DP Physics Questionbank

Additional higher level (AHL)
Description
[N/A]Directly related questions
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
Six identical capacitors, each of value C, are connected as shown.
What is the total capacitance?
A.
B.
C.
D. 6C
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Monochromatic light is incident on two identical slits to produce an interference pattern on a...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.27: A spring loaded with mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion. The amplitude of the motion...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.33: An isolated hollow metal sphere of radius R carries a positive charge. Which graph shows...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
A satellite in a circular orbit around the Earth needs to reduce its orbital radius.
What is the work done by the satellite rocket engine and the change in kinetic energy resulting from this shift in orbital height?
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Two charges, +Q and −Q, are placed as shown. What is the magnitude of the electric field...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A mass at the end of a vertical spring and a simple pendulum perform oscillations on Earth that...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.39: A particle of fixed energy is close to a potential barrier. Which changes to the width of the...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
The capacitor is fully charged and the space between the plates is then filled with a dielectric of permittivity ε = 3.0ε0.
Explain whether the magnitude of the charge on plate A increases, decreases or stays constant.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
The capacitor is connected to a 16 V cell as shown.
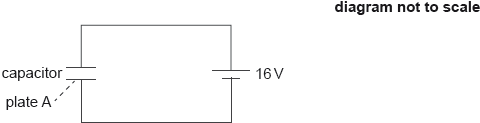
Calculate the magnitude and the sign of the charge on plate A when the capacitor is fully charged.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
Two samples X and Y of different radioactive isotopes have the same initial activity. Sample X has twice the number of atoms as sample Y. The half-life of X is T. What is the half-life of Y?
A. 2T
B. T
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5c:
The slit separation is increased. Outline one change observed on the screen.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8d:
State one assumption that needs to be made so that the Earth-thundercloud system may be modelled by a parallel plate capacitor.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9d.i:
Explain what may be deduced about the energy of the electron in the β– decay.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Describe the conditions required for an object to perform simple harmonic motion (SHM).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
A second identical spring is placed in parallel and the experiment in (b) is repeated. Suggest how this change affects the fractional uncertainty in the mass of the block.
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
A particle is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude x0 and maximum kinetic energy Ek. What is the potential energy of the system when the particle is a distance 0.20x0 from its maximum displacement?
A. 0.20Ek
B. 0.36Ek
C. 0.64Ek
D. 0.80Ek
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5a:
Monochromatic light from two identical lamps arrives on a screen.
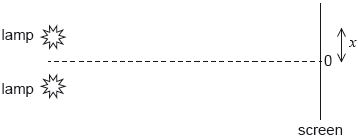
The intensity of light on the screen from each lamp separately is I0.
On the axes, sketch a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity I of light on the screen.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
In two different experiments, white light is passed through a single slit and then is either refracted through a prism or diffracted with a diffraction grating. The prism produces a band of colours from M to N. The diffraction grating produces a first order spectrum P to Q.
What are the colours observed at M and P?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
The four pendulums shown have been cut from the same uniform sheet of board. They are attached to the ceiling with strings of equal length.
Which pendulum has the shortest period?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.32: Two positive and two negative charges are located at the corners of a square as shown. Point X is...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
A simple pendulum has a time period on the Earth. The pendulum is taken to the Moon where the gravitational field strength is that of the Earth.
What is the time period of the pendulum on the Moon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A circuit consists of three identical capacitors of capacitance C and a battery of voltage V. Two...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A train is sounding its whistle when approaching a train station. Three statements about the...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The graph shows the variation with distance r of the electric potential V from a charge...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.34: Which two features are necessary for the operation of a transformer?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.35: A conducting bar with vertices PQRS is moving vertically downwards with constant velocity v...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.39:
The dashed line represents the variation with incident electromagnetic frequency of the kinetic energy EK of the photoelectrons ejected from a metal surface. The metal surface is then replaced with one that requires less energy to remove an electron from the surface.
Which graph of the variation of EK with will be observed?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
Which graph shows a possible probability density function for a given wave function of an electron?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.36: Two capacitors of 3 μF and 6 μF are connected in series and charged using a 9 V battery. What...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
The headlights of a car emit light of wavelength 400 nm and are separated by 1.2 m. The headlights are viewed by an observer whose eye has an aperture of 4.0 mm. The observer can just distinguish the headlights as separate images. What is the distance between the observer and the headlights?
A. 8 km
B. 10 km
C. 15 km
D. 20 km
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.29: In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the distance between fringes is too small to be...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.32: A negative charge Q is to be moved within an electric field E, to equidistant points from its...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: The cable between the satellites cuts the magnetic field lines of the Earth at right...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2b.ii: satellite Y requires a propulsion system.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii: Suggest the variation in the output voltage from the light sensor that will be observed as the...
-
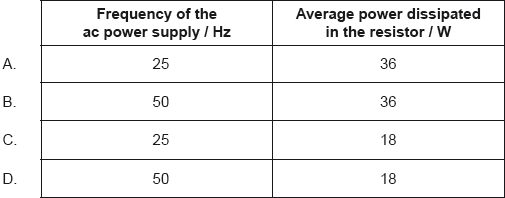
18M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
The graph shows the power dissipated in a resistor of 100 Ω when connected to an alternating current (ac) power supply of root mean square voltage (Vrms) 60 V.
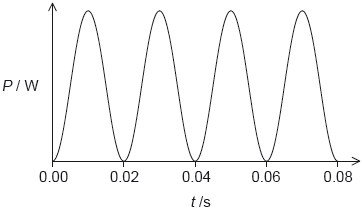
What are the frequency of the ac power supply and the average power dissipated in the resistor?
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.3d:
Loudspeaker A is switched off. Loudspeaker B moves away from M at a speed of 1.5 m s−1 while emitting a frequency of 3.0 kHz.
Determine the difference between the frequency detected at M and that emitted by B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the electric potential at O.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.7b: Sketch, on the axes, the variation of the electric potential V with distance between X and Y.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i: The switch is closed at time t = 0. Explain how the voltmeter reading varies after the switch is...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.9c:
Outline how the decay constant of potassium-40 was determined in the laboratory for a pure sample of the nuclide.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iv: In test 2, the maximum elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring is 44 J. When t = 0 the...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.i: Comment on the angle at which the object meets equipotential surfaces around the sphere.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii:
State the fundamental SI unit for your answer to (a)(i).
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.i: Identify a property of electrons demonstrated by this experiment.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Suggest, with reference to conservation of energy, how the variable voltage source can be used to stop all emitted electrons from reaching the collecting plate.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A conducting square coil is placed in a region where there is a uniform magnetic field. The...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The secondary coil of an alternating current (ac) transformer is connected to two diodes as shown.
Which graph shows the variation with time of the potential difference VXY between X and Y?
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Monochromatic electromagnetic radiation is incident on a metal surface. The kinetic energy of...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Which of the following, observed during a radioactive-decay experiment, provide evidence for the...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.iii: Calculate the work function of barium in eV.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.37: Three correct statements about the behaviour of electrons are: I. An electron beam is used to...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.iii:
Determine whether the object will reach the surface of the sphere.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.7a: Outline what is meant by electric potential at a point.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.7b:
The electric potential at a point a distance 2.8 m from the centre of the sphere is 7.71 kV. Determine the radius of the sphere.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.iv: An asteroid strikes the Earth and causes the orbital speed of the Earth to suddenly decrease....
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Monochromatic light is incident on a double slit. Both slits have a finite width. The light then...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A diffraction grating is used to observe light of wavelength 400 nm. The light illuminates 100...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A train travelling in a straight line emits a sound of constant frequency f. An observer at...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A charged sphere in a gravitational field is initially stationary between two parallel metal plates. There is a potential difference V between the plates.
Three changes can be made:
I. Increase the separation of the metal plates
II. Increase V
III. Apply a magnetic field into the plane of the paperWhat changes made separately will cause the charged sphere to accelerate?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Light of wavelength is diffracted after passing through a very narrow single slit of width . The intensity of the central maximum of the diffracted light is . The slit width is doubled.
What is the intensity of central maximum and the angular position of the first minimum?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.40:
The decay constant, , of a radioactive sample can be defined as
A. the number of disintegrations in the radioactive sample.
B. the number of disintegrations per unit time in the radioactive sample.
C. the probability that a nucleus decays in the radioactive sample.
D. the probability that a nucleus decays per unit time in the radioactive sample.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
The graph shows the variation of magnetic flux in a coil with time .
What represents the variation with time of the induced emf across the coil?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.37: Three identical capacitors are connected together as shown. What is the order of increasing...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.39: What is evidence for wave–particle duality? A. Line spectra of elements B. ...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
The arrangement shows four diodes connected to an alternating current (ac) supply. The output is connected to an external circuit.
What is the output to the external circuit?
A. Full-wave rectified current
B. Half-wave rectified current
C. Constant non-zero current
D. Zero current
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
Light with photons of energy 8.0 × 10−20 J are incident on a metal surface in a photoelectric experiment.
The work function of the metal surface is 4.8 × 10−20 J . What minimum voltage is required for the ammeter reading to fall to zero?
A. 0.2 V
B. 0.3 V
C. 0.5 V
D. 0.8 V
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.iv: Outline why deviations from Rutherford scattering are observed when high-energy alpha particles...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.i: Calculate, in m, the length of the thread. State your answer to an appropriate number of...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iv: The speed after the collision of the bob and the object was measured using a sensor. This sensor...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2e: The magnetic field strength of the Earth is 31 μT at the orbital radius of the satellites. The...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.29: Two lines X and Y in the emission spectrum of hydrogen gas are measured by an observer stationary...
-
18M.3.HL.TZ1.11b.i:
determine the initial energy.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i:
Determine the width of one of the slits.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
The gravitational potential due to the Sun at a distance r from its centre is VS. Show that
rVS = constant.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The plane of a coil is positioned at right angles to a magnetic field of flux density B. The coil has N turns, each of area A. The coil is rotated through 180˚ in time t.
What is the magnitude of the induced emf?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A fully charged capacitor is connected to a resistor. When the switch is closed the capacitor...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.32: A satellite of mass 1500 kg is in the Earth’s gravitational field. It moves from a point where...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.36: Three capacitors are arranged as shown. What is the total capacitance of the arrangement? A....
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.37: Pair production by a photon occurs in the presence of a nucleus. For this process, which of...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.30: A satellite at the surface of the Earth has a weight W and gravitational potential energy Ep. The...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.39: A photon of energy E and wavelength λ is scattered from an electron initially at rest. What is...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
A train moving at speed u relative to the ground, sounds a whistle of constant frequency f as it moves towards a vertical cliff face.
The sound from the whistle reaches the cliff face and is reflected back to the train. The speed of sound in stationary air is c.
What whistle frequency is observed on the train after the reflection?
A.
B. (c + u)f
C. (c – u)f
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.33: What are the units of magnetic flux and magnetic field strength?
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.6a: Outline how this diagram shows that the gravitational field strength of planet X decreases with...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.32: Four uniform planets have masses and radii as shown. Which planet has the smallest escape speed?
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.ii:
Sketch a graph to show the variation with time of the generator output power. Label the time axis with a suitable scale.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.i: Suggest the advantage of using a step-up transformer in this way.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelengths of two spectral lines of the light differ by and have a mean wavelength of . The spectral lines are just resolved in the fourth order of the grating. What is the minimum number of grating lines that were illuminated?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.35: Two capacitors of different capacitance are connected in series to a source of emf of...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoes simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude 0. When the displacement of the object is , the speed of the object is . What is the speed when the displacement is 0?
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.11a:
A current is observed on the ammeter when violet light illuminates C. With V held constant the current becomes zero when the violet light is replaced by red light of the same intensity. Explain this observation.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The graph shows the variation of the peak output power P with time of an alternating current (ac) generator.
Which graph shows the variation of the peak output power with time when the frequency of rotation is decreased?
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.38: Which is the correct Feynman diagram for pair annihilation and pair production?
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.27: The graph shows the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light when monochromatic...
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.31: The gravitational potential at point P due to Earth is V. What is the definition of the...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a diffraction grating. The grating spacing is d. The angles between the different orders are shown on the diagram.
What is the expression for the wavelength of light used?
A.
B.
C. d sin α
D. d sin β
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.40: A radioactive nuclide is known to have a very long half-life. Three quantities known for a pure...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are one metre apart. The graph shows the variation of electric potential V with distance from Q1.
What is ?
A.
B.
C. 4
D. 16
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) has a period T and total energy E. The amplitude of oscillations is halved. What are the new period and total energy of the system?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.33:
A ring of area S is in a uniform magnetic field X. Initially the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The ring is rotated by 180° about the axis in time T.
What is the average induced emf in the ring?
A. 0
B.
C.
D. - 18N.1.HL.TZ0.37: When green light is incident on a clean zinc plate no photoelectrons are emitted. What change may...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.i: Outline how eddy currents reduce transformer efficiency.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.iii: The light source is changed so that white light is incident on the diffraction grating. Outline...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii: Calculate the angle between the first-order line of the red light in the hydrogen spectrum and...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7c: An additional identical capacitor is connected in series with the first capacitor and...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7a: The battery has an emf of 7.5 V. Determine the charge that flows through the motor when the mass...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.6d.i: State what is meant by decay constant.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i: State how the density of a nucleus varies with the number of nucleons in the nucleus.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6c:
undergoes beta-minus (β–) decay. Explain why the energy gained by the emitted beta particles in this decay is not the same for every beta particle.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Outline why the particles must be accelerated to high energies in scattering experiments.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A current of 1.0 × 10–3 A flows in the primary coil of a step-up transformer. The number of turns in the primary coil is Np and the number of turns in the secondary coil is Ns. One coil has 1000 times more turns than the other coil.
What is and what is the current in the secondary coil for this transformer?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
The graph shows the variation of the natural log of activity, ln (activity), against time for a radioactive nuclide.
What is the decay constant, in days–1, of the radioactive nuclide?
A.
B.
C. 3
D. 6
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
Calculate the final total energy, in J, stored in X and Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(i):
Show that the speed of the electron with mass , is given by .
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.29: Sea waves move towards a beach at a constant speed of 2.0 m s–1. They arrive at the beach with a...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.33: X and Y are two plane coils parallel to each other that have a common axis. There is a constant...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Light of frequency 500 THz is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern. The...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.32: An electron enters a uniform electric field of strength E with a velocity v. The direction of v...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.34: A coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field. An alternating emf is induced in the coil. What is...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.36: A diode bridge rectification circuit is constructed as shown. An alternating potential difference...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.37: An electron of low energy is enclosed within a high potential barrier. What is the process by...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
A beam of electrons moving in the direction shown is incident on a rectangular slit of width .
