| Date | May 2021 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | 2 |
| Command term | Show that | Question number | 8 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
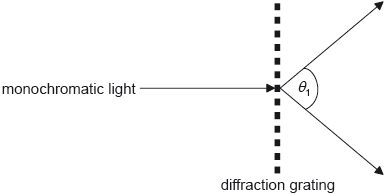
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diagram shows adjacent slits of the diffraction grating labelled V, W and X. Light waves are diffracted through an angle θ to form a second-order diffraction maximum. Points Z and Y are labelled.
State the effect on the graph of the variation of sin θ with n of:
State the phase difference between the waves at V and Y.
State, in terms of λ, the path length between points X and Z.
The separation of adjacent slits is d. Show that for the second-order diffraction maximum .
Monochromatic light of wavelength 633 nm is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diffraction maxima incident on a screen are detected and their angle θ to the central beam is determined. The graph shows the variation of sinθ with the order n of the maximum. The central order corresponds to n = 0.
Determine a mean value for the number of slits per millimetre of the grating.
using a light source with a smaller wavelength.
increasing the distance between the diffraction grating and the screen.
Markscheme
0 OR 2π OR 360° ✓
4λ ✓
✓
Do not award ECF from(a)(ii).
identifies gradient with OR use of ✓
gradient = 0.08 OR correct replacement in equation with coordinates of a point ✓
✓
✓
Allow ECF from MP3
gradient smaller ✓
no change ✓