| Date | May 2021 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 21M.2.HL.TZ1.5 |
| Level | Higher level | Paper | Paper 2 | Time zone | 1 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 5 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
A device sends an impulse of electrical energy to maintain a regular heartbeat in a person. The device is powered by an alternating current (ac) supply connected to a step-up transformer that charges a capacitor of capacitance 30 μF.
The voltage across the primary coil of the transformer is 220 V. The number of turns on the secondary coil is 15 times greater than the number of turns on the primary coil.
The switch is moved to position B.
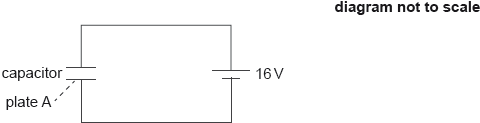
Explain the role of the diode in the circuit when the switch is at position A.
Show that the maximum energy stored by the capacitor is about 160 J.
Calculate the maximum charge Q0 stored in the capacitor.
Identify, using the label + on the diagram, the polarity of the capacitor.
Describe what happens to the energy stored in the capacitor when the switch is moved to position B.
Show that the charge remaining in the capacitor after a time equal to one time constant of the circuit will be 0.37 Q0.
The graph shows the variation with time of the charge in the capacitor as it is being discharged through the heart.
Determine the electrical resistance of the closed circuit with the switch in position B.
In practice, two electrodes connect the heart to the circuit. These electrodes introduce an additional capacitance.
Explain the effect of the electrode capacitance on the discharge time.
Markscheme
to charge a capacitor current must be direct ✓
diode will only allow current to flow in one direction
OR
the diode provides half wave rectification ✓
✓
OR
163 «J» ✓
Allow use of 220 V as an RMS value to calculate Vs = 467 V and E = 327 J for full marks if appropriate work is provided.
Answer must be to 3 or more sf or working shown for MP2
✓
Allow ECF from (b)(i) (Q = 30 μF x V)
labels + on the lower side of the capacitor ✓
the energy stored in the capacitor is delivered to the resistor/heart ✓
✓
ALTERNATIVE 1
reads from the graph ✓
so ✓
ALTERNATIVE 2
reads a correct value from the graph for and ✓
so ✓
«the capacitors are in parallel hence» capacitances are added / more charge is stored
OR
Ceq is larger
OR
electrode capacitor charges and discharges ✓
«therefore» discharge takes longer/increases ✓