DP Physics Questionbank

Topic 11: Electromagnetic induction
Description
Overview of essential ideas for this topic.
11.1: The majority of electricity generated throughout the world is generated by machines that were designed to operate using the principles of electromagnetic induction.
11.2: Generation and transmission of alternating current (ac) electricity has transformed the world.
11.3: Capacitors can be used to store electrical energy for later use.
Directly related questions
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10b:
Electrical power output is produced by several alternating current (ac) generators which use transformers to deliver energy to the national electricity grid.
The following data are available. Root mean square (rms) values are given.
ac generator output voltage to a transformer = 25 kV ac generator output current to a transformer = 3.9 kA Transformer output voltage to the grid = 330 kV Transformer efficiency = 96%(i) Calculate the current output by the transformer to the grid. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
(ii) Electrical energy is often delivered across large distances at 330 kV. Identify the main advantage of using this very high potential difference.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
In an alternating current (ac) generator, a square coil ABCD rotates in a magnetic field.
The ends of the coil are connected to slip rings and brushes. The plane of the coil is shown at the instant when it is parallel to the magnetic field. Only one coil is shown for clarity.
The following data are available.
Dimensions of the coil = 8.5 cm×8.5 cm Number of turns on the coil = 80 Speed of edge AB = 2.0 ms–1 Uniform magnetic field strength = 0.34 T(i) Explain, with reference to the diagram, how the rotation of the generator produces an electromotive force (emf ) between the brushes.
(ii) Calculate, for the position in the diagram, the magnitude of the instantaneous emf generated by a single wire between A and B of the coil.
(iii) Hence, calculate the total instantaneous peak emf between the brushes.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.35: Two capacitors of different capacitance are connected in series to a source of emf of...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.38: A capacitor of capacitance C discharges through a resistor of resistance R. The graph shows...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2e: The magnetic field strength of the Earth is 31 μT at the orbital radius of the satellites. The...
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.i: Describe what happens to the energy stored in the capacitor when the switch is moved to position B.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.33: A conducting ring encloses an area of 2.0 cm2 and is perpendicular to a magnetic field...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The current I flowing in loop A in a clockwise direction is increasing so as to induce a...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The root mean square (rms) current in the primary coil of an ideal transformer is 2.0 A. The rms voltage in the secondary coil is 50 V. The average power transferred from the secondary coil is 20 W.
What is and what is the average power transferred from the primary coil?
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The motor can transfer one-third of the electrical energy stored in the capacitor into gravitational potential energy of the mass. Determine the maximum height through which a mass of 45 g can be raised.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
The arrangement shows four diodes connected to an alternating current (ac) supply. The output is connected to an external circuit.
What is the output to the external circuit?
A. Full-wave rectified current
B. Half-wave rectified current
C. Constant non-zero current
D. Zero current
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
Calculate the energy transferred from capacitor C1.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.35: A conducting bar with vertices PQRS is moving vertically downwards with constant velocity v...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8c: Predict the changes to the graph when the magnet is dropped from a lower height above the coil.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.ii: The plastic film begins to conduct when the electric field strength in it exceeds 1.5 MN C–1....
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
Three identical capacitors are connected in series. The total capacitance of the arrangement is mF. The three capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the capacitance of the parallel arrangement?
A. mF
B. 1 mF
C. 3 mF
D. 81 mF
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.26: The input to a diode bridge rectification circuit is sinusoidal with a time period of 20...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A transformer with 600 turns in the primary coil is used to change an alternating root mean square (rms) potential difference of 240 Vrms to 12 Vrms.
When connected to the secondary coil, a lamp labelled “120 W, 12 V” lights normally. The current in the primary coil is 0.60 A when the lamp is lit.
What are the number of secondary turns and the efficiency of the transformer?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
The graph below shows the variation with time of the magnetic flux through a coil.
Which of the following gives three times for which the magnitude of the induced emf is a maximum?
A. 0, ,
B. 0, , T
C. 0, , T
D. , ,
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A fully charged capacitor is connected to a resistor. When the switch is closed the capacitor...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: The cable between the satellites cuts the magnetic field lines of the Earth at right...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A resistor designed for use in a direct current (dc) circuit is labelled “50 W, 2 Ω”. The resistor is connected in series with an alternating current (ac) power supply of peak potential difference 10 V. What is the average power dissipated by the resistor in the ac circuit?
