Economic Growth
- Economic growth is a central macroeconomic aim of most governments
- Many developed nations have an annual target rate of 2-3%
- This is considered to be sustainable growth
- Growth at this rate is less likely to cause excessive demand pull inflation
- Politicians often use the economic growth rate as a metric of the effectiveness of their policies and leadership
- Economic growth has positive impacts on confidence, consumption, investment, employment, incomes, living standards and government budgets
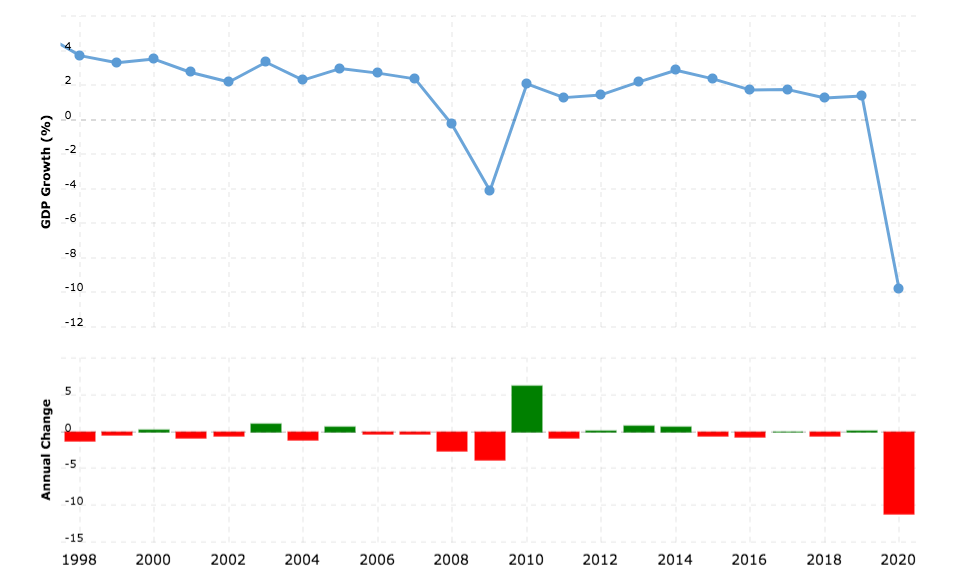
The economic growth rate of the UK since 1998
Source: Macrotrends
Some of the Economic Growth Trends in the UK Since 1998
1998 - 2007 |
2008 - 2015 |
2016 - 2019 |
2020 - |
|
|
|
|
|
Low Unemployment
- The target unemployment rate for many economies is between 2-5%. In December 2022 the unemployment rate in the USA was 3.7% and in Singapore it was 2.6%
- Low unemployment rates like this are close to the full employment level of labour (YFE)
- There will always be a level of frictional, seasonal and structural unemployment
- This makes it impossible to achieve 100% employment and is called the natural rate of unemployment (NRU)
- Different economies have different unemployment rates that are considered to be close to the full employment level of labour e.g. Japan's level is about 2.5% while India's is about 5.7%
- Within the broader unemployment rate, there is an increased emphasis on the unemployment rate within different sections of the population