The component of momentum of the electrons in direction after passing through the slit is . The uncertainty in is
A. proportional toB. proportional to
C. proportional to
D. zero
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.30: The diagram shows equipotential lines for an electric field. Which arrow represents...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.31: Two charged parallel plates have electric potentials of 10 V and 20 V. A particle with charge...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.27: When monochromatic light is incident on a single slit a diffraction pattern forms on a...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident normally on a thin liquid film of refractive index that is suspended in air. The rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity.
What is the minimum thickness of the film so that the reflected light undergoes constructive interference?
A.B.
C.
D.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.7b.ii:
Predict the charge on each sphere.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.34: An alternating supply is connected to a diode bridge rectification circuit. The conventional...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The root mean square (rms) current in the primary coil of an ideal transformer is 2.0 A. The rms voltage in the secondary coil is 50 V. The average power transferred from the secondary coil is 20 W.
What is and what is the average power transferred from the primary coil?
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
The resistor R in the circuit has a resistance of 1.2 kΩ. Calculate the time taken for the charge on the capacitor to fall to 50 % of its fully charged value.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State the maximum distance between the centres of the nuclei for which the production of is likely to occur.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
The following data for the Mars–Phobos system and the Earth–Moon system are available:
Mass of Earth = 5.97 × 1024 kg
The Earth–Moon distance is 41 times the Mars–Phobos distance.
The orbital period of the Moon is 86 times the orbital period of Phobos.
Calculate, in kg, the mass of Mars.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
The escape speed for the Earth is esc. Planet X has half the density of the Earth and twice the radius. What is the escape speed for planet X?
A.
B.
C. esc
D. esc
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.4dii: Suggest, in terms of conservation of energy, the cause for the above change.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.2: A proton has momentum 10-20 N s and the uncertainty in the position of the proton is 10-10 m....
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.17: A mass on a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position. Which graph represents the...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Suggest one change to the discharge circuit, apart from changes to the coil, that will increase the maximum induced emf in the coil.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.30: An electron is fixed in position in a uniform electric field. What is the position for which the...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.40: Photons of discrete energy are emitted during gamma decay. This is evidence for A. atomic energy...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A circular coil of wire moves through a region of uniform magnetic field directed out of the...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.26: The input to a diode bridge rectification circuit is sinusoidal with a time period of 20...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A transformer with 600 turns in the primary coil is used to change an alternating root mean square (rms) potential difference of 240 Vrms to 12 Vrms.
When connected to the secondary coil, a lamp labelled “120 W, 12 V” lights normally. The current in the primary coil is 0.60 A when the lamp is lit.
What are the number of secondary turns and the efficiency of the transformer?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.39: Three possible features of an atomic model are I. orbital radius II. quantized energy III....
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.22: Two stars are viewed with a telescope using a green filter. The images of the stars are just...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Photons of a certain frequency incident on a metal surface cause the emission of electrons from the surface. The intensity of the light is constant and the frequency of photons is increased. What is the effect, if any, on the number of emitted electrons and the energy of emitted electrons?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of the object.
What is the velocity of the object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i:
Show that about –11 C of charge is delivered to the Earth’s surface.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A direct current (dc) of 5A dissipates a power P in a resistor. Which peak value of the alternating current (ac) will dissipate an average power P in the same resistor?
A. 5A
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
What can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a particular region of space?
A.
B.
C. The magnitude of the wave function
D. The magnitude of the (wave function)2
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.i:
Use the graph to show that the nuclear radius of silicon-30 is about 4 fm.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The ratio for a transformer is 2.5.
The primary coil of the transformer draws a current of 0.25 A from a 200 V alternating current (ac) supply. The current in the secondary coil is 0.5 A. What is the efficiency of the transformer?
A. 20 %
B. 50 %
C. 80 %
D. 100 %
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
Three identical capacitors are connected in series. The total capacitance of the arrangement is mF. The three capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the capacitance of the parallel arrangement?
A. mF
B. 1 mF
C. 3 mF
D. 81 mF
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.38: A capacitor of capacitance C discharges through a resistor of resistance R. The graph shows...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2b.i: the orbital times for X and Y are different.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.33:
The escape velocity for an object at the surface of the Earth is vesc. The diameter of the Moon is 4 times smaller than that of the Earth and the mass of the Moon is 81 times smaller than that of the Earth. What is the escape velocity of the object on the Moon?
A. vesc
B. vesc
C. vesc
D. vesc
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.39:
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 8.0 s. The initial activity of a pure sample of the nuclide is 10 000 Bq. What is the approximate activity of the sample after 4.0 s?
A. 2500 Bq
B. 5000 Bq
C. 7100 Bq
D. 7500 Bq
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Four identical, positive, point charges of magnitude Q are placed at the vertices of a square of side 2d. What is the electric potential produced at the centre of the square by the four charges?
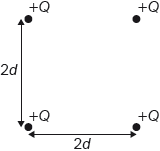
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
The diagram shows the path of an asteroid as it moves past the planet.
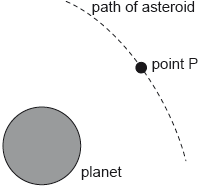
When the asteroid was far away from the planet it had negligible speed. Estimate the speed of the asteroid at point P as defined in (b).
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4di:
Calculate the change in the energy stored in the capacitor.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9aii:
Suppose the star could contract to half its original radius without any loss of mass. Discuss the effect, if any, this has on the total energy of the planet.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.11b:
The graph shows the variation of photoelectric current I with potential difference V between C and A when violet light of a particular intensity is used.
The intensity of the light source is increased without changing its wavelength.
(i) Draw, on the axes, a graph to show the variation of I with V for the increased intensity.
(ii) The wavelength of the violet light is 400 nm. Determine, in eV, the work function of caesium.
(iii) V is adjusted to +2.50V. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons just before they reach A.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: State what is meant by the Doppler effect.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.iii: State what will happen to the intensity of the secondary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.ii: State what will happen to the width of the primary maxima.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Which of the following reduces the energy losses in a transformer? A. Using thinner wires for...
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): state, in terms of d, the path difference between the reflected rays X and Y.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(i): Draw, on the axes, the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light incident on the...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9c:
Suggest why the answers to (a) and (b)(ii) are different.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.11a(i): does not support the wave nature of light.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.11a(ii): does support the photon nature of light.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.23:
Samples of different radioactive nuclides have equal numbers of nuclei. Which graph shows the relationship between the half-life and the activity A for the samples?
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
A stationary sound source emits waves of wavelength and speed v. The source now moves away from a stationary observer. What are the wavelength and speed of the sound as measured by the observer?
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.31: A charge of −3 C is moved from A to B and then back to A. The electric potential at A is +10 V...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8a: State Faraday’s law of induction.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Explain, using Faraday’s law of induction, how the transformer steps down the voltage.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
An alternating current (ac) generator produces a peak emf E0 and periodic time T. What are the peak emf and periodic time when the frequency of rotation is doubled?
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.31:
The graph shows the variation of the gravitational potential V with distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical planet. The radius of the planet is R. The shaded area is S.
What is the work done by the gravitational force as a point mass m is moved from the surface of the planet to a distance 6R from the centre?
A. m (V2 – V1 )
B. m (V1 – V2 )
C. mS
D. S
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
Three conducting loops, X, Y and Z, are moving with the same speed from a region of zero magnetic field to a region of uniform non-zero magnetic field.
Which loop(s) has/have the largest induced electromotive force (emf) at the instant when the loops enter the magnetic field?
A. Z only
B. Y only
C. Y and Z only
D. X and Y only
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.40: Alpha particles with energy E are directed at nuclei with atomic number Z. Small deviations from...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.iii:
Calculate the electron’s orbital radius in (c)(ii).
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.31: Two parallel metal plates are connected to a dc power supply. An electric field forms in the...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.30: What is the unit of Gε0, where G is the gravitational constant and ε0 is the permittivity of free...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.31: Two point charges are at rest as shown. At which position is the electric field strength...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.40: Electron capture can be represented by the equation p + e– → X + Y. What are X and Y?
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.29: An electric field acts in the space between two charged parallel plates. One plate is at zero...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.ii: State what is meant by the work function of a metal.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9c: The experiment is repeated with a metal surface of cadmium, which has a greater work function....
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8d: Step-up transformers are used in power stations to increase the voltage at which the electricity...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.30: A positive charge Q is deposited on the surface of a small sphere. The dotted lines...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The diagram shows a bar magnet near an aluminium ring. The ring is supported so that it is...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.28: Two points illuminated by monochromatic light are separated by a small distance. The light...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.ii: Electrons emitted from the surface of the photocell have almost no kinetic energy. Explain why...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Outline why the gravitational potential is negative.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.7a:
Explain what is meant by the gravitational potential at the surface of a planet.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.27: For fringes to be observed in a double-slit interference experiment, the slits must emit waves...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.ii:
The use of alternating current (ac) in a transformer gives rise to energy losses. State how eddy current loss is minimized in the transformer.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a battery. What happens when a sheet of dielectric...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8ci: Suggest why, after this change, the intensity at P will be less than that at M.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.2c.i:
Show that the gravitational potential due to the planet and the star at the surface of the planet is about −5 × 109 J kg−1.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
In an alternating current (ac) generator, a square coil ABCD rotates in a magnetic field.
The ends of the coil are connected to slip rings and brushes. The plane of the coil is shown at the instant when it is parallel to the magnetic field. Only one coil is shown for clarity.
The following data are available.
Dimensions of the coil = 8.5 cm×8.5 cm Number of turns on the coil = 80 Speed of edge AB = 2.0 ms–1 Uniform magnetic field strength = 0.34 T(i) Explain, with reference to the diagram, how the rotation of the generator produces an electromotive force (emf ) between the brushes.
(ii) Calculate, for the position in the diagram, the magnitude of the instantaneous emf generated by a single wire between A and B of the coil.
(iii) Hence, calculate the total instantaneous peak emf between the brushes.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii: The ammeter is replaced by a coil. Explain why there will be an induced emf in the coil while the...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.21: A train approaches a station and sounds a horn of constant frequency and constant intensity. An...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.26: A simple pendulum undergoes simple harmonic motion. The gravitational potential energy of the...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10b.i:
Show that the is about 80.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.ii: Describe the energy changes in the satellite Y-cable system during one cycle of the oscillation.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.3d.ii:
Plot the position of magnesium-24 on the graph.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
A transparent liquid film of refractive index 1.5 coats the outside of a glass lens of higher refractive index. The liquid film is used to eliminate reflection from the lens at wavelength λ in air.
What is the minimum thickness of the liquid film coating and the phase change at the liquid–glass interface?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The circuit diagram shows a capacitor that is charged by the battery after the switch is connected to terminal X. The cell has emf V and internal resistance r. After the switch is connected to terminal Y the capacitor discharges through the resistor of resistance R.
What is the nature of the current and magnitude of the initial current in the resistor after the switch is connected to terminal Y?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.40: A particle is confined within a nucleus. What is the order of magnitude of the uncertainty in the...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Explain why q will perform simple harmonic oscillations when it is released.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.i: At t = 0, the switch is connected to X. On the axes, draw a sketch graph to show the variation...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.4d.ii: State and explain what happens to the rate at which charge leaves the metallic surface.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
A transparent liquid forms a parallel-sided thin film in air. The diagram shows a ray I incident on the upper air–film boundary at normal incidence (the rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity).
Reflections from the top and bottom surfaces of the film result in three rays J, K and L. Which of the rays has undergone a phase change of rad?
A. J only
B. J and L only
C. J and K only
D. J, K and L
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.40: A photon interacts with a nearby nucleus to produce an electron. What is the name of this...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Outline how these experiments are carried out.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.3d.iii: Draw a line on the graph, to show the variation of nuclear radius with nucleon number.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i:
Explain why zero intensity is observed at position A.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.38: A metallic surface is first irradiated with infrared radiation and photoelectrons are emitted...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.5c: The graph shows the variation of the gravitational potential between the Earth and Moon with...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
Two radioactive nuclides, X and Y, have half-lives of 50 s and 100 s respectively. At time t = 0 samples of X and Y contain the same number of nuclei.
What is when t = 200 s?
A. 4
B. 2
C.
D.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Three observations of the behaviour of electrons are I. electron emission as a result of the...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Predict whether reflected ray X undergoes a phase change.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.11b(ii):
The intensity of the light incident on the surface is reduced by half without changing the wavelength. Draw, on the graph, the variation of the current with potential after this change.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.iii:
Suggest one reason why a beam of electrons is better for investigating the size of a nucleus than a beam of alpha particles of the same energy.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
The graph below shows the variation with time of the magnetic flux through a coil.
Which of the following gives three times for which the magnitude of the induced emf is a maximum?
A. 0, ,
B. 0, , T
C. 0, , T
D. , ,
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Monochromatic light is incident on 4 rectangular, parallel slits. The first principal maximum is...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.30: A positive point charge is placed above a metal plate at zero electric potential. Which...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.38: Which of the following is evidence for the wave nature of the electron? A. Continuous energy...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
A beam of monochromatic radiation is made up of photons each of momentum . The intensity of the beam is doubled without changing frequency. What is the momentum of each photon after the change?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
In a different circuit, a transformer is connected to an alternating current (ac) supply.
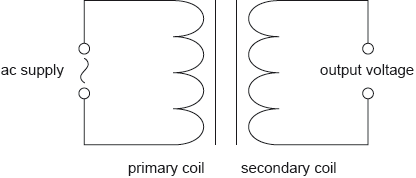
The transformer has 100 turns in the primary coil and 1200 turns in the secondary coil. The peak value of the voltage of the ac supply is 220 V. Determine the root mean square (rms) value of the output voltage.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.i:
Calculate the angular separation between the central peak and the missing peak in the double-slit interference intensity pattern. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.10:
Satellite X is in orbit around the Earth. An identical satellite Y is in a higher orbit. What is correct for the total energy and the kinetic energy of the satellite Y compared with satellite X?
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.ii: The plastic film begins to conduct when the electric field strength in it exceeds 1.5 MN C–1....
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(i):
Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the cylinder.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
The input voltage is 240 V. Calculate the output voltage.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.ii:
State and explain the effect on the maximum photoelectric current as a result of increasing the photon energy in this way.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7e:
Describe the use of transformers in electrical power distribution.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.iii:
The amplitude of oscillation is 0.12 m. On the axes, draw a graph to show the variation with time t of the velocity v of the ball during one period.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The mass of the cylinder is and the cross-sectional area of the cylinder is . The density of water is . Show that the angular frequency of oscillation of the cylinder is about .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Show that the wavelength of an electron in the beam is about .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
The accepted value of the diameter of the carbon-12 nucleus is . Estimate the angle at which the minimum of the intensity is formed.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Draw a graph, on the axes, to show the variation of the gravitational potential V of the planet with height h above the surface of the planet.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of amplitude xo. Its total energy is 16 J.
What is the kinetic energy of the mass when its displacement is ?