A. 25 W
B. 35 W
C. 50 W
D. 100 W
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
Calculate in V, the potential difference between the thundercloud and the Earth’s surface.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The graph shows the variation of the peak output power P with time of an alternating current (ac) generator.
Which graph shows the variation of the peak output power with time when the frequency of rotation is decreased?
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7c: An additional identical capacitor is connected in series with the first capacitor and...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
The graph shows the variation of magnetic flux in a coil with time .
What represents the variation with time of the induced emf across the coil?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.34: Which two features are necessary for the operation of a transformer?
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i: Explain why the graph becomes negative.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10b: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, sketch, using an arrow on Diagram 2, the direction...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A capacitor of capacitance 1.0 μF stores a charge of 15 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.35: A capacitor is charged by a constant current of 2.5 μA for 100 s. As a result the potential...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The diagram shows a bar magnet near an aluminium ring. The ring is supported so that it is...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
The voltage output from the generator is stepped up before transmission to the consumer. Estimate the factor by which voltage has to be stepped up in order to reduce power loss in the transmission line by a factor of .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.iii:
The graph shows the variation with time of the charge in the capacitor as it is being discharged through the heart.
Determine the electrical resistance of the closed circuit with the switch in position B.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5a: Explain the role of the diode in the circuit when the switch is at position A.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.iii: Identify, using the label + on the diagram, the polarity of the capacitor.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.33: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a cell of constant emf. The capacitor plates are then...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the distance between the plates.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7e:
Describe the use of transformers in electrical power distribution.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The graph shows the variation with time t of the current I in the primary coil of an ideal...
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
The graph shows the power dissipated in a resistor of 100 Ω when connected to an alternating current (ac) power supply of root mean square voltage (Vrms) 60 V.
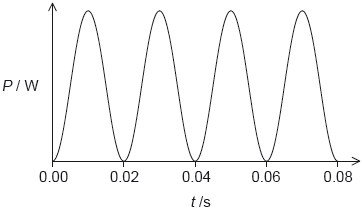
What are the frequency of the ac power supply and the average power dissipated in the resistor?
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.ii:
Determine the peak current in the primary coil when operating with the maximum number of lamps.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.36: Two capacitors of 3 μF and 6 μF are connected in series and charged using a 9 V battery. What...
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Two charges, +Q and −Q, are placed as shown. What is the magnitude of the electric field...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
The input voltage is 240 V. Calculate the output voltage.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
Three conducting loops, X, Y and Z, are moving with the same speed from a region of zero magnetic field to a region of uniform non-zero magnetic field.
Which loop(s) has/have the largest induced electromotive force (emf) at the instant when the loops enter the magnetic field?
A. Z only
B. Y only
C. Y and Z only
D. X and Y only
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.33: What are the units of magnetic flux and magnetic field strength?
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.i: Suggest the advantage of using a step-up transformer in this way.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.ii:
The use of alternating current (ac) in a transformer gives rise to energy losses. State how eddy current loss is minimized in the transformer.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Why are high voltages and low currents used when electricity is transmitted over long...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Explain, by reference to Faraday’s law of induction, how an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the coil.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The plane of a coil is positioned at right angles to a magnetic field of flux density B. The coil has N turns, each of area A. The coil is rotated through 180˚ in time t.
What is the magnitude of the induced emf?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.7b: A pendulum with a metal bob comes to rest after 200 swings. The same pendulum, released from the...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
A magnet connected to a spring oscillates above a solenoid with a 240 turn coil as shown.
The graph below shows the variation with time of the emf across the solenoid with the period, , of the system shown.
The spring is replaced with one that allows the magnet to oscillate with a higher frequency. Which graph shows the new variation with time of the current in the resistor for this new set-up?
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
The graph shows the variation of an alternating current with time in a resistor.
What is the average power dissipated in the resistor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.33: Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
The capacitor is fully charged and the space between the plates is then filled with a dielectric of permittivity ε = 3.0ε0.
Explain whether the magnitude of the charge on plate A increases, decreases or stays constant.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
The capacitor is connected to a 16 V cell as shown.
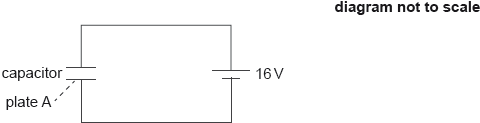
Calculate the magnitude and the sign of the charge on plate A when the capacitor is fully charged.
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Two initially uncharged capacitors X and Y are connected in series to a cell as shown.
