Price Ceilings (Maximum Prices)
- Price controls are used by governments to influence the levels of production or consumption
- Two types of control are commonly used: maximum price (price ceiling) and minimum price (price floor)
Price Ceiling (Maximum Price)
- A price ceiling is set by the government below the existing free market equilibrium price and sellers cannot legally sell the good/service at a higher price
- Governments will often use price ceilings in order to help consumers
- Sometimes they are used for long periods of time e.g. to keep rents lower in housing rental markets
- Other times they are short-term solutions to unusual price increases e.g. petrol

The price ceiling (Pmax) sits below the free market price (Pe) and creates a condition of excess demand (shortage)
Diagram Analysis
- The initial market equilibrium is at PeQe
- A price ceiling is imposed at Pmax
- The lower price reduces the incentive to supply and there is a contraction in quantity supplied (QS) from Qe → Qs
- The lower price increases the incentive to consume and there is an extension in quantity demanded (QD) from Qe → Qd
- This creates a condition of excess demand equal to QsQd
An Evaluation of Price Ceilings
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Price Ceilings (Maximum Prices)
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Price Floors (Minimum Prices)
- A price floor (minimum price) is set by the government above the existing free market equilibrium price and sellers cannot legally sell the good/service at a lower price
- Governments will often use price floors in order to help producers or to decrease consumption of a demerit good e.g. alcohol
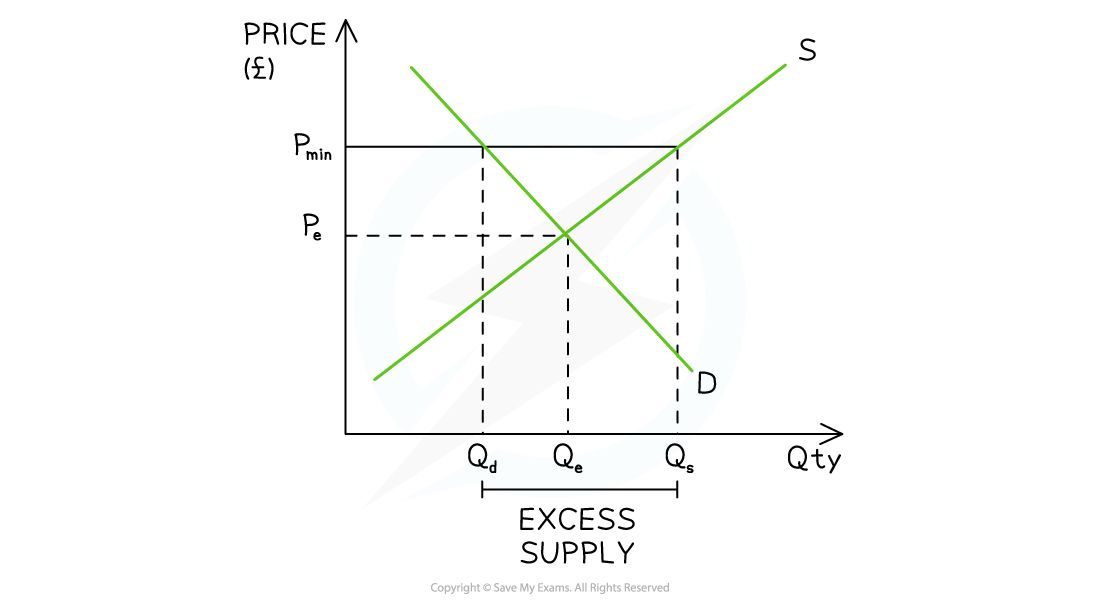
The imposition of a price floor (Pmin) above the free market price (Pe) creates a condition of excess supply (surplus)
Diagram Analysis
- The initial market equilibrium is at PeQe
- A price floor is imposed at Pmin
- The higher price increases the incentive to supply and there is an extension in QS from Qe → Qs
- The higher price decreases the incentive to consume and there is a contraction in QD from Qe → Qd
- This creates a condition of excess supply equal to QdQs
An Evaluation of Price Floors
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Price Floors (Minimum Prices) in Product Markets
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Price Floors (Minimum Prices) in Labour Markets
- Minimum prices are also used in the labour market to protect workers from wage exploitation
- A national minimum wage (NMW) is a legally imposed wage level that employers must pay their workers
- It is set above the market rate
- The minimum wage/hour usually varies based on age

A national minimum wage (NMW1) is imposed above the market wage rate (We) at W1
Diagram Analysis
- The demand for labour (DL) represents the demand for workers by firms
- The supply of labour (SL) represents the supply of labour by workers
- The market equilibrium wage & quantity for truck drivers in the UK is seen at WeQe
- The UK government imposes a national minimum wage (NMW) at W1
- Incentivised by higher wages, the supply of labour increases from Qe to Qs
- Facing higher production costs, the demand for labour by firms decreases from Qe to Qd
- This means that at a wage rate of W1 there is excess supply of labour & the potential for unemployment equal to QdQs
An Evaluation of Minimum Wages
The Advantages and Disadvantages of using Minimum Wages in Labour Markets
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Direct Provision of Services
- Many public goods and services improve the lives of a country's population
- Governments often provide services to improve the level of equity e.g. healthcare services ensure everyone can access the same medical treatment
An Explanation and Evaluation of the State Provision of Public Services
Method |
Explanation |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
State provision of public goods/services |
|
|
|
Regulation & Legislation
- Legislation is the process of creating laws
- Regulation is the process of monitoring and enforcing the laws
- The use of legislation and regulation are referred to as command and control as it involves ongoing government intervention
An Explanation & Evaluation of Government Regulation & Legislation
Method |
Explanation |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Legislation and Regulation |
|
|
|