A. 4 J
B. 8 J
C. 12 J
D. 16 J
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
Show that the nuclear radius of phosphorus-31 () is about 4 fm.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.ii:
Label on the graph with the letter X a point where the speed of the pendulum is half that of its initial speed.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Four identical capacitors of capacitance X are connected as shown in the diagram.
What is the effective capacitance between P and Q?
A.
B. X
C.
D. 4X
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
An electron of mass me orbits an alpha particle of mass mα in a circular orbit of radius r. Which expression gives the speed of the electron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.40:
A pure sample of a radioactive nuclide contains N0 atoms at time t = 0. At time t, there are N atoms of the nuclide remaining in the sample. The half-life of the nuclide is .
What is the decay rate of this sample proportional to?
A. N
B. N0 – N
C. t
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A pendulum oscillating near the surface of the Earth swings with a time period T. What is the...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.34: A battery is used to charge a capacitor fully through a resistor of resistance R. The energy...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.35: A capacitor is charged by a constant current of 2.5 μA for 100 s. As a result the potential...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.6b: The diagram shows part of the surface of planet X. The gravitational potential at the surface of...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
An electron of mass m has an uncertainty in its position r. What is the uncertainty in the speed of this electron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.33: Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The graph shows the variation with time t of the current I in the primary coil of an ideal...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.38: According to the Bohr model for hydrogen, visible light is emitted when electrons make...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.i:
Calculate the time taken for the block to return to the equilibrium position for the first time.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the energy of photons from the UV lamp is about 10 eV.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i:
On the diagram, draw and label the equipotential lines at –0.4 V and –0.8 V.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
The gravitational potential is at a distance above the surface of a spherical planet of radius and uniform density. What is the gravitational potential a distance above the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3c:
The wavelength of the light in the beam when emitted by the galaxy was 621.4 nm.
Explain, without further calculation, what can be deduced about the relative motion of the galaxy and the Earth.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is normally incident on a diffraction grating of spacing 3λ. What is the angle between the two second-order maxima?
A.
B.
C.
D. >90° so no second orders appear
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State and explain the differences between the pattern on the screen due to the grating and the pattern due to the double slit.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(ii):
Hence, deduce that the total energy of the electron is given by .
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(ii):
Estimate, in rad, the smallest angular separation of two distinct point sources of light of wavelength 656 nm that can be resolved by the eye of this observer.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A capacitor of capacitance 1.0 μF stores a charge of 15 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
Calculate in V, the potential difference between the thundercloud and the Earth’s surface.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii): discuss a practical advantage of this arrangement.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ in air is incident normally on a thin film of refractive index n. The film is surrounded by air. The intensity of the reflected light is a minimum. What is a possible thickness of the film?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Samples of two radioactive nuclides X and Y are held in a container. The number of particles of X is half the number of particles of Y. The half-life of X is twice the half-life of Y.
What is the initial value of ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.31: The diagram shows 5 gravitational equipotential lines. The gravitational potential on each line...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.35: The diagram shows a diode bridge rectification circuit and a load resistor. ...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Deduce .
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Determine the amplitude of oscillation for test 1.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
The motion sensor operates by detecting the sound waves reflected from the base of the mass. The sensor compares the frequency detected with the frequency emitted when the signal returns.
The sound frequency emitted by the sensor is 35 kHz. The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency change detected by the sensor for test 2.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i: Explain why the graph becomes negative.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii: Part of the graph is above the t-axis and part is below. Outline why the areas between the t-axis...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8c: Predict the changes to the graph when the magnet is dropped from a lower height above the coil.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.iii:
The de Broglie wavelength for an electron is given by . Show that the diameter of an oxygen-16 nucleus is about 4 fm.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
Estimate, using the result in (a)(iii), the volume of a tin-118 nucleus. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8a:
Show that the capacitance of this arrangement is C = 6.6 × 10–7 F.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Calculate, in J, the energy stored in X with the switch S open.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
The light illuminates a width of 3.5 mm of the grating. The deuterium and hydrogen red lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of the diffraction grating. Show that the grating spacing of the diffraction grating is about 2 × 10–6 m.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8b(i):
Show that the de Broglie wavelength of the electron in the state is m.
The formula for the de Broglie wavelength of a particle is .
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.5b.i:
Deduce that the activity of the radium-226 is almost constant during the experiment.
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating that has a slit separation of . What is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed using this arrangement?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 7
D. 9 -
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.i:
Estimate the value of k in the following expression.
T =
Give an appropriate unit for your answer. Ignore the mass of the cable and any oscillation of satellite X.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
Outline, without calculation, the change to the time period of the system for the model represented by graph B when is large.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii):
Outline why electrons with energy of approximately would be unsuitable for the investigation of nuclear radii.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
The orbital period T of a moon orbiting a planet of mass M is given by
where R is the average distance between the centre of the planet and the centre of the moon.
Show that
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10b:
Electrical power output is produced by several alternating current (ac) generators which use transformers to deliver energy to the national electricity grid.
The following data are available. Root mean square (rms) values are given.
ac generator output voltage to a transformer = 25 kV ac generator output current to a transformer = 3.9 kA Transformer output voltage to the grid = 330 kV Transformer efficiency = 96%(i) Calculate the current output by the transformer to the grid. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
(ii) Electrical energy is often delivered across large distances at 330 kV. Identify the main advantage of using this very high potential difference.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.ii:
Determine the peak current in the primary coil when operating with the maximum number of lamps.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.iii:
Calculate the separation of the two slits.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.31:
The force acting between two point charges is when the separation of the charges is . What is the force between the charges when the separation is increased to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.32:
A satellite orbits planet with a speed at a distance from the centre of planet . Another satellite orbits planet at a speed of at a distance from the centre of planet . The mass of planet is and the mass of planet is . What is the ratio of ?
A. 0.25B. 0.5
C. 2.0
D. 4.0
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Why are high voltages and low currents used when electricity is transmitted over long...
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.31: P and S are two points on a gravitational equipotential surface around a planet. Q and R are two...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
The diameter of a nucleus of a particular nuclide X is . What is the nucleon number of X?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.29: White light is incident normally on separate diffraction gratings X and Y. Y has a greater number...
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.37: Monochromatic light is incident on a metal surface and electrons are released. The intensity of...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
The graph shows the variation of electric field strength with distance from a point charge.
The shaded area X is the area under the graph between two separations and from the charge.
What is X?
A. The electric field average between and
B. The electric potential difference between and
C. The work done in moving a charge from to
D. The work done in moving a charge from to
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.40: The Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden experiment shows that A. alpha particles do not obey Coulomb’s...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
A photon has a wavelength . What are the energy and momentum of the photon?
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
Power is dissipated in a resistor of resistance when there is a direct current in the resistor.
What is the average power dissipation in a resistance when the alternating root-mean-square (rms) current in the resistor is ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A rectangular coil rotates at a constant angular velocity. At the instant shown, the plane of the coil is at right angles to the line . A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction .
What rotation of the coil about a specified axis will produce the graph of electromotive force (emf) against time ?
A. Through about
B. Through about
C. Through about
D. Through about
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.5b.ii:
Show that about 3 x 1015 alpha particles are emitted by the radium-226 in 6 days.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iv:
Flux leakage is one reason why a transformer may not be ideal. Explain the effect of flux leakage on the transformer.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6a:
Police use radar to detect speeding cars. A police officer stands at the side of the road and points a radar device at an approaching car. The device emits microwaves which reflect off the car and return to the device. A change in frequency between the emitted and received microwaves is measured at the radar device.
The frequency change Δf is given by
where f is the transmitter frequency, v is the speed of the car and c is the wave speed.
The following data are available.
Transmitter frequency f = 40 GHz Δf = 9.5 kHz Maximum speed allowed = 28 m s–1(i) Explain the reason for the frequency change.
(ii) Suggest why there is a factor of 2 in the frequency-change equation.
(iii) Determine whether the speed of the car is below the maximum speed allowed.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
The yellow light is made from two very similar wavelengths that produce two lines in the spectrum of sodium. The wavelengths are 588.995 nm and 589.592 nm. These two lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of this diffraction grating. Determine the beam width of the light incident on the diffraction grating.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.ii:
Show that the period of oscillation of the ball is about 6 s.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8c(ii):
Determine the charge of the sphere.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
Experiments with many nuclides suggest that the radius of a nucleus is proportional to , where is the number of nucleons in the nucleus. Show that the density of a nucleus remains approximately the same for all nuclei.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.39:
A neutron of mass m is confined within a nucleus of diameter d. Ignoring numerical constants, what is an approximate expression for the kinetic energy of the neutron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
The average power output of the generator is . Calculate the root mean square (rms) value of the generator output current.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.2c.ii:
Estimate the escape speed of the spacecraft from the planet–star system.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.iii: Identify, using the label + on the diagram, the polarity of the capacitor.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5a: Explain the role of the diode in the circuit when the switch is at position A.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
Calculate the maximum charge Q0 stored in the capacitor.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
State the phase change when a ray is reflected at B.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.i: Describe what happens to the energy stored in the capacitor when the switch is moved to position B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.ii:
Show that the charge remaining in the capacitor after a time equal to one time constant of the circuit will be 0.37 Q0.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.i: State the Rayleigh criterion for resolution.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.iii:
The graph shows the variation with time of the charge in the capacitor as it is being discharged through the heart.
Determine the electrical resistance of the closed circuit with the switch in position B.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5d: In practice, two electrodes connect the heart to the circuit. These electrodes introduce an...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8b(ii):
Estimate for , the ratio .
State your answer to one significant figure.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.27:
A simple pendulum and a mass–spring system oscillate with the same time period. The mass of the pendulum bob and the mass on the spring are initially identical. The masses are halved.
What is when the masses have been changed?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.7c: The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 × 109 years. The half-life of thallium-206 is about 4.2...
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.10a: Describe the photoelectric effect.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.v:
Estimate the displacement needed to double the energy of the string.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
Show that the maximum energy stored by the capacitor is about 160 J.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
An ambulance siren emits a sound of frequency 1200 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s–1. The ambulance moves towards a stationary observer at a constant speed of 40 m s–1. What is the frequency heard by the observer?
A. Hz
B. Hz
C. Hz
D. Hz
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Explain the condition for w that eliminates reflection for a particular light wavelength in air .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.ii:
The painting contains a pattern of red dots with a spacing of 3 mm. Assume the wavelength of red light is 700 nm. The average diameter of the pupil of a human eye is 4 mm. Calculate the maximum possible distance at which these red dots are distinguished.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
A capacitor of capacitance X is connected to a power supply of voltage V. At time t = 0, the capacitor is disconnected from the supply and discharged through a resistor of resistance R. What is the variation with time of the charge on the capacitor?
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(i): Explain why the frequency recorded by the microphone is lower than the frequency emitted by the...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Explain, by reference to Faraday’s law of induction, how an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the coil.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
Calculate the final charge on X and the final charge on Y.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
Determine, in J, the minimum initial kinetic energy that the deuterium nucleus must have in order to produce . Assume that the phosphorus nucleus is stationary throughout the interaction and that only electrostatic forces act.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The motor can transfer one-third of the electrical energy stored in the capacitor into gravitational potential energy of the mass. Determine the maximum height through which a mass of 45 g can be raised.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3d.ii:
Outline, without calculation, whether or not the electric potential at P is zero.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential with distance from the centre of the sphere.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(ii):
Draw, on the axes, the graph to show how the kinetic energy of the cylinder varies with time during one period of oscillation .
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.8d: The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
In the Bohr model for hydrogen an electron in the ground state has orbit radius r and speed v. In the first excited state the electron has orbit radius 4r. What is the speed of the electron in the first excited state?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(iii):
The frequency of the generator is doubled with no other changes being made. Draw, on the axes, the variation with time of the voltage output of the generator.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii: State, in terms of λ, the path length between points X and Z.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
The primary coil has 3300 turns. Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil.
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): Discuss how the results of the experiment provide evidence for matter waves.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i: using a light source with a smaller wavelength.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.i: Outline the cause of the electron emission for radiation A.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iii:
Calculate the current in the primary of the transformer assuming that it is ideal.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.iii:
The separation of adjacent slits is d. Show that for the second-order diffraction maximum .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
The voltage output from the generator is stepped up before transmission to the consumer. Estimate the factor by which voltage has to be stepped up in order to reduce power loss in the transmission line by a factor of .
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: State the phase difference between the waves at V and Y.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii: increasing the distance between the diffraction grating and the screen.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.ii: Outline why electrons are never emitted for radiation C.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.iii: Outline why radiation B gives different results.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9b: Explain why there is no effect on the table of results when the intensity of source B is doubled.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10b.ii:
Outline, using (b)(i), why it is not correct to use the equation to calculate the speed required for the spacecraft to reach infinity from the surface of .
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6d.ii:
In a fresh pure sample of the activity of the sample is 24 Bq. After one week the activity has become 17 Bq. Calculate, in s–1, the decay constant of .
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.4d:
C-14 decay is used to estimate the age of an old dead tree. The activity of C-14 in the dead tree is determined to have fallen to 21% of its original value. C-14 has a half-life of 5700 years.
(i) Explain why the activity of C-14 in the dead tree decreases with time.
(ii) Calculate, in years, the age of the dead tree. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Show that V = –g(R + h).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.i:
A wave of amplitude 4.3 m and wavelength 35 m, moves with a speed of 3.4 m s–1. Calculate the maximum vertical speed of the buoy.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8a:
Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
The diagram shows the diffraction pattern for light passing through a single slit.
What is
A. 0.01
B. 0.02
C. 1
D. 2
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The conservation of which quantity explains Lenz’s law? A. Charge B. Energy C. Magnetic...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelength lines 600.0 nm and 601.5 nm are...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.30: A particle with charge −2.5 × 10−6 C moves from point X to point Y due to a uniform electrostatic...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.26: Which is correct for the tangential acceleration of a simple pendulum at small amplitudes? A. It...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.29: On approaching a stationary observer, a train sounds its horn and decelerates at a constant rate....
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.31: Which is a correct unit for gravitational potential? A. m2 s−2 B. J kg C. m s−2 D. N m−1 kg−1
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
In a photoelectric effect experiment, a beam of light is incident on a metallic surface W in a vacuum.
The graph shows how the current varies with the potential difference V when three different beams X, Y, and Z are incident on W at different times.
I. X and Y have the same frequency.
II. Y and Z have different intensity.
III. Y and Z have the same frequency.Which statements are correct?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A resistor designed for use in a direct current (dc) circuit is labelled “50 W, 2 Ω”. The resistor is connected in series with an alternating current (ac) power supply of peak potential difference 10 V. What is the average power dissipated by the resistor in the ac circuit?
A. 25 W
B. 35 W
C. 50 W
D. 100 W
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.37: What is a consequence of the uncertainty principle? A. The absorption spectrum of hydrogen atoms...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.39:
The graphs show the variation with time of the activity and the number of remaining nuclei for a sample of a radioactive nuclide.
