Definition & Calculation of YED
- Changes in income result in changes to the demand for goods/services
- Economists are interested in how much the quantity demanded will change for different products
- Income elasticity of demand (YED) reveals how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in income
Calculation of YED
- YED can be calculated using the following formula
Worked Example
A consumer's income rises from SG$ 100 to SG$ 125 a week. They originally consumed 12 bubble teas but this increased to 15 bubble teas a week. Calculate the YED of the bubble teas [2]
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QD
Step 2: Calculate the % change in Y
Step 3: Insert the above values in the YED formula
(Two marks for the correct answer or 1 mark for any correct working)
Interpreting YED Values
- The YED value can be positive or negative and the value is important in determining the type of good
- A good with a positive YED value is considered to be a normal good
- Normal goods can be classified as necessities or luxuries
- A good with a negative YED value is considered to be an inferior good
- A good with a positive YED value is considered to be a normal good
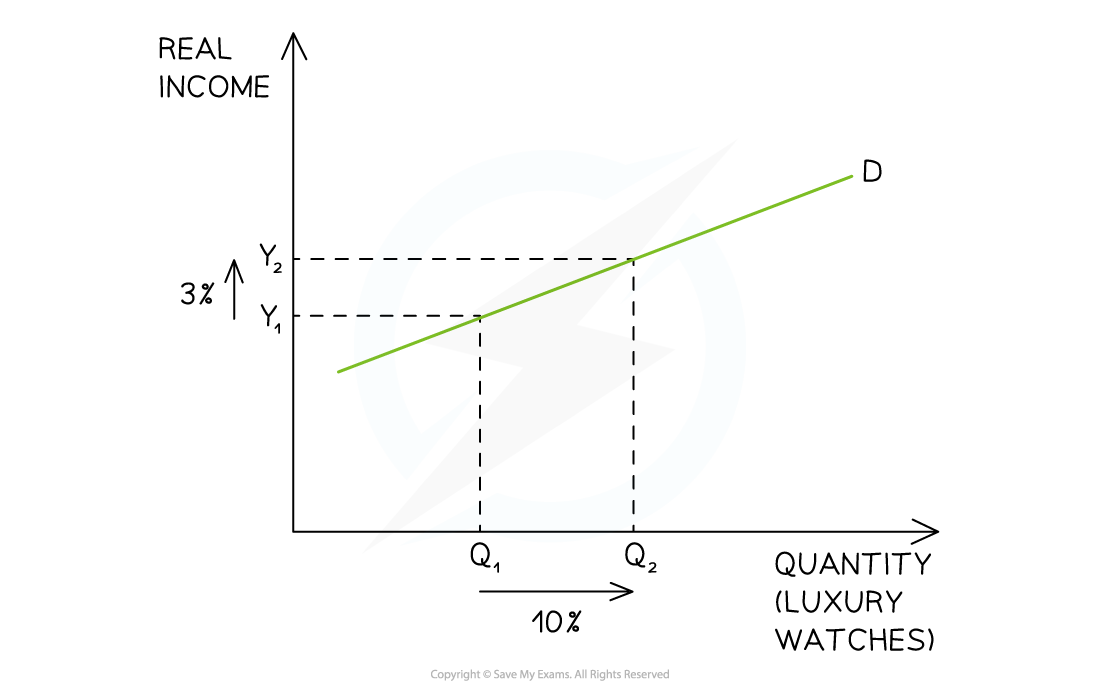
- Engle curves are a model used to illustrate the relationship between income and the quantity demanded (QD)
- Income is presented on the Y-axis and quantity demanded on the X-axis
- Income is presented on the Y-axis and quantity demanded on the X-axis
The Value of YED Determines the type of good and Response to Changes in Income
Value |
Type of Good |
Explanation |
Engel Curve |
|
0→1 |
Necessity |
|
|
|
YED > 1 |
Luxury |
|
|
|
YED < 0 |
Inferior Good |
|
|
Exam Tip
Remember this distinction! With PED values the negative sign is always ignored. However for YED, the sign is integral to understanding if the good is a normal (+) or inferior (-) good.
Factors that Influence YED
- YED is influenced by any factors in an economy which change the wages of workers
- During a recession wages usually fall and demand for inferior goods rises while demand for luxury goods falls
- During a period of economic growth and rising wages, demand for luxury goods increases while demand for inferior goods decreases
- Other influences on income include minimum wage legislation, taxation, increased international trade