The Definition & Calculation of PED
- The law of demand states that when there is an increase in price, there will be a fall in the quantity demanded
- Economists are interested by how much the quantity demanded will fall
- Price elasticity of demand reveals how responsive the change in quantity demanded is to a change in price
- The responsiveness is different for different types of products
- The responsiveness is different for different types of products
Calculation of PED
- PED can be calculated using the following formula
- To calculate a % change, use the following formula
Worked Example
A firm raises the price of its products from $10 to $15. Its sales fall from 100 to 40 units per day. Calculate the PED of its products [2]
Step 1: Calculate the % change in QD
Step 2: Calculate the % change in P
Step 3: Insert the above values in the PED formula
Step 4: Final answer = 1.2
The PED value will always be negative so economists ignore the sign and present the answer as 1.2
(Two marks for the correct answer or 1 mark for any correct working in the process)
Exam Tip
In Paper 2 you are occasionally given the PED value and the %Δ in QD - you are then asked to calculate the %Δ in price. Follow the standard math procedure as follows:
1. Substitute the values provided into the equation
2. Substitute X for %Δ in price
3. Solve for X
Interpreting PED Values
The size of PED Varies from 0 to Infinity (∞) and is Classified as Follows
Value |
Name |
Explanation |
Diagram |
0 |
Perfectly Inelastic |
|
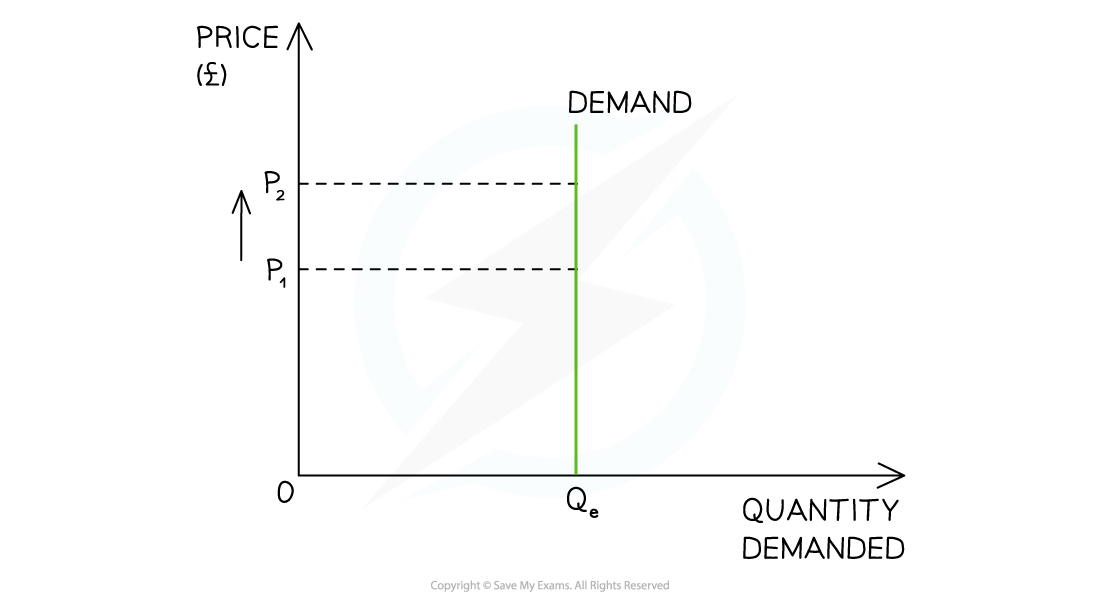 |
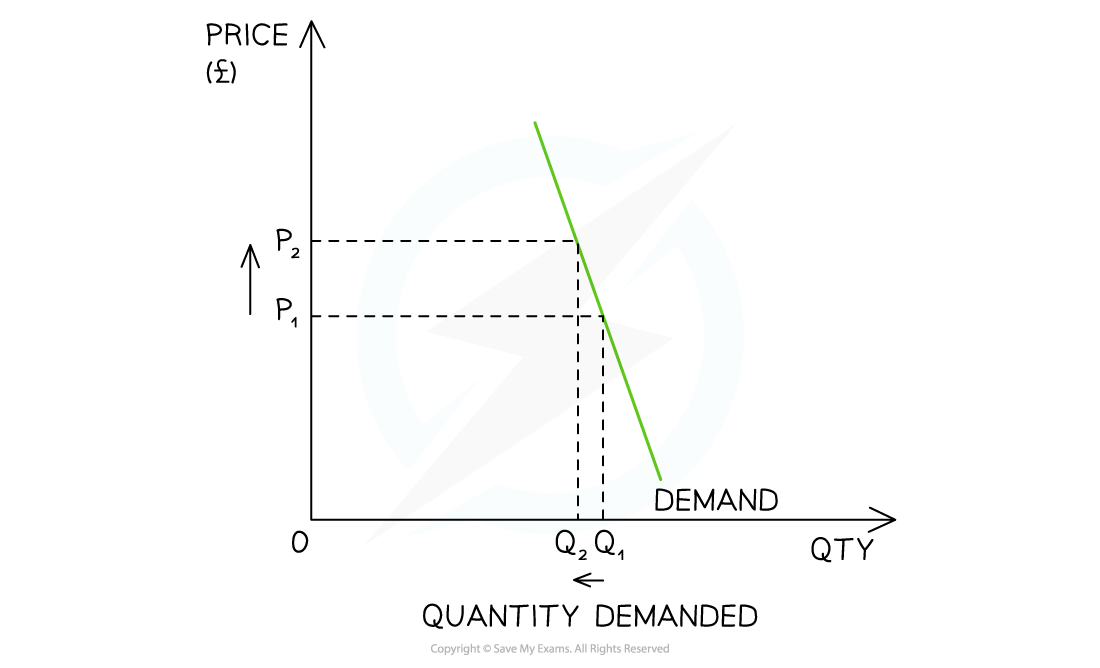
0→1 |
Relatively Inelastic |
|
 |
1 |
Unitary Elasticity |
|
 |
1→ ∞ |
Relatively Elastic |
|
 |
∞ |
Perfectly Elastic |
|
 |