What is the decay constant of the nuclide?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
calculate the smallest value of d that will result in destructive interference between ray X and ray Y.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The diameter of a silver-108 () nucleus is approximately three times that of the diameter of a nucleus of
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
A train is approaching an observer with constant speed
where c is the speed of sound in still air. The train emits sound of wavelength λ. What is the observed speed of the sound and observed wavelength as the train approaches?
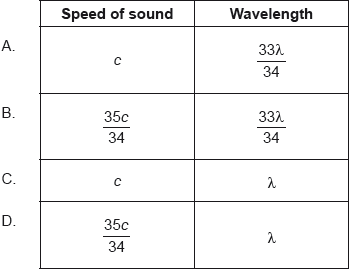
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
Monochromatic light of wavelength passes through a single-slit of width and produces a diffraction pattern on a screen. Which combination of changes to and will cause the greatest decrease in the width of the central maximum?
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.37:
A particle of energy is incident upon a barrier and has a certain probability of quantum tunnelling through the barrier. Assuming remains constant, which combination of changes in particle mass and barrier length will increase the probability of the particle tunnelling through the barrier?
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
The distance from the centre of the pattern to A is 4.1 x 10–2 m. The distance from the screen to the slits is 7.0 m.
Calculate the width of each slit.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A train is moving in a straight line away from a stationary observer when the train horn emits a sound of frequency . The speed of the train is where is the speed of sound. What is the frequency of the horn as heard by the observer?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Light passes through a diffraction grating. Which quantity must be decreased to improve...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
The graph shows the variation of an alternating current with time in a resistor.
What is the average power dissipated in the resistor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.36:
A capacitor is charged with a constant current . The graph shows the variation of potential difference across the capacitor with time . The gradient of the graph is . What is the capacitance of the capacitor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.33: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a cell of constant emf. The capacitor plates are then...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.39: What is true for the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom? A. Angular momentum of electrons is...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass–spring system oscillates vertically with a period of at the surface of the Earth. The gravitational field strength at the surface of Mars is . What is the period of the same mass–spring system on the surface of Mars?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.31:
The points X and Y are in a uniform electric field of strength . The distance OX is and the distance OY is .
What is the magnitude of the change in electric potential between X and Y?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
An object of mass released from rest near the surface of a planet has an initial acceleration . What is the gravitational field strength near the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
A magnet connected to a spring oscillates above a solenoid with a 240 turn coil as shown.
The graph below shows the variation with time of the emf across the solenoid with the period, , of the system shown.
The spring is replaced with one that allows the magnet to oscillate with a higher frequency. Which graph shows the new variation with time of the current in the resistor for this new set-up?
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Element X has a nucleon number and a nuclear density . Element Y has a nucleon number of . What is an estimate of the nuclear density of element Y?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
An unpowered projectile is fired vertically upwards into deep space from the surface of planet Venus. Assume that the gravitational effects of the Sun and the other planets are negligible.
The following data are available.
Mass of Venus = 4.87×1024 kg Radius of Venus = 6.05×106 m Mass of projectile = 3.50×103 kg Initial speed of projectile = 1.10×escape speed(i) Determine the initial kinetic energy of the projectile.
(ii) Describe the subsequent motion of the projectile until it is effectively beyond the gravitational field of Venus.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(ii):
Calculate .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Calculate, in m s−1, the maximum velocity of vibration of point P when it is vibrating with a frequency of 195 Hz.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iv:
Calculate, in terms of g, the maximum acceleration of P.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.40: What was a reason to postulate the existence of neutrinos? A. Nuclear energy levels had a...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.11b(i):
Calculate, in eV, the work function of the metal surface.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
Airports use radar to track the position of aircraft. The waves are reflected from the aircraft and detected by a large circular receiver. The receiver must be able to resolve the radar images of two aircraft flying close to each other.
The following data are available.
Diameter of circular radar receiver = 9.3 m Wavelength of radar = 2.5 cm Distance of two aircraft from the airport = 31 kmCalculate the minimum distance between the two aircraft when their images can just be resolved.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2a:
Satellite X orbits 6600 km from the centre of the Earth.
Mass of the Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
Show that the orbital speed of satellite X is about 8 km s–1.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
A capacitor of capacitance has initial charge . The capacitor is discharged through a resistor of resistance . The potential difference across the capacitor varies with time.
What is true for this capacitor?
A. After time the potential difference across the capacitor is halved.
B. The capacitor discharges more quickly when the resistance is changed to .
C. The rate of change of charge on the capacitor is proportional to .
D. The time for the capacitor to lose half its charge is .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.10b:
Show that the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons is .
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
The variable voltage can be adjusted so that no electrons reach the collecting plate. Write down the minimum value of the voltage for which no electrons reach the collecting plate.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
The diagram shows some of the electric field lines for two fixed, charged particles X and Y.
The magnitude of the charge on X is and that on Y is . The distance between X and Y is 0.600 m. The distance between P and Y is 0.820 m.
At P the electric field is zero. Determine, to one significant figure, the ratio .
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iii:
Beryllium-10 is used to investigate ice samples from Antarctica. A sample of ice initially contains 7.6 × 1011 atoms of beryllium-10. The present activity of the sample is 8.0 × 10−3 Bq.
Determine, in years, the age of the sample.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
An electron of non-relativistic speed interacts with an atom. All the energy of the electron is transferred to an emitted photon of frequency . An electron of speed now interacts with the same atom and all its energy is transmitted to a second photon. What is the frequency of the second photon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.7b: A pendulum with a metal bob comes to rest after 200 swings. The same pendulum, released from the...
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
A spacecraft moves towards the Earth under the influence of the gravitational field of the Earth.
The three quantities that depend on the distance r of the spacecraft from the centre of the Earth are the
I. gravitational potential energy of the spacecraft
II gravitational field strength acting on the spacecraft
III. gravitational force acting on the spacecraft.Which of the quantities are proportional to ?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(iii):
In this model the electron loses energy by emitting electromagnetic waves. Describe the predicted effect of this emission on the orbital radius of the electron.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.39: An electron of initial energy E tunnels through a potential barrier. What is the energy of...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.28: A moon of mass M orbits a planet of mass 100M. The radius of the planet is R and the...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.29: The diagram shows the electric field and the electric equipotential surfaces between two...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A satellite orbiting a planet moves from orbit X to orbit Y. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The current I flowing in loop A in a clockwise direction is increasing so as to induce a...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.34: A rectangular flat coil moves at constant speed through a uniform magnetic field. The direction...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.36: Three capacitors, each one with a capacitance C, are connected such that their...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.37: A photoelectric cell is connected in series with a battery of emf 2 V. Photons of energy 6 eV are...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
Calculate the root mean square (rms) current in each cable.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.32: A planet has radius R. The escape speed from the surface of the planet is v. At what...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.33: A conducting ring encloses an area of 2.0 cm2 and is perpendicular to a magnetic field...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.4a.ii:
The unstable lead nuclide has a half-life of 15 × 106 years. A sample initially contains 2.0 μmol of the lead nuclide. Calculate the number of thallium nuclei being formed each second 30 × 106 years later.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10a: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, state why the magnetic flux in the ring is increasing.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.3ei:
Calculate the frequency heard by the observer.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Deduce, in W m-2, the intensity at M.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.8cii:
Show that, due to single slit diffraction, the intensity at a point on the screen a distance of 28 mm from M is zero.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9ai:
Show that the total energy of the planet is given by the equation shown.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10b: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, sketch, using an arrow on Diagram 2, the direction...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10c: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, deduce the direction of the magnetic force on the...
- 18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Calculate, in J, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
A planet has a radius of 3.1 × 106 m. At a point P a distance 2.4 × 107 m above the surface of the planet the gravitational field strength is 2.2 N kg–1. Calculate the gravitational potential at point P, include an appropriate unit for your answer.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8c: Outline how energy losses are reduced in the core of a practical transformer.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Blue light is incident on two narrow slits. Constructive interference takes place along the lines...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.i: Describe the change in the number of photons per second incident on the surface of the photocell.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
Calculate the mass of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
In carrying out the experiment the student displaced the block horizontally by 4.8 cm from the equilibrium position. Determine the total energy in the oscillation of the wooden block.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9a: Explain how each observation provides support for the particle theory but not the wave theory of...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.37: When monochromatic light is incident on a metallic surface, electrons are emitted from the...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
A radioactive element has decay constant (expressed in s–1). The number of nuclei of this element at t = 0 is N. What is the expected number of nuclei that will have decayed after 1 s?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3a:
The capacitance of the capacitor is 22 mF. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor when it is fully charged.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3b:
The resistance of the wire is 8.0 Ω. Determine the time taken for the capacitor to discharge through the resistance wire. Assume that the capacitor is completely discharged when the potential difference across it has fallen to 0.24 V.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
Calculate the wavelength of the light.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.iii:
Calculate the total energy of the Earth in its orbit.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.24: A simple pendulum bob oscillates as shown. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.25: A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a single slit and a diffraction pattern forms on the...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6d:
The mass of the asteroid is 6.2 × 1012 kg. Calculate the gravitational force experienced by the planet when the asteroid is at point P.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate in J, the energy stored in the system.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
Bohr modified the Rutherford model by introducing the condition mvr = n. Outline the reason for this modification.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9d.iii:
Calculate the wavelength of the gamma ray photon in (d)(ii).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
A meteorite, very far from planet X begins to fall to the surface with a negligibly small initial speed. The mass of planet X is 3.1 × 1021 kg and its radius is 1.2 × 106 m. The planet has no atmosphere. Calculate the speed at which the meteorite will hit the surface.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.i:
Determine a value for Planck’s constant.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7b:
Radiation of photon energy 5.2 x 10–19 J is now incident on the photocell. Calculate the maximum velocity of the emitted electrons.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5b:
Monochromatic light from a single source is incident on two thin, parallel slits.
The following data are available.
The intensity I of light at the screen from each slit separately is I0. Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity of light on the screen for this arrangement.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.iii:
The mass of the pendulum bob is 75 g. Show that the maximum speed of the bob is about 0.7 m s–1.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating of N lines per unit length. The angle between the first orders is θ1.
What is the wavelength of the light?
A.
B. N sin θ1
C. N sin
D.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.32:
The mass of the Earth is ME and the mass of the Moon is MM. Their respective radii are RE and RM.
Which is the ratio ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.ii:
Calculate the speed of the block as it passes the equilibrium position.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.ii:
Deduce, in mm, the width of one slit.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the distance between the plates.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.ii:
Using the answer in (b) and (c)(i), deduce that the radius r of the electron’s orbit in the ground state of hydrogen is given by the following expression.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4c:
The cell is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor in a vacuum. The fully charged capacitor is then connected to an ideal voltmeter.
The capacitance of the capacitor is 6.0 μF and the reading of the voltmeter is 12 V.
Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.i:
Calculate the total length of aluminium foil that the student will require.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.11:
The escape speed from a planet of radius R is vesc. A satellite orbits the planet at a distance R from the surface of the planet. What is the orbital speed of the satellite?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.ii:
Estimate, using the result from (a)(i), the nuclear radius of thorium-232 .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.10c:
The photoelectrons are emitted from a sodium surface. Sodium has a work function of 2.3 eV.
Calculate the wavelength of the radiation incident on the sodium. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8b:
Monochromatic light of wavelength 633 nm is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diffraction maxima incident on a screen are detected and their angle θ to the central beam is determined. The graph shows the variation of sinθ with the order n of the maximum. The central order corresponds to n = 0.
Determine a mean value for the number of slits per millimetre of the grating.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.9c:
Photons with energy 1.1 × 10−18 J are incident on a third metal surface. The maximum energy of electrons emitted from the surface of the metal is 5.1 × 10−19 J.
Calculate, in eV, the work function of the metal.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10c:
An engineer needs to move a space probe of mass 3600 kg from Ganymede to Callisto. Calculate the energy required to move the probe from the orbital radius of Ganymede to the orbital radius of Callisto. Ignore the mass of the moons in your calculation.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A beam of light containing two different wavelengths is incident on a diffraction grating. The...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
In a photoelectric experiment a stopping voltage required to prevent photoelectrons from flowing across the photoelectric cell is measured for light of two frequencies and . The results obtained are shown.
The ratio is an estimate of
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.33: A small magnet is released from rest to drop through a stationary horizontal conducting...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
Some of the nuclear energy levels of oxygen-14 (14O) and nitrogen-14 (14N) are shown.
A nucleus of 14O decays into a nucleus of 14N with the emission of a positron and a gamma ray. What is the maximum energy of the positron and the energy of the gamma ray?
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Two initially uncharged capacitors X and Y are connected in series to a cell as shown.
What is ?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.40: The size of a nucleus can be estimated from electron diffraction experiments. What is the order...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.4c.ii:
The spacecraft will take 7.2 years (2.3 × 108 s) to reach a planet in the solar system. Estimate the power available to the spacecraft when it gets to the planet.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnetic flux linkage in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.6e:
Discuss, by reference to the answer in (b), whether it is likely that Titan will lose its atmosphere of nitrogen.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
A plate performs simple harmonic oscillations with a frequency of 39 Hz and an amplitude of 8.0 cm.
Show that the maximum speed of the oscillating plate is about 20 m s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the speed of the loop is 20 cm s−1.
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
A satellite of mass orbits a planet of mass in a circular orbit of radius . What is the work that must be done on the satellite to increase its orbital radius to ?
A.B.
C.
D.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Calculate the period of oscillations of q.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.ii:
The switch is then connected to Y and C discharges through the 20 MΩ resistor. The voltage Vc drops to 50 % of its initial value in 5.0 s. Determine the capacitance of C.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.4c.i:
Estimate the power, in kW, that is available from the plutonium at launch.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.4d.i: State and explain what happens to the kinetic energy of an emitted photoelectron.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5c.i:
There are 85 turns of wire in the loop. Calculate the maximum induced emf in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
The mass of Titan is 0.025 times the mass of the Earth and its radius is 0.404 times the radius of the Earth. The escape speed from Earth is 11.2 km s−1. Show that the escape speed from Titan is 2.8 km s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.7a:
Show that the charge on the surface of the sphere is +18 μC.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
Sound of frequency 2400 Hz is emitted from a stationary source towards the oscillating plate in (b). The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency of the sound that is received back at the source after reflection at the plate.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.i: State what will happen to the angular position of the primary maxima.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the charge stored on C1 is about 0.04 mC.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
An observer with an eye of pupil diameter views the headlights of a car that emit light of wavelength . The distance between the headlights is .
What is the greatest distance between the observer and the car at which the images of the headlights will be resolved by the observer’s eye?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Explain why the energy gained by capacitor C2 differs from your answer in (b)(i).