What is ?
A.B.
C.
D.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5c.i:
There are 85 turns of wire in the loop. Calculate the maximum induced emf in the loop.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A circuit consists of three identical capacitors of capacitance C and a battery of voltage V. Two...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii: The ammeter is replaced by a coil. Explain why there will be an induced emf in the coil while the...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Suggest one change to the discharge circuit, apart from changes to the coil, that will increase the maximum induced emf in the coil.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
The resistor R in the circuit has a resistance of 1.2 kΩ. Calculate the time taken for the charge on the capacitor to fall to 50 % of its fully charged value.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.34: A coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field. An alternating emf is induced in the coil. What is...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9c:
Suggest why the answers to (a) and (b)(ii) are different.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Calculate, in J, the energy stored in X with the switch S open.
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Which of the following reduces the energy losses in a transformer? A. Using thinner wires for...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The secondary coil of an alternating current (ac) transformer is connected to two diodes as shown.
Which graph shows the variation with time of the potential difference VXY between X and Y?
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A conducting square coil is placed in a region where there is a uniform magnetic field. The...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3a:
The capacitance of the capacitor is 22 mF. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor when it is fully charged.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A direct current (dc) of 5A dissipates a power P in a resistor. Which peak value of the alternating current (ac) will dissipate an average power P in the same resistor?
A. 5A
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8a: State Faraday’s law of induction.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3b:
The resistance of the wire is 8.0 Ω. Determine the time taken for the capacitor to discharge through the resistance wire. Assume that the capacitor is completely discharged when the potential difference across it has fallen to 0.24 V.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
A capacitor of capacitance has initial charge . The capacitor is discharged through a resistor of resistance . The potential difference across the capacitor varies with time.
What is true for this capacitor?
A. After time the potential difference across the capacitor is halved.
B. The capacitor discharges more quickly when the resistance is changed to .
C. The rate of change of charge on the capacitor is proportional to .
D. The time for the capacitor to lose half its charge is .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(iii):
The frequency of the generator is doubled with no other changes being made. Draw, on the axes, the variation with time of the voltage output of the generator.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
Calculate the maximum charge Q0 stored in the capacitor.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
An alternating current (ac) generator produces a peak emf E0 and periodic time T. What are the peak emf and periodic time when the frequency of rotation is doubled?
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.ii:
Show that the charge remaining in the capacitor after a time equal to one time constant of the circuit will be 0.37 Q0.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iv:
Flux leakage is one reason why a transformer may not be ideal. Explain the effect of flux leakage on the transformer.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.36:
A capacitor is charged with a constant current . The graph shows the variation of potential difference across the capacitor with time . The gradient of the graph is . What is the capacitance of the capacitor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.35: The diagram shows a diode bridge rectification circuit and a load resistor. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
In a different circuit, a transformer is connected to an alternating current (ac) supply.
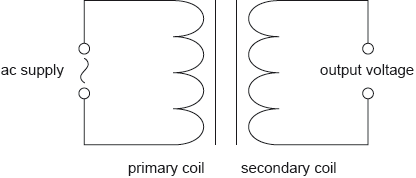
The transformer has 100 turns in the primary coil and 1200 turns in the secondary coil. The peak value of the voltage of the ac supply is 220 V. Determine the root mean square (rms) value of the output voltage.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8a:
Show that the capacitance of this arrangement is C = 6.6 × 10–7 F.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnetic flux linkage in the loop.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A current of 1.0 × 10–3 A flows in the primary coil of a step-up transformer. The number of turns in the primary coil is Np and the number of turns in the secondary coil is Ns. One coil has 1000 times more turns than the other coil.
What is and what is the current in the secondary coil for this transformer?
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.i: Outline how eddy currents reduce transformer efficiency.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
Determine the average emf induced across coil Y in the first 3.0 ms.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4c:
The cell is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor in a vacuum. The fully charged capacitor is then connected to an ideal voltmeter.
The capacitance of the capacitor is 6.0 μF and the reading of the voltmeter is 12 V.
Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10a: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, state why the magnetic flux in the ring is increasing.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.i:
Calculate the total length of aluminium foil that the student will require.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.33: X and Y are two plane coils parallel to each other that have a common axis. There is a constant...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.36: Three capacitors are arranged as shown. What is the total capacitance of the arrangement? A....
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
Six identical capacitors, each of value C, are connected as shown.
What is the total capacitance?
A.
B.
