The Multidimensional Nature of Economic Development
- The 17 Sustainable Development Goals demonstrate the complexity of the nature of economic development
- The different elements can be separated into three categories: economic, social and environmental
- Sustainable economic development occurs at the intersection of all three and is represented in the diagram below
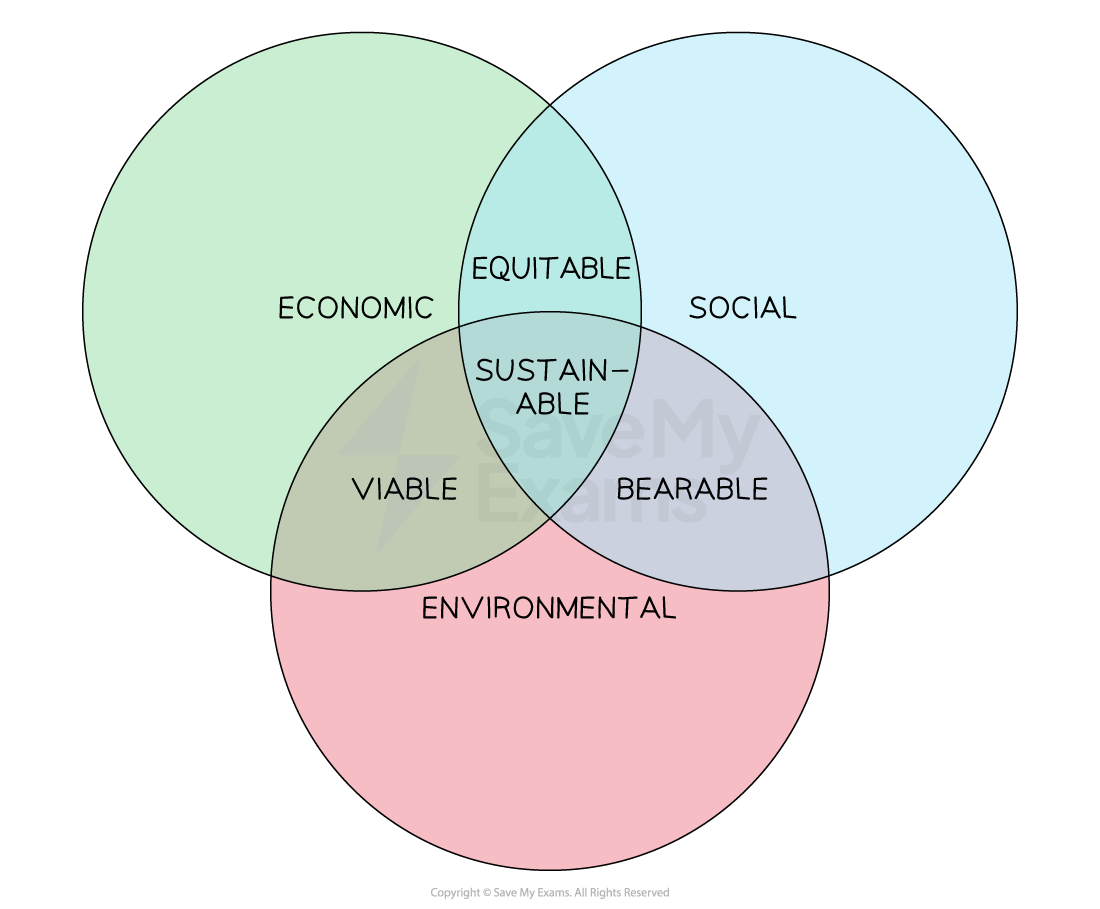
Sustainable economic development is a multi-dimensional concept incorporating economic growth, environmental care and social progress
- Viable refers to the fact that the combination of economic and environmental progress is happening with some care, however it is not sustainable in the long term
- Bearable refers to the fact that the interaction of society and the environment is happening with some thought, however it is still not sustainable in the long term
- Equitable refers to the fact that the interaction of the economy and society is happening with some attention to well-being, however it is still not sustainable in the long term
- Due to this complexity, elements of economic development can be measured using single or composite indicators
Single Indicators of Economic Development
- A single indicator is one factor, such as GDP per person (capita), used to measure the development of a country
- Single indicators measures only one development characteristic within a country
1, GDP/GNI per person (per capita) at PPP
- Real GDP is the value of all goods/services produced in an economy in a one-year period - and adjusted for inflation
- For example, if nominal GDP is £100bn and inflation is 10% then real GDP is £90bn
- For example, if nominal GDP is £100bn and inflation is 10% then real GDP is £90bn
- GDP per capita = GDP / the population
- It shows the mean wealth of each citizen in a country
- This makes it easier to compare standards of living between countries:
- For example, Switzerland has a much higher GDP/capita than Burundi
- For example, Switzerland has a much higher GDP/capita than Burundi
- Gross national income (GNI) measures the income earned by citizens operating outside of the country + the GDP
- Many citizens employ their resources outside of a country's borders - and then send the income home
- Many citizens employ their resources outside of a country's borders - and then send the income home
- Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a conversion factor that can be applied to GDP, GNI and GNP
- PPP calculates the relative purchasing power of different currencies
- It shows the number of units of a country's currency that are required to buy a product in the local economy, as $1 would buy of the same product in the USA
- The aim of PPP is to help make a more accurate standard of living comparison between countries where goods/services cost different amounts
- Using real GDP/Capita provides better information than real GDP as it takes population differences into account
- Using real GNI/capita is a more realistic metric for analysing the income available per person than GDP/capita
- Using GDP/GNI per person (per capita) at PPP allows for comparisons between countries which take into account the substantial differences in the cost of living
2. Health and education indicators
- Multiple single indicators for health and education can provide useful data for comparisons between countries
- Typical single health indicators include:
- Infant mortality rate
- Life expectancy
- Number of doctors per 1,000 of the population
- Diabetes incidence
- Typical single education indicators include:
- Youth literacy rate
- Adult literacy rate
- Mean years in school
- Ratio girls/boys in school
- Math achievement 8th grade
3. Economic/social inequality indicators
- Typical single economic and societal indicators include:
- The Gini Coefficient
- Murders per 1000 of the population
- Percentage of women in national parliaments
4. Energy indicators
- Typical single energy indicators include:
- Coal consumption per person
- Electricity generation per person
- Residential electricity usage
- Oil consumption per person
5. Environmental indicators
- Typical single environmental indicators include:
- CO2 emissions per person
- Total CO2 emissions
- Agricultural water withdrawal
- Primary forest area