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A direct current in a lamp dissipates power P. What root mean square (rms) value of an alternating current dissipates average power P through the same lamp?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.33:
An object of mass is launched from the surface of the Earth. The Earth has a mass and radius . The acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth is . What is the escape speed of the object from the surface of the Earth?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
Outline two reasons why both models predict that the motion is simple harmonic when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6d:
The graph shows for model A the variation with of elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring.
Describe the graph for model B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Determine the time period of the system when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
Calculate the energy transferred from capacitor C1.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
Determine the average emf induced across coil Y in the first 3.0 ms.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.ii:
The half-life of potassium-40 is 1.3 × 109 years. Estimate the age of the rock sample.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: Write down the maximum magnitude of the rate of change of flux linked with the coil.
- 957237: This is an example question for the example test. You can delete this question.
Sub sections and their related questions
Topic 9: Wave phenomena
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
A particle is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude x0 and maximum kinetic energy Ek. What is the potential energy of the system when the particle is a distance 0.20x0 from its maximum displacement?
A. 0.20Ek
B. 0.36Ek
C. 0.64Ek
D. 0.80Ek
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Monochromatic light is incident on a double slit. Both slits have a finite width. The light then...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating that has a slit separation of . What is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed using this arrangement?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 7
D. 9 - 16N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A diffraction grating is used to observe light of wavelength 400 nm. The light illuminates 100...
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6a:
Police use radar to detect speeding cars. A police officer stands at the side of the road and points a radar device at an approaching car. The device emits microwaves which reflect off the car and return to the device. A change in frequency between the emitted and received microwaves is measured at the radar device.
The frequency change Δf is given by
where f is the transmitter frequency, v is the speed of the car and c is the wave speed.
The following data are available.
Transmitter frequency f = 40 GHz Δf = 9.5 kHz Maximum speed allowed = 28 m s–1(i) Explain the reason for the frequency change.
(ii) Suggest why there is a factor of 2 in the frequency-change equation.
(iii) Determine whether the speed of the car is below the maximum speed allowed.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
Airports use radar to track the position of aircraft. The waves are reflected from the aircraft and detected by a large circular receiver. The receiver must be able to resolve the radar images of two aircraft flying close to each other.
The following data are available.
Diameter of circular radar receiver = 9.3 m Wavelength of radar = 2.5 cm Distance of two aircraft from the airport = 31 kmCalculate the minimum distance between the two aircraft when their images can just be resolved.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A pendulum oscillating near the surface of the Earth swings with a time period T. What is the...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.27: For fringes to be observed in a double-slit interference experiment, the slits must emit waves...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
A train moving at speed u relative to the ground, sounds a whistle of constant frequency f as it moves towards a vertical cliff face.
The sound from the whistle reaches the cliff face and is reflected back to the train. The speed of sound in stationary air is c.
What whistle frequency is observed on the train after the reflection?
A.
B. (c + u)f
C. (c – u)f
D.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Describe the conditions required for an object to perform simple harmonic motion (SHM).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
Calculate the mass of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
In carrying out the experiment the student displaced the block horizontally by 4.8 cm from the equilibrium position. Determine the total energy in the oscillation of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
A second identical spring is placed in parallel and the experiment in (b) is repeated. Suggest how this change affects the fractional uncertainty in the mass of the block.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of amplitude xo. Its total energy is 16 J.
What is the kinetic energy of the mass when its displacement is ?
A. 4 J
B. 8 J
C. 12 J
D. 16 J
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Blue light is incident on two narrow slits. Constructive interference takes place along the lines...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.28: Two points illuminated by monochromatic light are separated by a small distance. The light...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A train travelling in a straight line emits a sound of constant frequency f. An observer at...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.i:
A wave of amplitude 4.3 m and wavelength 35 m, moves with a speed of 3.4 m s–1. Calculate the maximum vertical speed of the buoy.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.ii:
Sketch a graph to show the variation with time of the generator output power. Label the time axis with a suitable scale.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i:
Determine the width of one of the slits.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii: Suggest the variation in the output voltage from the light sensor that will be observed as the...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.27: A spring loaded with mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion. The amplitude of the motion...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Monochromatic light is incident on two identical slits to produce an interference pattern on a...
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
A transparent liquid forms a parallel-sided thin film in air. The diagram shows a ray I incident on the upper air–film boundary at normal incidence (the rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity).
Reflections from the top and bottom surfaces of the film result in three rays J, K and L. Which of the rays has undergone a phase change of rad?
A. J only
B. J and L only
C. J and K only
D. J, K and L
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
A stationary sound source emits waves of wavelength and speed v. The source now moves away from a stationary observer. What are the wavelength and speed of the sound as measured by the observer?
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.i:
Estimate the value of k in the following expression.
T =
Give an appropriate unit for your answer. Ignore the mass of the cable and any oscillation of satellite X.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.ii: Describe the energy changes in the satellite Y-cable system during one cycle of the oscillation.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i:
Explain why zero intensity is observed at position A.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
The distance from the centre of the pattern to A is 4.1 x 10–2 m. The distance from the screen to the slits is 7.0 m.
Calculate the width of each slit.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.iii:
Calculate the separation of the two slits.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State and explain the differences between the pattern on the screen due to the grating and the pattern due to the double slit.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
The yellow light is made from two very similar wavelengths that produce two lines in the spectrum of sodium. The wavelengths are 588.995 nm and 589.592 nm. These two lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of this diffraction grating. Determine the beam width of the light incident on the diffraction grating.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A mass at the end of a vertical spring and a simple pendulum perform oscillations on Earth that...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ in air is incident normally on a thin film of refractive index n. The film is surrounded by air. The intensity of the reflected light is a minimum. What is a possible thickness of the film?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Monochromatic light is incident on 4 rectangular, parallel slits. The first principal maximum is...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.29: Two lines X and Y in the emission spectrum of hydrogen gas are measured by an observer stationary...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.i:
Calculate the time taken for the block to return to the equilibrium position for the first time.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.ii:
Calculate the speed of the block as it passes the equilibrium position.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.i:
Calculate the angular separation between the central peak and the missing peak in the double-slit interference intensity pattern. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.ii:
Deduce, in mm, the width of one slit.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3c:
The wavelength of the light in the beam when emitted by the galaxy was 621.4 nm.
Explain, without further calculation, what can be deduced about the relative motion of the galaxy and the Earth.
-
18M.3.HL.TZ1.11b.i:
determine the initial energy.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.24: A simple pendulum bob oscillates as shown. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.25: A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a single slit and a diffraction pattern forms on the...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating of N lines per unit length. The angle between the first orders is θ1.

What is the wavelength of the light?
A.
B. N sin θ1
C. N sin
D.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
A train is approaching an observer with constant speed
where c is the speed of sound in still air. The train emits sound of wavelength λ. What is the observed speed of the sound and observed wavelength as the train approaches?

-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.ii:
Show that the period of oscillation of the ball is about 6 s.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.iii:
The amplitude of oscillation is 0.12 m. On the axes, draw a graph to show the variation with time t of the velocity v of the ball during one period.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5a:
Monochromatic light from two identical lamps arrives on a screen.

The intensity of light on the screen from each lamp separately is I0.
On the axes, sketch a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity I of light on the screen.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5b:
Monochromatic light from a single source is incident on two thin, parallel slits.

The following data are available.
The intensity I of light at the screen from each slit separately is I0. Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity of light on the screen for this arrangement.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5c:
The slit separation is increased. Outline one change observed on the screen.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) has a period T and total energy E. The amplitude of oscillations is halved. What are the new period and total energy of the system?
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.27: The graph shows the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light when monochromatic...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a diffraction grating. The grating spacing is d. The angles between the different orders are shown on the diagram.
What is the expression for the wavelength of light used?
A.
B.
C. d sin α
D. d sin β
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
An ambulance siren emits a sound of frequency 1200 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s–1. The ambulance moves towards a stationary observer at a constant speed of 40 m s–1. What is the frequency heard by the observer?
A. Hz
B. Hz
C. Hz
D. Hz
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
The light illuminates a width of 3.5 mm of the grating. The deuterium and hydrogen red lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of the diffraction grating. Show that the grating spacing of the diffraction grating is about 2 × 10–6 m.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii: Calculate the angle between the first-order line of the red light in the hydrogen spectrum and...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.iii: The light source is changed so that white light is incident on the diffraction grating. Outline...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.3ei:
Calculate the frequency heard by the observer.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Deduce, in W m-2, the intensity at M.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8ci: Suggest why, after this change, the intensity at P will be less than that at M.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.8cii:
Show that, due to single slit diffraction, the intensity at a point on the screen a distance of 28 mm from M is zero.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of the object.
What is the velocity of the object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.17: A mass on a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position. Which graph represents the...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.i: Calculate, in m, the length of the thread. State your answer to an appropriate number of...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.ii:
Label on the graph with the letter X a point where the speed of the pendulum is half that of its initial speed.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.iii:
The mass of the pendulum bob is 75 g. Show that the maximum speed of the bob is about 0.7 m s–1.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iv: The speed after the collision of the bob and the object was measured using a sensor. This sensor...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.21: A train approaches a station and sounds a horn of constant frequency and constant intensity. An...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.22: Two stars are viewed with a telescope using a green filter. The images of the stars are just...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
The four pendulums shown have been cut from the same uniform sheet of board. They are attached to the ceiling with strings of equal length.
Which pendulum has the shortest period?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.29: In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the distance between fringes is too small to be...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
The headlights of a car emit light of wavelength 400 nm and are separated by 1.2 m. The headlights are viewed by an observer whose eye has an aperture of 4.0 mm. The observer can just distinguish the headlights as separate images. What is the distance between the observer and the headlights?
A. 8 km
B. 10 km
C. 15 km
D. 20 km
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
A transparent liquid film of refractive index 1.5 coats the outside of a glass lens of higher refractive index. The liquid film is used to eliminate reflection from the lens at wavelength λ in air.
What is the minimum thickness of the liquid film coating and the phase change at the liquid–glass interface?
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoes simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude 0. When the displacement of the object is , the speed of the object is . What is the speed when the displacement is 0?
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Light of frequency 500 THz is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern. The...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is normally incident on a diffraction grating of spacing 3λ. What is the angle between the two second-order maxima?
A.
B.
C.
D. >90° so no second orders appear
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.29: Sea waves move towards a beach at a constant speed of 2.0 m s–1. They arrive at the beach with a...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Predict whether reflected ray X undergoes a phase change.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): state, in terms of d, the path difference between the reflected rays X and Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
calculate the smallest value of d that will result in destructive interference between ray X and ray Y.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii): discuss a practical advantage of this arrangement.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(i): Draw, on the axes, the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light incident on the...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(ii):
Estimate, in rad, the smallest angular separation of two distinct point sources of light of wavelength 656 nm that can be resolved by the eye of this observer.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.27:
A simple pendulum and a mass–spring system oscillate with the same time period. The mass of the pendulum bob and the mass on the spring are initially identical. The masses are halved.
What is when the masses have been changed?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelengths of two spectral lines of the light differ by and have a mean wavelength of . The spectral lines are just resolved in the fourth order of the grating. What is the minimum number of grating lines that were illuminated?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.29: White light is incident normally on separate diffraction gratings X and Y. Y has a greater number...
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(i): Explain why the frequency recorded by the microphone is lower than the frequency emitted by the...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(ii):
Calculate .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The mass of the cylinder is and the cross-sectional area of the cylinder is . The density of water is . Show that the angular frequency of oscillation of the cylinder is about .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(i):
Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the cylinder.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(ii):
Draw, on the axes, the graph to show how the kinetic energy of the cylinder varies with time during one period of oscillation .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
State the phase change when a ray is reflected at B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Explain the condition for w that eliminates reflection for a particular light wavelength in air .
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.i: State the Rayleigh criterion for resolution.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.ii:
The painting contains a pattern of red dots with a spacing of 3 mm. Assume the wavelength of red light is 700 nm. The average diameter of the pupil of a human eye is 4 mm. Calculate the maximum possible distance at which these red dots are distinguished.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Calculate, in m s−1, the maximum velocity of vibration of point P when it is vibrating with a frequency of 195 Hz.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.v:
Estimate the displacement needed to double the energy of the string.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: State the phase difference between the waves at V and Y.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii: State, in terms of λ, the path length between points X and Z.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.iii:
The separation of adjacent slits is d. Show that for the second-order diffraction maximum .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8b:
Monochromatic light of wavelength 633 nm is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diffraction maxima incident on a screen are detected and their angle θ to the central beam is determined. The graph shows the variation of sinθ with the order n of the maximum. The central order corresponds to n = 0.
Determine a mean value for the number of slits per millimetre of the grating.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i: using a light source with a smaller wavelength.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii: increasing the distance between the diffraction grating and the screen.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.26: Which is correct for the tangential acceleration of a simple pendulum at small amplitudes? A. It...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
The diagram shows the diffraction pattern for light passing through a single slit.
What is
A. 0.01
B. 0.02
C. 1
D. 2
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelength lines 600.0 nm and 601.5 nm are...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.29: On approaching a stationary observer, a train sounds its horn and decelerates at a constant rate....
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass–spring system oscillates vertically with a period of at the surface of the Earth. The gravitational field strength at the surface of Mars is . What is the period of the same mass–spring system on the surface of Mars?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Light passes through a diffraction grating. Which quantity must be decreased to improve...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A train is moving in a straight line away from a stationary observer when the train horn emits a sound of frequency . The speed of the train is where is the speed of sound. What is the frequency of the horn as heard by the observer?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
Monochromatic light of wavelength passes through a single-slit of width and produces a diffraction pattern on a screen. Which combination of changes to and will cause the greatest decrease in the width of the central maximum?
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iv:
Calculate, in terms of g, the maximum acceleration of P.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.26: A simple pendulum undergoes simple harmonic motion. The gravitational potential energy of the...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.27: When monochromatic light is incident on a single slit a diffraction pattern forms on a...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident normally on a thin liquid film of refractive index that is suspended in air. The rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity.
What is the minimum thickness of the film so that the reflected light undergoes constructive interference?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A beam of light containing two different wavelengths is incident on a diffraction grating. The...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Explain why q will perform simple harmonic oscillations when it is released.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Calculate the period of oscillations of q.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: State what is meant by the Doppler effect.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
A plate performs simple harmonic oscillations with a frequency of 39 Hz and an amplitude of 8.0 cm.
Show that the maximum speed of the oscillating plate is about 20 m s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
Sound of frequency 2400 Hz is emitted from a stationary source towards the oscillating plate in (b). The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency of the sound that is received back at the source after reflection at the plate.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.i: State what will happen to the angular position of the primary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.ii: State what will happen to the width of the primary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.iii: State what will happen to the intensity of the secondary maxima.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
A simple pendulum has a time period on the Earth. The pendulum is taken to the Moon where the gravitational field strength is that of the Earth.