C.
D. 6C
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
The primary coil has 3300 turns. Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iii:
Calculate the current in the primary of the transformer assuming that it is ideal.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
A capacitor of capacitance X is connected to a power supply of voltage V. At time t = 0, the capacitor is disconnected from the supply and discharged through a resistor of resistance R. What is the variation with time of the charge on the capacitor?
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.36: Three capacitors, each one with a capacitance C, are connected such that their...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.i: At t = 0, the switch is connected to X. On the axes, draw a sketch graph to show the variation...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.ii:
The switch is then connected to Y and C discharges through the 20 MΩ resistor. The voltage Vc drops to 50 % of its initial value in 5.0 s. Determine the capacitance of C.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Four identical capacitors of capacitance X are connected as shown in the diagram.
What is the effective capacitance between P and Q?
A.
B. X
C.
D. 4X
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the charge stored on C1 is about 0.04 mC.
- 957237: This is an example question for the example test. You can delete this question.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.36: A diode bridge rectification circuit is constructed as shown. An alternating potential difference...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
Calculate the final total energy, in J, stored in X and Y.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.34: A battery is used to charge a capacitor fully through a resistor of resistance R. The energy...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
Power is dissipated in a resistor of resistance when there is a direct current in the resistor.
What is the average power dissipation in a resistance when the alternating root-mean-square (rms) current in the resistor is ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A rectangular coil rotates at a constant angular velocity. At the instant shown, the plane of the coil is at right angles to the line . A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction .
What rotation of the coil about a specified axis will produce the graph of electromotive force (emf) against time ?
A. Through about
B. Through about
C. Through about
D. Through about
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
The average power output of the generator is . Calculate the root mean square (rms) value of the generator output current.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5d: In practice, two electrodes connect the heart to the circuit. These electrodes introduce an...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
Show that the maximum energy stored by the capacitor is about 160 J.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The conservation of which quantity explains Lenz’s law? A. Charge B. Energy C. Magnetic...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8d:
State one assumption that needs to be made so that the Earth-thundercloud system may be modelled by a parallel plate capacitor.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.34: A rectangular flat coil moves at constant speed through a uniform magnetic field. The direction...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate in J, the energy stored in the system.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.33: A small magnet is released from rest to drop through a stationary horizontal conducting...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the speed of the loop is 20 cm s−1.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.33:
A ring of area S is in a uniform magnetic field X. Initially the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The ring is rotated by 180° about the axis in time T.
What is the average induced emf in the ring?
A. 0
B.
C.
D. - 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7a: The battery has an emf of 7.5 V. Determine the charge that flows through the motor when the mass...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A direct current in a lamp dissipates power P. What root mean square (rms) value of an alternating current dissipates average power P through the same lamp?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Explain why the energy gained by capacitor C2 differs from your answer in (b)(i).
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: Write down the maximum magnitude of the rate of change of flux linked with the coil.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii: Part of the graph is above the t-axis and part is below. Outline why the areas between the t-axis...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4di:
Calculate the change in the energy stored in the capacitor.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.4dii: Suggest, in terms of conservation of energy, the cause for the above change.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A circular coil of wire moves through a region of uniform magnetic field directed out of the...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a battery. What happens when a sheet of dielectric...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Explain, using Faraday’s law of induction, how the transformer steps down the voltage.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8c: Outline how energy losses are reduced in the core of a practical transformer.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8d: Step-up transformers are used in power stations to increase the voltage at which the electricity...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
Calculate the root mean square (rms) current in each cable.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The ratio for a transformer is 2.5.
The primary coil of the transformer draws a current of 0.25 A from a 200 V alternating current (ac) supply. The current in the secondary coil is 0.5 A. What is the efficiency of the transformer?
A. 20 %
B. 50 %
C. 80 %
D. 100 %
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i:
Show that about –11 C of charge is delivered to the Earth’s surface.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.34: An alternating supply is connected to a diode bridge rectification circuit. The conventional...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.37: Three identical capacitors are connected together as shown. What is the order of increasing...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i: The switch is closed at time t = 0. Explain how the voltmeter reading varies after the switch is...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii:
State the fundamental SI unit for your answer to (a)(i).
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10c: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, deduce the direction of the magnetic force on the...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The circuit diagram shows a capacitor that is charged by the battery after the switch is connected to terminal X. The cell has emf V and internal resistance r. After the switch is connected to terminal Y the capacitor discharges through the resistor of resistance R.