- E.g. youth unemployment, ethnic/racial unemployment by group
- In 2021, black unemployment in the UK was 11% and white unemployment was 4.%
- E.g. youth unemployment, ethnic/racial unemployment by group
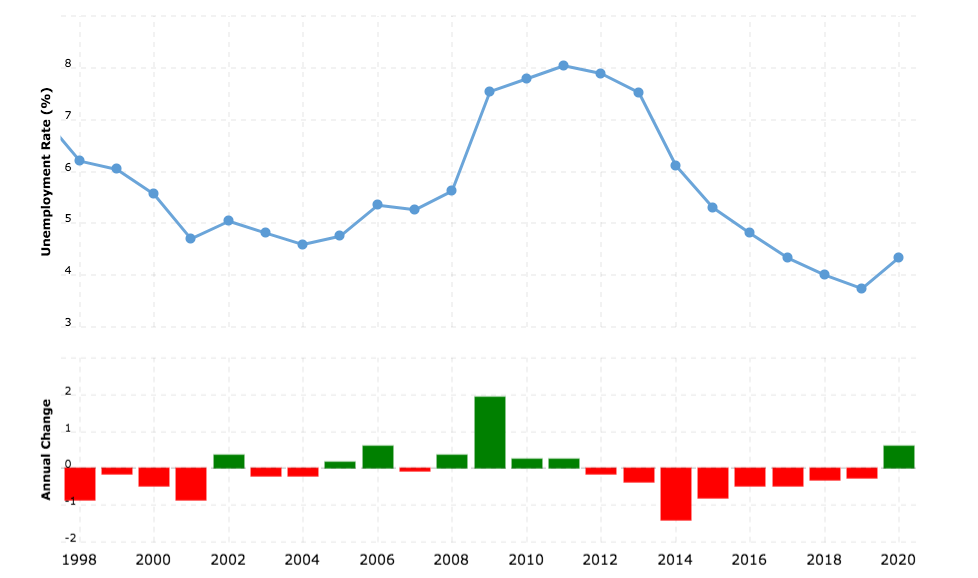
The unemployment rate in the UK from 1998 - 2020
Source: Macrotrends
- Unemployment tends to be inversely proportional to real GDP growth
- When real GDP increases, unemployment falls
- When real GDP decreases, unemployment rises
Low and Stable Rate of Inflation
- Many economies have a target inflation rate of 2% using the Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- A low rate of inflation is desirable as it is a symptom of economic growth
- The different causes of inflation (cost push or demand pull) require different policy responses from the Government
- Demand-side policies ease demand pull inflation
- Supply-side policies ease cost push inflation
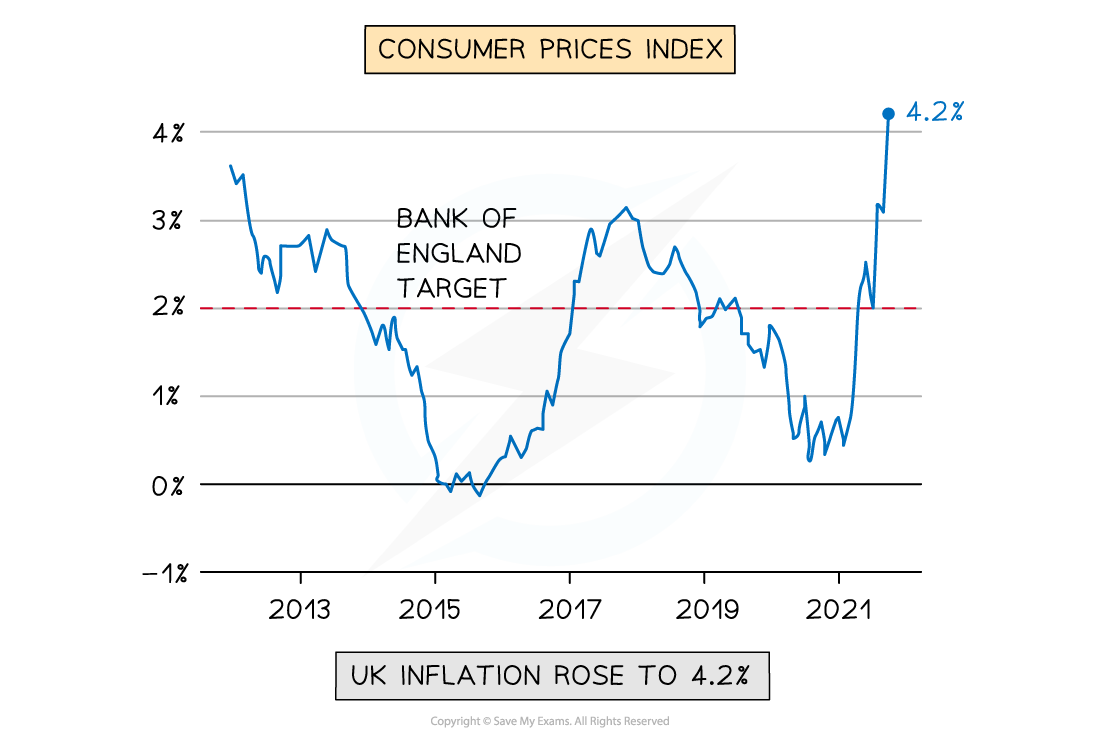
The inflation rate in the UK from 2012 to 2021 using the CPI
- In the UK, a continual deviation from the target of 2% would not be considered stable
- An inflation rate in April 2022 of 4-5% was considered to be unstable, eroding household purchasing power
- By October 2022 the inflation rate had risen to 11.1%
- A low and stable rate of inflation is important as it
- Allows firms to confidently plan for future investment
- Offers price stability to consumers