What is the time period of the pendulum on the Moon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
In two different experiments, white light is passed through a single slit and then is either refracted through a prism or diffracted with a diffraction grating. The prism produces a band of colours from M to N. The diffraction grating produces a first order spectrum P to Q.
What are the colours observed at M and P?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A train is sounding its whistle when approaching a train station. Three statements about the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Deduce .
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Determine the amplitude of oscillation for test 1.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iv: In test 2, the maximum elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring is 44 J. When t = 0 the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
The motion sensor operates by detecting the sound waves reflected from the base of the mass. The sensor compares the frequency detected with the frequency emitted when the signal returns.
The sound frequency emitted by the sensor is 35 kHz. The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency change detected by the sensor for test 2.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Light of wavelength is diffracted after passing through a very narrow single slit of width . The intensity of the central maximum of the diffracted light is . The slit width is doubled.
What is the intensity of central maximum and the angular position of the first minimum?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
An observer with an eye of pupil diameter views the headlights of a car that emit light of wavelength . The distance between the headlights is .
What is the greatest distance between the observer and the car at which the images of the headlights will be resolved by the observer’s eye?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.3d:
Loudspeaker A is switched off. Loudspeaker B moves away from M at a speed of 1.5 m s−1 while emitting a frequency of 3.0 kHz.
Determine the difference between the frequency detected at M and that emitted by B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
Outline two reasons why both models predict that the motion is simple harmonic when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Determine the time period of the system when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
Outline, without calculation, the change to the time period of the system for the model represented by graph B when is large.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6d:
The graph shows for model A the variation with of elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring.
Describe the graph for model B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.
Topic 10: Fields
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.30: What is the unit of Gε0, where G is the gravitational constant and ε0 is the permittivity of free...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.31: Two parallel metal plates are connected to a dc power supply. An electric field forms in the...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.32: A satellite of mass 1500 kg is in the Earth’s gravitational field. It moves from a point where...
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.7a:
Explain what is meant by the gravitational potential at the surface of a planet.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
An unpowered projectile is fired vertically upwards into deep space from the surface of planet Venus. Assume that the gravitational effects of the Sun and the other planets are negligible.
The following data are available.
Mass of Venus = 4.87×1024 kg Radius of Venus = 6.05×106 m Mass of projectile = 3.50×103 kg Initial speed of projectile = 1.10×escape speed(i) Determine the initial kinetic energy of the projectile.
(ii) Describe the subsequent motion of the projectile until it is effectively beyond the gravitational field of Venus.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.29: An electric field acts in the space between two charged parallel plates. One plate is at zero...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.30: A satellite at the surface of the Earth has a weight W and gravitational potential energy Ep. The...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.31: Two point charges are at rest as shown. At which position is the electric field strength...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.6a: Outline how this diagram shows that the gravitational field strength of planet X decreases with...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.6b: The diagram shows part of the surface of planet X. The gravitational potential at the surface of...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
A meteorite, very far from planet X begins to fall to the surface with a negligibly small initial speed. The mass of planet X is 3.1 × 1021 kg and its radius is 1.2 × 106 m. The planet has no atmosphere. Calculate the speed at which the meteorite will hit the surface.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.30: A positive charge Q is deposited on the surface of a small sphere. The dotted lines...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.31:
The graph shows the variation of the gravitational potential V with distance r from the centre of a uniform spherical planet. The radius of the planet is R. The shaded area is S.
What is the work done by the gravitational force as a point mass m is moved from the surface of the planet to a distance 6R from the centre?
A. m (V2 – V1 )
B. m (V1 – V2 )
C. mS
D. S
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.32: Four uniform planets have masses and radii as shown. Which planet has the smallest escape speed?
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Outline why the gravitational potential is negative.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
The gravitational potential due to the Sun at a distance r from its centre is VS. Show that
rVS = constant.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.iii:
Calculate the total energy of the Earth in its orbit.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.iv: An asteroid strikes the Earth and causes the orbital speed of the Earth to suddenly decrease....
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.31: A charge of −3 C is moved from A to B and then back to A. The electric potential at A is +10 V...
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
A spacecraft moves towards the Earth under the influence of the gravitational field of the Earth.
The three quantities that depend on the distance r of the spacecraft from the centre of the Earth are the
I. gravitational potential energy of the spacecraft
II gravitational field strength acting on the spacecraft
III. gravitational force acting on the spacecraft.Which of the quantities are proportional to ?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.33: An isolated hollow metal sphere of radius R carries a positive charge. Which graph shows...
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2a:
Satellite X orbits 6600 km from the centre of the Earth.
Mass of the Earth = 6.0 x 1024 kg
Show that the orbital speed of satellite X is about 8 km s–1.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2b.i: the orbital times for X and Y are different.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2b.ii: satellite Y requires a propulsion system.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Four identical, positive, point charges of magnitude Q are placed at the vertices of a square of side 2d. What is the electric potential produced at the centre of the square by the four charges?

A. 0
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.31: The diagram shows 5 gravitational equipotential lines. The gravitational potential on each line...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
An electron of mass me orbits an alpha particle of mass mα in a circular orbit of radius r. Which expression gives the speed of the electron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i:
On the diagram, draw and label the equipotential lines at –0.4 V and –0.8 V.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.28: A moon of mass M orbits a planet of mass 100M. The radius of the planet is R and the...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.29: The diagram shows the electric field and the electric equipotential surfaces between two...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.30: A positive point charge is placed above a metal plate at zero electric potential. Which...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A satellite orbiting a planet moves from orbit X to orbit Y. ...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.32:
The mass of the Earth is ME and the mass of the Moon is MM. Their respective radii are RE and RM.
Which is the ratio ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Show that V = –g(R + h).
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Draw a graph, on the axes, to show the variation of the gravitational potential V of the planet with height h above the surface of the planet.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
A planet has a radius of 3.1 × 106 m. At a point P a distance 2.4 × 107 m above the surface of the planet the gravitational field strength is 2.2 N kg–1. Calculate the gravitational potential at point P, include an appropriate unit for your answer.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
The diagram shows the path of an asteroid as it moves past the planet.

When the asteroid was far away from the planet it had negligible speed. Estimate the speed of the asteroid at point P as defined in (b).
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.6d:
The mass of the asteroid is 6.2 × 1012 kg. Calculate the gravitational force experienced by the planet when the asteroid is at point P.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
Two point charges Q1 and Q2 are one metre apart. The graph shows the variation of electric potential V with distance from Q1.
What is ?
A.
B.
C. 4
D. 16
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.31: The gravitational potential at point P due to Earth is V. What is the definition of the...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
The escape speed for the Earth is esc. Planet X has half the density of the Earth and twice the radius. What is the escape speed for planet X?
A.
B.
C. esc
D. esc
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State the maximum distance between the centres of the nuclei for which the production of is likely to occur.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
Determine, in J, the minimum initial kinetic energy that the deuterium nucleus must have in order to produce . Assume that the phosphorus nucleus is stationary throughout the interaction and that only electrostatic forces act.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9ai:
Show that the total energy of the planet is given by the equation shown.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9aii:
Suppose the star could contract to half its original radius without any loss of mass. Discuss the effect, if any, this has on the total energy of the planet.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
The diagram shows some of the electric field lines for two fixed, charged particles X and Y.
The magnitude of the charge on X is and that on Y is . The distance between X and Y is 0.600 m. The distance between P and Y is 0.820 m.
At P the electric field is zero. Determine, to one significant figure, the ratio .
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.10:
Satellite X is in orbit around the Earth. An identical satellite Y is in a higher orbit. What is correct for the total energy and the kinetic energy of the satellite Y compared with satellite X?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.11:
The escape speed from a planet of radius R is vesc. A satellite orbits the planet at a distance R from the surface of the planet. What is the orbital speed of the satellite?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
The orbital period T of a moon orbiting a planet of mass M is given by
where R is the average distance between the centre of the planet and the centre of the moon.
Show that
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
The following data for the Mars–Phobos system and the Earth–Moon system are available:
Mass of Earth = 5.97 × 1024 kg
The Earth–Moon distance is 41 times the Mars–Phobos distance.
The orbital period of the Moon is 86 times the orbital period of Phobos.
Calculate, in kg, the mass of Mars.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.5c: The graph shows the variation of the gravitational potential between the Earth and Moon with...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.ii: The plastic film begins to conduct when the electric field strength in it exceeds 1.5 MN C–1....
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.30: An electron is fixed in position in a uniform electric field. What is the position for which the...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.32: A negative charge Q is to be moved within an electric field E, to equidistant points from its...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.33:
The escape velocity for an object at the surface of the Earth is vesc. The diameter of the Moon is 4 times smaller than that of the Earth and the mass of the Moon is 81 times smaller than that of the Earth. What is the escape velocity of the object on the Moon?
A. vesc
B. vesc
C. vesc
D. vesc
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
A satellite in a circular orbit around the Earth needs to reduce its orbital radius.
What is the work done by the satellite rocket engine and the change in kinetic energy resulting from this shift in orbital height?
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
The gravitational potential is at a distance above the surface of a spherical planet of radius and uniform density. What is the gravitational potential a distance above the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.31:
The force acting between two point charges is when the separation of the charges is . What is the force between the charges when the separation is increased to ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.32: An electron enters a uniform electric field of strength E with a velocity v. The direction of v...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(i):
Show that the speed of the electron with mass , is given by .
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(ii):
Hence, deduce that the total energy of the electron is given by .
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8a(iii):
In this model the electron loses energy by emitting electromagnetic waves. Describe the predicted effect of this emission on the orbital radius of the electron.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.31: P and S are two points on a gravitational equipotential surface around a planet. Q and R are two...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
The graph shows the variation of electric field strength with distance from a point charge.
The shaded area X is the area under the graph between two separations and from the charge.
What is X?
A. The electric field average between and
B. The electric potential difference between and
C. The work done in moving a charge from to
D. The work done in moving a charge from to
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8a:
Explain why the electric potential decreases from A to B.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
Draw, on the axes, the variation of electric potential with distance from the centre of the sphere.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.8c(ii):
Determine the charge of the sphere.
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.8d: The concept of potential is also used in the context of gravitational fields. Suggest why...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.2c.i:
Show that the gravitational potential due to the planet and the star at the surface of the planet is about −5 × 109 J kg−1.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.2c.ii:
Estimate the escape speed of the spacecraft from the planet–star system.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.3d.ii:
Outline, without calculation, whether or not the electric potential at P is zero.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10b.i:
Show that the is about 80.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10b.ii:
Outline, using (b)(i), why it is not correct to use the equation to calculate the speed required for the spacecraft to reach infinity from the surface of .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.10c:
An engineer needs to move a space probe of mass 3600 kg from Ganymede to Callisto. Calculate the energy required to move the probe from the orbital radius of Ganymede to the orbital radius of Callisto. Ignore the mass of the moons in your calculation.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.30: A particle with charge −2.5 × 10−6 C moves from point X to point Y due to a uniform electrostatic...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.31: Which is a correct unit for gravitational potential? A. m2 s−2 B. J kg C. m s−2 D. N m−1 kg−1
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.32: A planet has radius R. The escape speed from the surface of the planet is v. At what...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
An object of mass released from rest near the surface of a planet has an initial acceleration . What is the gravitational field strength near the surface of the planet?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.31:
The points X and Y are in a uniform electric field of strength . The distance OX is and the distance OY is .
What is the magnitude of the change in electric potential between X and Y?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.32:
A satellite orbits planet with a speed at a distance from the centre of planet . Another satellite orbits planet at a speed of at a distance from the centre of planet . The mass of planet is and the mass of planet is . What is the ratio of ?
A. 0.25B. 0.5
C. 2.0
D. 4.0
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.30: The diagram shows equipotential lines for an electric field. Which arrow represents...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.31: Two charged parallel plates have electric potentials of 10 V and 20 V. A particle with charge...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.32:
A satellite of mass orbits a planet of mass in a circular orbit of radius . What is the work that must be done on the satellite to increase its orbital radius to ?
A.B.
C.
D.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
The mass of Titan is 0.025 times the mass of the Earth and its radius is 0.404 times the radius of the Earth. The escape speed from Earth is 11.2 km s−1. Show that the escape speed from Titan is 2.8 km s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.6e:
Discuss, by reference to the answer in (b), whether it is likely that Titan will lose its atmosphere of nitrogen.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.7a:
Show that the charge on the surface of the sphere is +18 μC.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.7b.ii:
Predict the charge on each sphere.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.32: Two positive and two negative charges are located at the corners of a square as shown. Point X is...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The graph shows the variation with distance r of the electric potential V from a charge...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.7a: Outline what is meant by electric potential at a point.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.7b:
The electric potential at a point a distance 2.8 m from the centre of the sphere is 7.71 kV. Determine the radius of the sphere.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.i: Comment on the angle at which the object meets equipotential surfaces around the sphere.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.iii:
Determine whether the object will reach the surface of the sphere.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A charged sphere in a gravitational field is initially stationary between two parallel metal plates. There is a potential difference V between the plates.
Three changes can be made:
I. Increase the separation of the metal plates
II. Increase V
III. Apply a magnetic field into the plane of the paperWhat changes made separately will cause the charged sphere to accelerate?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.33:
An object of mass is launched from the surface of the Earth. The Earth has a mass and radius . The acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth is . What is the escape speed of the object from the surface of the Earth?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the electric potential at O.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.7b: Sketch, on the axes, the variation of the electric potential V with distance between X and Y.
Topic 11: Electromagnetic induction
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Which of the following reduces the energy losses in a transformer? A. Using thinner wires for...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The secondary coil of an alternating current (ac) transformer is connected to two diodes as shown.
Which graph shows the variation with time of the potential difference VXY between X and Y?
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a battery. What happens when a sheet of dielectric...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.36: Three capacitors are arranged as shown. What is the total capacitance of the arrangement? A....
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10b:
Electrical power output is produced by several alternating current (ac) generators which use transformers to deliver energy to the national electricity grid.
The following data are available. Root mean square (rms) values are given.
ac generator output voltage to a transformer = 25 kV ac generator output current to a transformer = 3.9 kA Transformer output voltage to the grid = 330 kV Transformer efficiency = 96%(i) Calculate the current output by the transformer to the grid. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
(ii) Electrical energy is often delivered across large distances at 330 kV. Identify the main advantage of using this very high potential difference.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
In an alternating current (ac) generator, a square coil ABCD rotates in a magnetic field.
The ends of the coil are connected to slip rings and brushes. The plane of the coil is shown at the instant when it is parallel to the magnetic field. Only one coil is shown for clarity.
The following data are available.
Dimensions of the coil = 8.5 cm×8.5 cm Number of turns on the coil = 80 Speed of edge AB = 2.0 ms–1 Uniform magnetic field strength = 0.34 T(i) Explain, with reference to the diagram, how the rotation of the generator produces an electromotive force (emf ) between the brushes.