What is the nature of the current and magnitude of the initial current in the resistor after the switch is connected to terminal Y?
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
Calculate the final charge on X and the final charge on Y.
Sub sections and their related questions
11.1 – Electromagnetic induction
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.33: What are the units of magnetic flux and magnetic field strength?
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A conducting square coil is placed in a region where there is a uniform magnetic field. The...
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8a: State Faraday’s law of induction.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Explain, using Faraday’s law of induction, how the transformer steps down the voltage.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The diagram shows a bar magnet near an aluminium ring. The ring is supported so that it is...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
Three conducting loops, X, Y and Z, are moving with the same speed from a region of zero magnetic field to a region of uniform non-zero magnetic field.
Which loop(s) has/have the largest induced electromotive force (emf) at the instant when the loops enter the magnetic field?
A. Z only
B. Y only
C. Y and Z only
D. X and Y only
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The plane of a coil is positioned at right angles to a magnetic field of flux density B. The coil has N turns, each of area A. The coil is rotated through 180˚ in time t.
What is the magnitude of the induced emf?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2c: The cable between the satellites cuts the magnetic field lines of the Earth at right...
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2e: The magnetic field strength of the Earth is 31 μT at the orbital radius of the satellites. The...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.33: Two identical circular coils are placed one below the other so that their planes are both...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.33: The current I flowing in loop A in a clockwise direction is increasing so as to induce a...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.34: A rectangular flat coil moves at constant speed through a uniform magnetic field. The direction...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.33:
A ring of area S is in a uniform magnetic field X. Initially the magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. The ring is rotated by 180° about the axis in time T.
What is the average induced emf in the ring?
A. 0
B.
C.
D. - 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10a: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, state why the magnetic flux in the ring is increasing.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10b: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, sketch, using an arrow on Diagram 2, the direction...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.10c: While the magnet is moving towards the ring, deduce the direction of the magnetic force on the...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A circular coil of wire moves through a region of uniform magnetic field directed out of the...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
The graph below shows the variation with time of the magnetic flux through a coil.
Which of the following gives three times for which the magnitude of the induced emf is a maximum?
A. 0, ,
B. 0, , T
C. 0, , T
D. , ,
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.33: X and Y are two plane coils parallel to each other that have a common axis. There is a constant...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.34: A coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field. An alternating emf is induced in the coil. What is...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A rectangular coil rotates at a constant angular velocity. At the instant shown, the plane of the coil is at right angles to the line . A uniform magnetic field acts in the direction .
What rotation of the coil about a specified axis will produce the graph of electromotive force (emf) against time ?
A. Through about
B. Through about
C. Through about
D. Through about
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Explain, by reference to Faraday’s law of induction, how an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the coil.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.7b: A pendulum with a metal bob comes to rest after 200 swings. The same pendulum, released from the...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.33: A conducting ring encloses an area of 2.0 cm2 and is perpendicular to a magnetic field...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The conservation of which quantity explains Lenz’s law? A. Charge B. Energy C. Magnetic...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
A magnet connected to a spring oscillates above a solenoid with a 240 turn coil as shown.
The graph below shows the variation with time of the emf across the solenoid with the period, , of the system shown.
The spring is replaced with one that allows the magnet to oscillate with a higher frequency. Which graph shows the new variation with time of the current in the resistor for this new set-up?
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.33: A small magnet is released from rest to drop through a stationary horizontal conducting...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5a:
Show that the speed of the loop is 20 cm s−1.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnetic flux linkage in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii:
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with time of the magnitude of the emf induced in the loop.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.5c.i:
There are 85 turns of wire in the loop. Calculate the maximum induced emf in the loop.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.35: A conducting bar with vertices PQRS is moving vertically downwards with constant velocity v...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: Write down the maximum magnitude of the rate of change of flux linked with the coil.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii:
State the fundamental SI unit for your answer to (a)(i).
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i: Explain why the graph becomes negative.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii: Part of the graph is above the t-axis and part is below. Outline why the areas between the t-axis...
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.8c: Predict the changes to the graph when the magnet is dropped from a lower height above the coil.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.34:
The graph shows the variation of magnetic flux in a coil with time .
What represents the variation with time of the induced emf across the coil?
- 22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.i: The switch is closed at time t = 0. Explain how the voltmeter reading varies after the switch is...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8c.ii:
Determine the average emf induced across coil Y in the first 3.0 ms.
