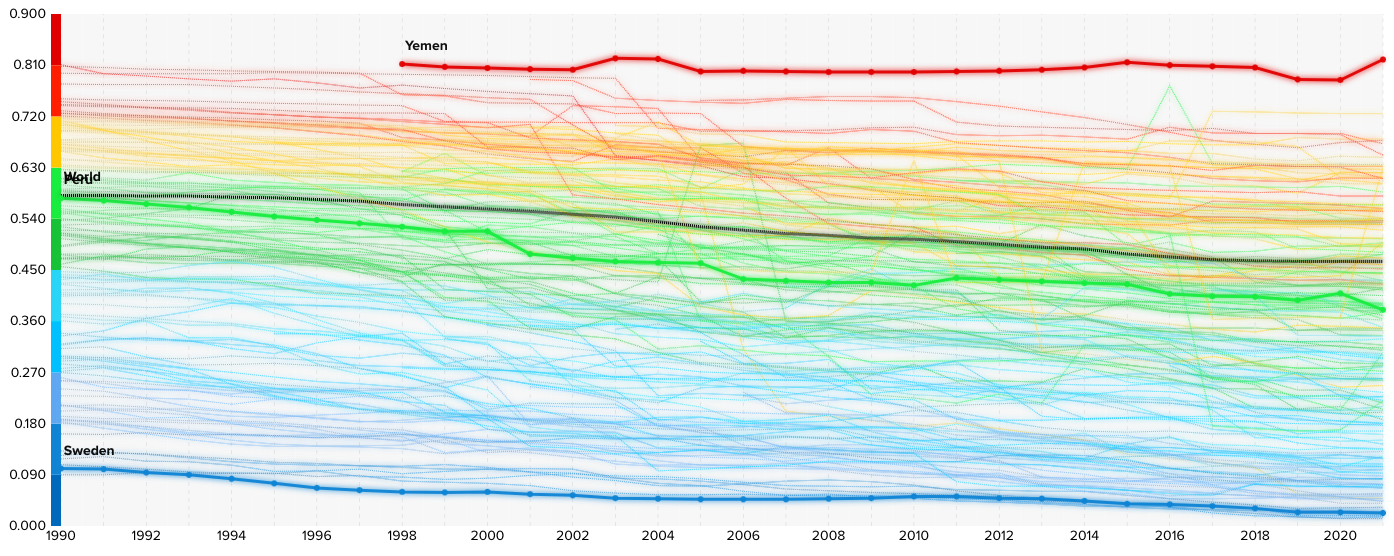
Sweden, Peru and Yemen all score vastly differently on the GII index with Sweden the most equal and Yemen the least equal (Source: UNDP Data Centre)
Happy Planet Index (HPI)
- The Happy Planet Index (HPI) attempts to measure sustainable wellbeing
- Countries are ranked by how efficiently they deliver long, happy lives using the earth's scarce resources in a sustainable way
- The HPI scores countries with a lower ecological footprint higher than countries with more environmental degradation
- The HPI measures a country's progress using three variables
- Wellbeing
- Life expectancy
- Ecological footprint
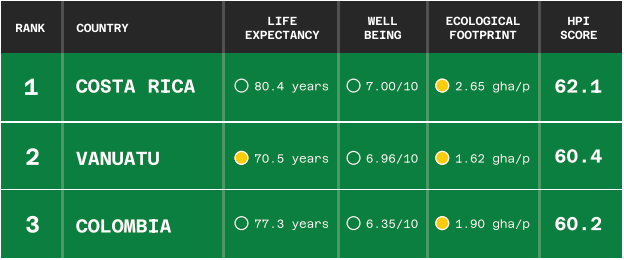
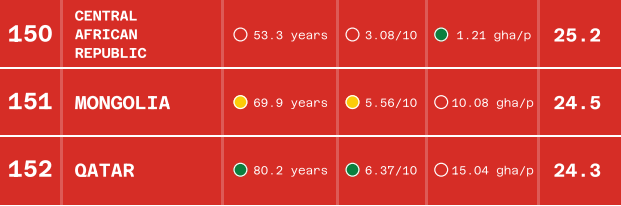
The top 3 and bottom 3 countries on the HPI in December 2022 (Source: Happy Planet Index)