(ii) Calculate, for the position in the diagram, the magnitude of the instantaneous emf generated by a single wire between A and B of the coil.
(iii) Hence, calculate the total instantaneous peak emf between the brushes.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A direct current (dc) of 5A dissipates a power P in a resistor. Which peak value of the alternating current (ac) will dissipate an average power P in the same resistor?
A. 5A
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.33: What are the units of magnetic flux and magnetic field strength?
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.34: A battery is used to charge a capacitor fully through a resistor of resistance R. The energy...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.35: A capacitor is charged by a constant current of 2.5 μA for 100 s. As a result the potential...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A conducting square coil is placed in a region where there is a uniform magnetic field. The...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8a: State Faraday’s law of induction.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Explain, using Faraday’s law of induction, how the transformer steps down the voltage.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
The input voltage is 240 V. Calculate the output voltage.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8c: Outline how energy losses are reduced in the core of a practical transformer.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8d: Step-up transformers are used in power stations to increase the voltage at which the electricity...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The diagram shows a bar magnet near an aluminium ring. The ring is supported so that it is...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
Three conducting loops, X, Y and Z, are moving with the same speed from a region of zero magnetic field to a region of uniform non-zero magnetic field.
Which loop(s) has/have the largest induced electromotive force (emf) at the instant when the loops enter the magnetic field?
A. Z only
B. Y only
C. Y and Z only
D. X and Y only
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.35: Two capacitors of different capacitance are connected in series to a source of emf of...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A fully charged capacitor is connected to a resistor. When the switch is closed the capacitor...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3a:
The capacitance of the capacitor is 22 mF. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor when it is fully charged.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3b:
The resistance of the wire is 8.0 Ω. Determine the time taken for the capacitor to discharge through the resistance wire. Assume that the capacitor is completely discharged when the potential difference across it has fallen to 0.24 V.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
Calculate the root mean square (rms) current in each cable.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.i: Suggest the advantage of using a step-up transformer in this way.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.ii:
The use of alternating current (ac) in a transformer gives rise to energy losses. State how eddy current loss is minimized in the transformer.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The plane of a coil is positioned at right angles to a magnetic field of flux density B. The coil has N turns, each of area A. The coil is rotated through 180˚ in time t.
What is the magnitude of the induced emf?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The ratio for a transformer is 2.5.
The primary coil of the transformer draws a current of 0.25 A from a 200 V alternating current (ac) supply. The current in the secondary coil is 0.5 A. What is the efficiency of the transformer?
A. 20 %
B. 50 %
C. 80 %
D. 100 %
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
An alternating current (ac) generator produces a peak emf E0 and periodic time T. What are the peak emf and periodic time when the frequency of rotation is doubled?
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
Six identical capacitors, each of value C, are connected as shown.
What is the total capacitance?
A.
B.
C.
D. 6C
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.38: A capacitor of capacitance C discharges through a resistor of resistance R. The graph shows...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: The cable between the satellites cuts the magnetic field lines of the Earth at right...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2e: The magnetic field strength of the Earth is 31 μT at the orbital radius of the satellites. The...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.33: Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The graph shows the variation with time t of the current I in the primary coil of an ideal...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.35: The diagram shows a diode bridge rectification circuit and a load resistor. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the distance between the plates.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
The capacitor is connected to a 16 V cell as shown.

Calculate the magnitude and the sign of the charge on plate A when the capacitor is fully charged.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
The capacitor is fully charged and the space between the plates is then filled with a dielectric of permittivity ε = 3.0ε0.
Explain whether the magnitude of the charge on plate A increases, decreases or stays constant.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
In a different circuit, a transformer is connected to an alternating current (ac) supply.

The transformer has 100 turns in the primary coil and 1200 turns in the secondary coil. The peak value of the voltage of the ac supply is 220 V. Determine the root mean square (rms) value of the output voltage.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7e:
Describe the use of transformers in electrical power distribution.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The current I flowing in loop A in a clockwise direction is increasing so as to induce a...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.34: A rectangular flat coil moves at constant speed through a uniform magnetic field. The direction...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
The graph shows the power dissipated in a resistor of 100 Ω when connected to an alternating current (ac) power supply of root mean square voltage (Vrms) 60 V.

What are the frequency of the ac power supply and the average power dissipated in the resistor?

- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.36: Three capacitors, each one with a capacitance C, are connected such that their...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8a:
Show that the capacitance of this arrangement is C = 6.6 × 10–7 F.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
Calculate in V, the potential difference between the thundercloud and the Earth’s surface.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate in J, the energy stored in the system.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i:
Show that about –11 C of charge is delivered to the Earth’s surface.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8d:
State one assumption that needs to be made so that the Earth-thundercloud system may be modelled by a parallel plate capacitor.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.33:
A ring of area S is in a uniform magnetic field X. Initially the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The ring is rotated by 180° about the axis in time T.
What is the average induced emf in the ring?
A. 0
B.
C.
D. -
18N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The graph shows the variation of the peak output power P with time of an alternating current (ac) generator.
Which graph shows the variation of the peak output power with time when the frequency of rotation is decreased?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A current of 1.0 × 10–3 A flows in the primary coil of a step-up transformer. The number of turns in the primary coil is Np and the number of turns in the secondary coil is Ns. One coil has 1000 times more turns than the other coil.
What is and what is the current in the secondary coil for this transformer?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Four identical capacitors of capacitance X are connected as shown in the diagram.
What is the effective capacitance between P and Q?
A.
B. X
C.
D. 4X
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.i: Outline how eddy currents reduce transformer efficiency.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.ii:
Determine the peak current in the primary coil when operating with the maximum number of lamps.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7a: The battery has an emf of 7.5 V. Determine the charge that flows through the motor when the mass...
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The motor can transfer one-third of the electrical energy stored in the capacitor into gravitational potential energy of the mass. Determine the maximum height through which a mass of 45 g can be raised.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7c: An additional identical capacitor is connected in series with the first capacitor and...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4c:
The cell is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor in a vacuum. The fully charged capacitor is then connected to an ideal voltmeter.
The capacitance of the capacitor is 6.0 μF and the reading of the voltmeter is 12 V.
Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4di:
Calculate the change in the energy stored in the capacitor.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.4dii: Suggest, in terms of conservation of energy, the cause for the above change.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10a: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, state why the magnetic flux in the ring is increasing.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10b: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, sketch, using an arrow on Diagram 2, the direction...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10c: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, deduce the direction of the magnetic force on the...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Two charges, +Q and −Q, are placed as shown. What is the magnitude of the electric field...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.i:
Calculate the total length of aluminium foil that the student will require.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.ii: The plastic film begins to conduct when the electric field strength in it exceeds 1.5 MN C–1....
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
The resistor R in the circuit has a resistance of 1.2 kΩ. Calculate the time taken for the charge on the capacitor to fall to 50 % of its fully charged value.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii: The ammeter is replaced by a coil. Explain why there will be an induced emf in the coil while the...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Suggest one change to the discharge circuit, apart from changes to the coil, that will increase the maximum induced emf in the coil.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.26: The input to a diode bridge rectification circuit is sinusoidal with a time period of 20...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
Three identical capacitors are connected in series. The total capacitance of the arrangement is mF. The three capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the capacitance of the parallel arrangement?
A. mF
B. 1 mF
C. 3 mF
D. 81 mF
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A transformer with 600 turns in the primary coil is used to change an alternating root mean square (rms) potential difference of 240 Vrms to 12 Vrms.
When connected to the secondary coil, a lamp labelled “120 W, 12 V” lights normally. The current in the primary coil is 0.60 A when the lamp is lit.
What are the number of secondary turns and the efficiency of the transformer?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A circular coil of wire moves through a region of uniform magnetic field directed out of the...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
The graph below shows the variation with time of the magnetic flux through a coil.
Which of the following gives three times for which the magnitude of the induced emf is a maximum?
A. 0, ,
B. 0, , T
C. 0, , T
D. , ,
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.36: Two capacitors of 3 μF and 6 μF are connected in series and charged using a 9 V battery. What...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The circuit diagram shows a capacitor that is charged by the battery after the switch is connected to terminal X. The cell has emf V and internal resistance r. After the switch is connected to terminal Y the capacitor discharges through the resistor of resistance R.
What is the nature of the current and magnitude of the initial current in the resistor after the switch is connected to terminal Y?
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.33: X and Y are two plane coils parallel to each other that have a common axis. There is a constant...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.34: A coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field. An alternating emf is induced in the coil. What is...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A capacitor of capacitance 1.0 μF stores a charge of 15 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.36: A diode bridge rectification circuit is constructed as shown. An alternating potential difference...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Calculate, in J, the energy stored in X with the switch S open.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
Calculate the final charge on X and the final charge on Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
Calculate the final total energy, in J, stored in X and Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9c:
Suggest why the answers to (a) and (b)(ii) are different.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Why are high voltages and low currents used when electricity is transmitted over long...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
Power is dissipated in a resistor of resistance when there is a direct current in the resistor.
What is the average power dissipation in a resistance when the alternating root-mean-square (rms) current in the resistor is ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A rectangular coil rotates at a constant angular velocity. At the instant shown, the plane of the coil is at right angles to the line . A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction .
What rotation of the coil about a specified axis will produce the graph of electromotive force (emf) against time ?
A. Through about
B. Through about
C. Through about
D. Through about
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
A capacitor of capacitance has initial charge . The capacitor is discharged through a resistor of resistance . The potential difference across the capacitor varies with time.
What is true for this capacitor?
A. After time the potential difference across the capacitor is halved.
B. The capacitor discharges more quickly when the resistance is changed to .
C. The rate of change of charge on the capacitor is proportional to .
D. The time for the capacitor to lose half its charge is .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Explain, by reference to Faraday’s law of induction, how an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the coil.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
The average power output of the generator is . Calculate the root mean square (rms) value of the generator output current.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
The voltage output from the generator is stepped up before transmission to the consumer. Estimate the factor by which voltage has to be stepped up in order to reduce power loss in the transmission line by a factor of .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(iii):
The frequency of the generator is doubled with no other changes being made. Draw, on the axes, the variation with time of the voltage output of the generator.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5a: Explain the role of the diode in the circuit when the switch is at position A.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
Show that the maximum energy stored by the capacitor is about 160 J.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
Calculate the maximum charge Q0 stored in the capacitor.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.iii: Identify, using the label + on the diagram, the polarity of the capacitor.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.i: Describe what happens to the energy stored in the capacitor when the switch is moved to position B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.ii:
Show that the charge remaining in the capacitor after a time equal to one time constant of the circuit will be 0.37 Q0.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.iii:
The graph shows the variation with time of the charge in the capacitor as it is being discharged through the heart.
Determine the electrical resistance of the closed circuit with the switch in position B.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5d: In practice, two electrodes connect the heart to the circuit. These electrodes introduce an...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
The primary coil has 3300 turns. Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iii:
Calculate the current in the primary of the transformer assuming that it is ideal.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iv:
Flux leakage is one reason why a transformer may not be ideal. Explain the effect of flux leakage on the transformer.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.7b: A pendulum with a metal bob comes to rest after 200 swings. The same pendulum, released from the...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.33: A conducting ring encloses an area of 2.0 cm2 and is perpendicular to a magnetic field...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The conservation of which quantity explains Lenz’s law? A. Charge B. Energy C. Magnetic...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A resistor designed for use in a direct current (dc) circuit is labelled “50 W, 2 Ω”. The resistor is connected in series with an alternating current (ac) power supply of peak potential difference 10 V. What is the average power dissipated by the resistor in the ac circuit?
A. 25 W
B. 35 W
C. 50 W
D. 100 W
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
A capacitor of capacitance X is connected to a power supply of voltage V. At time t = 0, the capacitor is disconnected from the supply and discharged through a resistor of resistance R. What is the variation with time of the charge on the capacitor?
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.33: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a cell of constant emf. The capacitor plates are then...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
The graph shows the variation of an alternating current with time in a resistor.
What is the average power dissipated in the resistor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
A magnet connected to a spring oscillates above a solenoid with a 240 turn coil as shown.
The graph below shows the variation with time of the emf across the solenoid with the period, , of the system shown.
The spring is replaced with one that allows the magnet to oscillate with a higher frequency. Which graph shows the new variation with time of the current in the resistor for this new set-up?
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.36:
A capacitor is charged with a constant current . The graph shows the variation of potential difference across the capacitor with time . The gradient of the graph is . What is the capacitance of the capacitor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.33: A small magnet is released from rest to drop through a stationary horizontal conducting...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.34: An alternating supply is connected to a diode bridge rectification circuit. The conventional...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The root mean square (rms) current in the primary coil of an ideal transformer is 2.0 A. The rms voltage in the secondary coil is 50 V. The average power transferred from the secondary coil is 20 W.
What is and what is the average power transferred from the primary coil?
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Two initially uncharged capacitors X and Y are connected in series to a cell as shown.
What is ?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.i: At t = 0, the switch is connected to X. On the axes, draw a sketch graph to show the variation...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.ii:
The switch is then connected to Y and C discharges through the 20 MΩ resistor. The voltage Vc drops to 50 % of its initial value in 5.0 s. Determine the capacitance of C.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the speed of the loop is 20 cm s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnetic flux linkage in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5c.i:
There are 85 turns of wire in the loop. Calculate the maximum induced emf in the loop.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.34: Which two features are necessary for the operation of a transformer?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.35: A conducting bar with vertices PQRS is moving vertically downwards with constant velocity v...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A circuit consists of three identical capacitors of capacitance C and a battery of voltage V. Two...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: Write down the maximum magnitude of the rate of change of flux linked with the coil.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii:
State the fundamental SI unit for your answer to (a)(i).
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i: Explain why the graph becomes negative.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii: Part of the graph is above the t-axis and part is below. Outline why the areas between the t-axis...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8c: Predict the changes to the graph when the magnet is dropped from a lower height above the coil.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
The graph shows the variation of magnetic flux in a coil with time .
What represents the variation with time of the induced emf across the coil?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A direct current in a lamp dissipates power P. What root mean square (rms) value of an alternating current dissipates average power P through the same lamp?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
The arrangement shows four diodes connected to an alternating current (ac) supply. The output is connected to an external circuit.
What is the output to the external circuit?
A. Full-wave rectified current
B. Half-wave rectified current
C. Constant non-zero current
D. Zero current
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.37: Three identical capacitors are connected together as shown. What is the order of increasing...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the charge stored on C1 is about 0.04 mC.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
Calculate the energy transferred from capacitor C1.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Explain why the energy gained by capacitor C2 differs from your answer in (b)(i).
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i: The switch is closed at time t = 0. Explain how the voltmeter reading varies after the switch is...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
Determine the average emf induced across coil Y in the first 3.0 ms.
- 957237: This is an example question for the example test. You can delete this question.