- 957237: This is an example question for the example test. You can delete this question.
11.2 – Power generation and transmission
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Which of the following reduces the energy losses in a transformer? A. Using thinner wires for...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The secondary coil of an alternating current (ac) transformer is connected to two diodes as shown.
Which graph shows the variation with time of the potential difference VXY between X and Y?
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10b:
Electrical power output is produced by several alternating current (ac) generators which use transformers to deliver energy to the national electricity grid.
The following data are available. Root mean square (rms) values are given.
ac generator output voltage to a transformer = 25 kV ac generator output current to a transformer = 3.9 kA Transformer output voltage to the grid = 330 kV Transformer efficiency = 96%(i) Calculate the current output by the transformer to the grid. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
(ii) Electrical energy is often delivered across large distances at 330 kV. Identify the main advantage of using this very high potential difference.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.10c:
In an alternating current (ac) generator, a square coil ABCD rotates in a magnetic field.
The ends of the coil are connected to slip rings and brushes. The plane of the coil is shown at the instant when it is parallel to the magnetic field. Only one coil is shown for clarity.
The following data are available.
Dimensions of the coil = 8.5 cm×8.5 cm Number of turns on the coil = 80 Speed of edge AB = 2.0 ms–1 Uniform magnetic field strength = 0.34 T(i) Explain, with reference to the diagram, how the rotation of the generator produces an electromotive force (emf ) between the brushes.
(ii) Calculate, for the position in the diagram, the magnitude of the instantaneous emf generated by a single wire between A and B of the coil.
(iii) Hence, calculate the total instantaneous peak emf between the brushes.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.32:
A direct current (dc) of 5A dissipates a power P in a resistor. Which peak value of the alternating current (ac) will dissipate an average power P in the same resistor?
A. 5A
B.
C.
D.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i: Explain, using Faraday’s law of induction, how the transformer steps down the voltage.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
The input voltage is 240 V. Calculate the output voltage.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8c: Outline how energy losses are reduced in the core of a practical transformer.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ1.8d: Step-up transformers are used in power stations to increase the voltage at which the electricity...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6c:
Calculate the root mean square (rms) current in each cable.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.i: Suggest the advantage of using a step-up transformer in this way.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.6e.ii:
The use of alternating current (ac) in a transformer gives rise to energy losses. State how eddy current loss is minimized in the transformer.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The ratio for a transformer is 2.5.
The primary coil of the transformer draws a current of 0.25 A from a 200 V alternating current (ac) supply. The current in the secondary coil is 0.5 A. What is the efficiency of the transformer?
A. 20 %
B. 50 %
C. 80 %
D. 100 %
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
An alternating current (ac) generator produces a peak emf E0 and periodic time T. What are the peak emf and periodic time when the frequency of rotation is doubled?
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.34: The graph shows the variation with time t of the current I in the primary coil of an ideal...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.35: The diagram shows a diode bridge rectification circuit and a load resistor. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
In a different circuit, a transformer is connected to an alternating current (ac) supply.

The transformer has 100 turns in the primary coil and 1200 turns in the secondary coil. The peak value of the voltage of the ac supply is 220 V. Determine the root mean square (rms) value of the output voltage.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7e:
Describe the use of transformers in electrical power distribution.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.35:
The graph shows the power dissipated in a resistor of 100 Ω when connected to an alternating current (ac) power supply of root mean square voltage (Vrms) 60 V.

What are the frequency of the ac power supply and the average power dissipated in the resistor?

-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
The graph shows the variation of the peak output power P with time of an alternating current (ac) generator.
Which graph shows the variation of the peak output power with time when the frequency of rotation is decreased?
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
A current of 1.0 × 10–3 A flows in the primary coil of a step-up transformer. The number of turns in the primary coil is Np and the number of turns in the secondary coil is Ns. One coil has 1000 times more turns than the other coil.
What is and what is the current in the secondary coil for this transformer?
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.i: Outline how eddy currents reduce transformer efficiency.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.2d.ii:
Determine the peak current in the primary coil when operating with the maximum number of lamps.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.26: The input to a diode bridge rectification circuit is sinusoidal with a time period of 20...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A transformer with 600 turns in the primary coil is used to change an alternating root mean square (rms) potential difference of 240 Vrms to 12 Vrms.
When connected to the secondary coil, a lamp labelled “120 W, 12 V” lights normally. The current in the primary coil is 0.60 A when the lamp is lit.
What are the number of secondary turns and the efficiency of the transformer?
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.36: A diode bridge rectification circuit is constructed as shown. An alternating potential difference...
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.33: Why are high voltages and low currents used when electricity is transmitted over long...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.34:
Power is dissipated in a resistor of resistance when there is a direct current in the resistor.
What is the average power dissipation in a resistance when the alternating root-mean-square (rms) current in the resistor is ?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
The average power output of the generator is . Calculate the root mean square (rms) value of the generator output current.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
The voltage output from the generator is stepped up before transmission to the consumer. Estimate the factor by which voltage has to be stepped up in order to reduce power loss in the transmission line by a factor of .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(iii):
The frequency of the generator is doubled with no other changes being made. Draw, on the axes, the variation with time of the voltage output of the generator.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5a: Explain the role of the diode in the circuit when the switch is at position A.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.i:
The primary coil has 3300 turns. Calculate the number of turns on the secondary coil.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iii:
Calculate the current in the primary of the transformer assuming that it is ideal.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.7a.iv:
Flux leakage is one reason why a transformer may not be ideal. Explain the effect of flux leakage on the transformer.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A resistor designed for use in a direct current (dc) circuit is labelled “50 W, 2 Ω”. The resistor is connected in series with an alternating current (ac) power supply of peak potential difference 10 V. What is the average power dissipated by the resistor in the ac circuit?
A. 25 W
B. 35 W
C. 50 W
D. 100 W
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.34:
The graph shows the variation of an alternating current with time in a resistor.
What is the average power dissipated in the resistor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.34: An alternating supply is connected to a diode bridge rectification circuit. The conventional...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.35:
The root mean square (rms) current in the primary coil of an ideal transformer is 2.0 A. The rms voltage in the secondary coil is 50 V. The average power transferred from the secondary coil is 20 W.
What is and what is the average power transferred from the primary coil?
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.34: Which two features are necessary for the operation of a transformer?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.35:
A direct current in a lamp dissipates power P. What root mean square (rms) value of an alternating current dissipates average power P through the same lamp?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
The arrangement shows four diodes connected to an alternating current (ac) supply. The output is connected to an external circuit.
What is the output to the external circuit?
A. Full-wave rectified current
B. Half-wave rectified current
C. Constant non-zero current
D. Zero current
11.3 – Capacitance
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a battery. What happens when a sheet of dielectric...
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.36: Three capacitors are arranged as shown. What is the total capacitance of the arrangement? A....
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.34: A battery is used to charge a capacitor fully through a resistor of resistance R. The energy...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.35: A capacitor is charged by a constant current of 2.5 μA for 100 s. As a result the potential...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.35: Two capacitors of different capacitance are connected in series to a source of emf of...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A fully charged capacitor is connected to a resistor. When the switch is closed the capacitor...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3a:
The capacitance of the capacitor is 22 mF. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor when it is fully charged.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.3b:
The resistance of the wire is 8.0 Ω. Determine the time taken for the capacitor to discharge through the resistance wire. Assume that the capacitor is completely discharged when the potential difference across it has fallen to 0.24 V.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.37:
Six identical capacitors, each of value C, are connected as shown.
What is the total capacitance?
A.
B.
C.
D. 6C
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.38: A capacitor of capacitance C discharges through a resistor of resistance R. The graph shows...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.36: A parallel plate capacitor is connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Calculate the distance between the plates.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
The capacitor is connected to a 16 V cell as shown.

Calculate the magnitude and the sign of the charge on plate A when the capacitor is fully charged.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
The capacitor is fully charged and the space between the plates is then filled with a dielectric of permittivity ε = 3.0ε0.
Explain whether the magnitude of the charge on plate A increases, decreases or stays constant.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.36: Three capacitors, each one with a capacitance C, are connected such that their...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8a:
Show that the capacitance of this arrangement is C = 6.6 × 10–7 F.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.i:
Calculate in V, the potential difference between the thundercloud and the Earth’s surface.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8b.ii:
Calculate in J, the energy stored in the system.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i:
Show that about –11 C of charge is delivered to the Earth’s surface.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.8d:
State one assumption that needs to be made so that the Earth-thundercloud system may be modelled by a parallel plate capacitor.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Four identical capacitors of capacitance X are connected as shown in the diagram.
What is the effective capacitance between P and Q?
A.
B. X
C.