Topic 12: Quantum and nuclear physics
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.37: Pair production by a photon occurs in the presence of a nucleus. For this process, which of...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
An electron of mass m has an uncertainty in its position r. What is the uncertainty in the speed of this electron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Which of the following, observed during a radioactive-decay experiment, provide evidence for the...
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.4d:
C-14 decay is used to estimate the age of an old dead tree. The activity of C-14 in the dead tree is determined to have fallen to 21% of its original value. C-14 has a half-life of 5700 years.
(i) Explain why the activity of C-14 in the dead tree decreases with time.
(ii) Calculate, in years, the age of the dead tree. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.11a:
A current is observed on the ammeter when violet light illuminates C. With V held constant the current becomes zero when the violet light is replaced by red light of the same intensity. Explain this observation.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.11b:
The graph shows the variation of photoelectric current I with potential difference V between C and A when violet light of a particular intensity is used.
The intensity of the light source is increased without changing its wavelength.
(i) Draw, on the axes, a graph to show the variation of I with V for the increased intensity.
(ii) The wavelength of the violet light is 400 nm. Determine, in eV, the work function of caesium.
(iii) V is adjusted to +2.50V. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons just before they reach A.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The diameter of a silver-108 () nucleus is approximately three times that of the diameter of a nucleus of
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
What can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a particular region of space?
A.
B.
C. The magnitude of the wave function
D. The magnitude of the (wave function)2
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.39: A photon of energy E and wavelength λ is scattered from an electron initially at rest. What is...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.40: Electron capture can be represented by the equation p + e– → X + Y. What are X and Y?
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9a: Explain how each observation provides support for the particle theory but not the wave theory of...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.i:
Determine a value for Planck’s constant.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.ii: State what is meant by the work function of a metal.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.iii: Calculate the work function of barium in eV.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.9c: The experiment is repeated with a metal surface of cadmium, which has a greater work function....
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.37: When monochromatic light is incident on a metallic surface, electrons are emitted from the...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
In the Bohr model for hydrogen an electron in the ground state has orbit radius r and speed v. In the first excited state the electron has orbit radius 4r. What is the speed of the electron in the first excited state?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.39:
A neutron of mass m is confined within a nucleus of diameter d. Ignoring numerical constants, what is an approximate expression for the kinetic energy of the neutron?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
A radioactive element has decay constant (expressed in s–1). The number of nuclei of this element at t = 0 is N. What is the expected number of nuclei that will have decayed after 1 s?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.5b.i:
Deduce that the activity of the radium-226 is almost constant during the experiment.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.5b.ii:
Show that about 3 x 1015 alpha particles are emitted by the radium-226 in 6 days.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
Calculate the wavelength of the light.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.ii: Electrons emitted from the surface of the photocell have almost no kinetic energy. Explain why...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7b:
Radiation of photon energy 5.2 x 10–19 J is now incident on the photocell. Calculate the maximum velocity of the emitted electrons.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.i: Describe the change in the number of photons per second incident on the surface of the photocell.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.7c.ii:
State and explain the effect on the maximum photoelectric current as a result of increasing the photon energy in this way.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.23:
Samples of different radioactive nuclides have equal numbers of nuclei. Which graph shows the relationship between the half-life and the activity A for the samples?
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Monochromatic electromagnetic radiation is incident on a metal surface. The kinetic energy of...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.40: A photon interacts with a nearby nucleus to produce an electron. What is the name of this...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Outline how these experiments are carried out.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Outline why the particles must be accelerated to high energies in scattering experiments.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.3d.ii:
Plot the position of magnesium-24 on the graph.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.3d.iii: Draw a line on the graph, to show the variation of nuclear radius with nucleon number.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
Two radioactive nuclides, X and Y, have half-lives of 50 s and 100 s respectively. At time t = 0 samples of X and Y contain the same number of nuclei.
What is when t = 200 s?
A. 4
B. 2
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.38: According to the Bohr model for hydrogen, visible light is emitted when electrons make...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.39: A particle of fixed energy is close to a potential barrier. Which changes to the width of the...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.40: Alpha particles with energy E are directed at nuclei with atomic number Z. Small deviations from...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iii:
Beryllium-10 is used to investigate ice samples from Antarctica. A sample of ice initially contains 7.6 × 1011 atoms of beryllium-10. The present activity of the sample is 8.0 × 10−3 Bq.
Determine, in years, the age of the sample.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the energy of photons from the UV lamp is about 10 eV.
- 18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Calculate, in J, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Suggest, with reference to conservation of energy, how the variable voltage source can be used to stop all emitted electrons from reaching the collecting plate.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
The variable voltage can be adjusted so that no electrons reach the collecting plate. Write down the minimum value of the voltage for which no electrons reach the collecting plate.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.37: A photoelectric cell is connected in series with a battery of emf 2 V. Photons of energy 6 eV are...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.38: Which of the following is evidence for the wave nature of the electron? A. Continuous energy...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.39: An electron of initial energy E tunnels through a potential barrier. What is the energy of...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
Two samples X and Y of different radioactive isotopes have the same initial activity. Sample X has twice the number of atoms as sample Y. The half-life of X is T. What is the half-life of Y?
A. 2T
B. T
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
Bohr modified the Rutherford model by introducing the condition mvr = n. Outline the reason for this modification.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.ii:
Using the answer in (b) and (c)(i), deduce that the radius r of the electron’s orbit in the ground state of hydrogen is given by the following expression.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9c.iii:
Calculate the electron’s orbital radius in (c)(ii).
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9d.i:
Explain what may be deduced about the energy of the electron in the β– decay.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.9d.iii:
Calculate the wavelength of the gamma ray photon in (d)(ii).
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.37: When green light is incident on a clean zinc plate no photoelectrons are emitted. What change may...
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.38: Which is the correct Feynman diagram for pair annihilation and pair production?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
The graph shows the variation of the natural log of activity, ln (activity), against time for a radioactive nuclide.
What is the decay constant, in days–1, of the radioactive nuclide?
A.
B.
C. 3
D. 6
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.40: A radioactive nuclide is known to have a very long half-life. Three quantities known for a pure...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i: State how the density of a nucleus varies with the number of nucleons in the nucleus.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
Show that the nuclear radius of phosphorus-31 () is about 4 fm.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6c:
undergoes beta-minus (β–) decay. Explain why the energy gained by the emitted beta particles in this decay is not the same for every beta particle.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.6d.i: State what is meant by decay constant.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.6d.ii:
In a fresh pure sample of the activity of the sample is 24 Bq. After one week the activity has become 17 Bq. Calculate, in s–1, the decay constant of .
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.2: A proton has momentum 10-20 N s and the uncertainty in the position of the proton is 10-10 m....
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.i:
Use the graph to show that the nuclear radius of silicon-30 is about 4 fm.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.ii:
Estimate, using the result from (a)(i), the nuclear radius of thorium-232 .
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.iii:
Suggest one reason why a beam of electrons is better for investigating the size of a nucleus than a beam of alpha particles of the same energy.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.2a.iv: Outline why deviations from Rutherford scattering are observed when high-energy alpha particles...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Photons of a certain frequency incident on a metal surface cause the emission of electrons from the surface. The intensity of the light is constant and the frequency of photons is increased. What is the effect, if any, on the number of emitted electrons and the energy of emitted electrons?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.39: Three possible features of an atomic model are I. orbital radius II. quantized energy III....
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.40: Photons of discrete energy are emitted during gamma decay. This is evidence for A. atomic energy...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.38: A metallic surface is first irradiated with infrared radiation and photoelectrons are emitted...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.39:
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 8.0 s. The initial activity of a pure sample of the nuclide is 10 000 Bq. What is the approximate activity of the sample after 4.0 s?
A. 2500 Bq
B. 5000 Bq
C. 7100 Bq
D. 7500 Bq
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.40: A particle is confined within a nucleus. What is the order of magnitude of the uncertainty in the...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.37: An electron of low energy is enclosed within a high potential barrier. What is the process by...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
A beam of monochromatic radiation is made up of photons each of momentum . The intensity of the beam is doubled without changing frequency. What is the momentum of each photon after the change?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.39: Three observations of the behaviour of electrons are I. electron emission as a result of the...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.40:
A pure sample of a radioactive nuclide contains N0 atoms at time t = 0. At time t, there are N atoms of the nuclide remaining in the sample. The half-life of the nuclide is .
What is the decay rate of this sample proportional to?
A. N
B. N0 – N
C. t
D.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8b(i):
Show that the de Broglie wavelength of the electron in the state is m.
The formula for the de Broglie wavelength of a particle is .
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.8b(ii):
Estimate for , the ratio .
State your answer to one significant figure.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.11a(i): does not support the wave nature of light.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.11a(ii): does support the photon nature of light.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.11b(i):
Calculate, in eV, the work function of the metal surface.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.11b(ii):
The intensity of the light incident on the surface is reduced by half without changing the wavelength. Draw, on the graph, the variation of the current with potential after this change.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.37: Monochromatic light is incident on a metal surface and electrons are released. The intensity of...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
The diameter of a nucleus of a particular nuclide X is . What is the nucleon number of X?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
A photon has a wavelength . What are the energy and momentum of the photon?
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.40: The Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden experiment shows that A. alpha particles do not obey Coulomb’s...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Show that the wavelength of an electron in the beam is about .
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): Discuss how the results of the experiment provide evidence for matter waves.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
The accepted value of the diameter of the carbon-12 nucleus is . Estimate the angle at which the minimum of the intensity is formed.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii):
Outline why electrons with energy of approximately would be unsuitable for the investigation of nuclear radii.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
Experiments with many nuclides suggest that the radius of a nucleus is proportional to , where is the number of nucleons in the nucleus. Show that the density of a nucleus remains approximately the same for all nuclei.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.7c: The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 × 109 years. The half-life of thallium-206 is about 4.2...
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.10a: Describe the photoelectric effect.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.10c:
The photoelectrons are emitted from a sodium surface. Sodium has a work function of 2.3 eV.
Calculate the wavelength of the radiation incident on the sodium. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.4a.ii:
The unstable lead nuclide has a half-life of 15 × 106 years. A sample initially contains 2.0 μmol of the lead nuclide. Calculate the number of thallium nuclei being formed each second 30 × 106 years later.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.i: Outline the cause of the electron emission for radiation A.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.ii: Outline why electrons are never emitted for radiation C.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.iii: Outline why radiation B gives different results.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.9b: Explain why there is no effect on the table of results when the intensity of source B is doubled.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.9c:
Photons with energy 1.1 × 10−18 J are incident on a third metal surface. The maximum energy of electrons emitted from the surface of the metal is 5.1 × 10−19 J.
Calculate, in eV, the work function of the metal.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.37: What is a consequence of the uncertainty principle? A. The absorption spectrum of hydrogen atoms...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
In a photoelectric effect experiment, a beam of light is incident on a metallic surface W in a vacuum.
The graph shows how the current varies with the potential difference V when three different beams X, Y, and Z are incident on W at different times.
I. X and Y have the same frequency.
II. Y and Z have different intensity.
III. Y and Z have the same frequency.Which statements are correct?
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.39:
The graphs show the variation with time of the activity and the number of remaining nuclei for a sample of a radioactive nuclide.
What is the decay constant of the nuclide?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.40: What was a reason to postulate the existence of neutrinos? A. Nuclear energy levels had a...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.37:
A particle of energy is incident upon a barrier and has a certain probability of quantum tunnelling through the barrier. Assuming remains constant, which combination of changes in particle mass and barrier length will increase the probability of the particle tunnelling through the barrier?
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Element X has a nucleon number and a nuclear density . Element Y has a nucleon number of . What is an estimate of the nuclear density of element Y?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.39: What is true for the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom? A. Angular momentum of electrons is...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
An electron of non-relativistic speed interacts with an atom. All the energy of the electron is transferred to an emitted photon of frequency . An electron of speed now interacts with the same atom and all its energy is transmitted to a second photon. What is the frequency of the second photon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.10b:
Show that the maximum velocity of the photoelectrons is .
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
In a photoelectric experiment a stopping voltage required to prevent photoelectrons from flowing across the photoelectric cell is measured for light of two frequencies and . The results obtained are shown.
The ratio is an estimate of
A.B.
C.
D.
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.38:
A beam of electrons moving in the direction shown is incident on a rectangular slit of width .
The component of momentum of the electrons in direction after passing through the slit is . The uncertainty in is
A. proportional toB. proportional to
C. proportional to
D. zero
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.39:
Some of the nuclear energy levels of oxygen-14 (14O) and nitrogen-14 (14N) are shown.
A nucleus of 14O decays into a nucleus of 14N with the emission of a positron and a gamma ray. What is the maximum energy of the positron and the energy of the gamma ray?
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.40: The size of a nucleus can be estimated from electron diffraction experiments. What is the order...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.4c.i:
Estimate the power, in kW, that is available from the plutonium at launch.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.4c.ii:
The spacecraft will take 7.2 years (2.3 × 108 s) to reach a planet in the solar system. Estimate the power available to the spacecraft when it gets to the planet.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.4d.i: State and explain what happens to the kinetic energy of an emitted photoelectron.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.4d.ii: State and explain what happens to the rate at which charge leaves the metallic surface.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.37: Three correct statements about the behaviour of electrons are: I. An electron beam is used to...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.38:
Samples of two radioactive nuclides X and Y are held in a container. The number of particles of X is half the number of particles of Y. The half-life of X is twice the half-life of Y.
What is the initial value of ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.39:
The dashed line represents the variation with incident electromagnetic frequency of the kinetic energy EK of the photoelectrons ejected from a metal surface. The metal surface is then replaced with one that requires less energy to remove an electron from the surface.
Which graph of the variation of EK with will be observed?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.40:
Which graph shows a possible probability density function for a given wave function of an electron?
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.i: Identify a property of electrons demonstrated by this experiment.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.9a.iii:
The de Broglie wavelength for an electron is given by . Show that the diameter of an oxygen-16 nucleus is about 4 fm.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.9b:
Estimate, using the result in (a)(iii), the volume of a tin-118 nucleus. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.38:
Light with photons of energy 8.0 × 10−20 J are incident on a metal surface in a photoelectric experiment.
The work function of the metal surface is 4.8 × 10−20 J . What minimum voltage is required for the ammeter reading to fall to zero?
A. 0.2 V
B. 0.3 V
C. 0.5 V
D. 0.8 V
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.39: What is evidence for wave–particle duality? A. Line spectra of elements B. ...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.40:
The decay constant, , of a radioactive sample can be defined as
A. the number of disintegrations in the radioactive sample.
B. the number of disintegrations per unit time in the radioactive sample.
C. the probability that a nucleus decays in the radioactive sample.
D. the probability that a nucleus decays per unit time in the radioactive sample.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.9b.ii:
The half-life of potassium-40 is 1.3 × 109 years. Estimate the age of the rock sample.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.9c:
Outline how the decay constant of potassium-40 was determined in the laboratory for a pure sample of the nuclide.