D. 4X
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7a: The battery has an emf of 7.5 V. Determine the charge that flows through the motor when the mass...
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The motor can transfer one-third of the electrical energy stored in the capacitor into gravitational potential energy of the mass. Determine the maximum height through which a mass of 45 g can be raised.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.7c: An additional identical capacitor is connected in series with the first capacitor and...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4c:
The cell is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor in a vacuum. The fully charged capacitor is then connected to an ideal voltmeter.
The capacitance of the capacitor is 6.0 μF and the reading of the voltmeter is 12 V.
Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.4di:
Calculate the change in the energy stored in the capacitor.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.4dii: Suggest, in terms of conservation of energy, the cause for the above change.
- 19M.1.SL.TZ1.20: Two charges, +Q and −Q, are placed as shown. What is the magnitude of the electric field...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.i:
Calculate the total length of aluminium foil that the student will require.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.8a.ii: The plastic film begins to conduct when the electric field strength in it exceeds 1.5 MN C–1....
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
The resistor R in the circuit has a resistance of 1.2 kΩ. Calculate the time taken for the charge on the capacitor to fall to 50 % of its fully charged value.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
Three identical capacitors are connected in series. The total capacitance of the arrangement is mF. The three capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the capacitance of the parallel arrangement?
A. mF
B. 1 mF
C. 3 mF
D. 81 mF
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.36: Two capacitors of 3 μF and 6 μF are connected in series and charged using a 9 V battery. What...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.37:
The circuit diagram shows a capacitor that is charged by the battery after the switch is connected to terminal X. The cell has emf V and internal resistance r. After the switch is connected to terminal Y the capacitor discharges through the resistor of resistance R.
What is the nature of the current and magnitude of the initial current in the resistor after the switch is connected to terminal Y?
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.35: A capacitor of capacitance 1.0 μF stores a charge of 15 μC. The capacitor is discharged through a...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9a:
Calculate, in J, the energy stored in X with the switch S open.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(i):
Calculate the final charge on X and the final charge on Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9b(ii):
Calculate the final total energy, in J, stored in X and Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.9c:
Suggest why the answers to (a) and (b)(ii) are different.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
A capacitor of capacitance has initial charge . The capacitor is discharged through a resistor of resistance . The potential difference across the capacitor varies with time.
What is true for this capacitor?
A. After time the potential difference across the capacitor is halved.
B. The capacitor discharges more quickly when the resistance is changed to .
C. The rate of change of charge on the capacitor is proportional to .
D. The time for the capacitor to lose half its charge is .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.i:
Show that the maximum energy stored by the capacitor is about 160 J.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.ii:
Calculate the maximum charge Q0 stored in the capacitor.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5b.iii: Identify, using the label + on the diagram, the polarity of the capacitor.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.i: Describe what happens to the energy stored in the capacitor when the switch is moved to position B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.ii:
Show that the charge remaining in the capacitor after a time equal to one time constant of the circuit will be 0.37 Q0.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.5c.iii:
The graph shows the variation with time of the charge in the capacitor as it is being discharged through the heart.
Determine the electrical resistance of the closed circuit with the switch in position B.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5d: In practice, two electrodes connect the heart to the circuit. These electrodes introduce an...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.36:
A capacitor of capacitance X is connected to a power supply of voltage V. At time t = 0, the capacitor is disconnected from the supply and discharged through a resistor of resistance R. What is the variation with time of the charge on the capacitor?
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.33: A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a cell of constant emf. The capacitor plates are then...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.36:
A capacitor is charged with a constant current . The graph shows the variation of potential difference across the capacitor with time . The gradient of the graph is . What is the capacitance of the capacitor?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.36:
Two initially uncharged capacitors X and Y are connected in series to a cell as shown.
What is ?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.i: At t = 0, the switch is connected to X. On the axes, draw a sketch graph to show the variation...
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3c.ii:
The switch is then connected to Y and C discharges through the 20 MΩ resistor. The voltage Vc drops to 50 % of its initial value in 5.0 s. Determine the capacitance of C.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.36: A circuit consists of three identical capacitors of capacitance C and a battery of voltage V. Two...
- 22M.1.HL.TZ1.37: Three identical capacitors are connected together as shown. What is the order of increasing...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8a:
Show that the charge stored on C1 is about 0.04 mC.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.i:
Calculate the energy transferred from capacitor C1.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.ii:
Explain why the energy gained by capacitor C2 differs from your answer in (b)(i).
