DP Physics Questionbank

Topic 9: Wave phenomena
Description
Overview of the essential ideas for this topic.
9.1: The solution of the harmonic oscillator can be framed around the variation of kinetic and potential energy in the system.
9.2: Single-slit diffraction occurs when a wave is incident upon a slit of approximately the same size as the wavelength.
9.3: Interference patterns from multiple slits and thin films produce accurately repeatable patterns.
9.4: Resolution places an absolute limit on the extent to which an optical or other system can separate images of objects.
9.5: The Doppler effect describes the phenomenon of wavelength/frequency shift when relative motion occurs.
Directly related questions
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Monochromatic light is incident on a double slit. Both slits have a finite width. The light then...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating that has a slit separation of . What is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed using this arrangement?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 7
D. 9 - 16N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A diffraction grating is used to observe light of wavelength 400 nm. The light illuminates 100...
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
Airports use radar to track the position of aircraft. The waves are reflected from the aircraft and detected by a large circular receiver. The receiver must be able to resolve the radar images of two aircraft flying close to each other.
The following data are available.
Diameter of circular radar receiver = 9.3 m Wavelength of radar = 2.5 cm Distance of two aircraft from the airport = 31 kmCalculate the minimum distance between the two aircraft when their images can just be resolved.
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6a:
Police use radar to detect speeding cars. A police officer stands at the side of the road and points a radar device at an approaching car. The device emits microwaves which reflect off the car and return to the device. A change in frequency between the emitted and received microwaves is measured at the radar device.
The frequency change Δf is given by
where f is the transmitter frequency, v is the speed of the car and c is the wave speed.
The following data are available.
Transmitter frequency f = 40 GHz Δf = 9.5 kHz Maximum speed allowed = 28 m s–1(i) Explain the reason for the frequency change.
(ii) Suggest why there is a factor of 2 in the frequency-change equation.
(iii) Determine whether the speed of the car is below the maximum speed allowed.
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
A particle is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude x0 and maximum kinetic energy Ek. What is the potential energy of the system when the particle is a distance 0.20x0 from its maximum displacement?
A. 0.20Ek
B. 0.36Ek
C. 0.64Ek
D. 0.80Ek
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
A second identical spring is placed in parallel and the experiment in (b) is repeated. Suggest how this change affects the fractional uncertainty in the mass of the block.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A pendulum oscillating near the surface of the Earth swings with a time period T. What is the...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A train travelling in a straight line emits a sound of constant frequency f. An observer at...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.27: For fringes to be observed in a double-slit interference experiment, the slits must emit waves...
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
A train moving at speed u relative to the ground, sounds a whistle of constant frequency f as it moves towards a vertical cliff face.
The sound from the whistle reaches the cliff face and is reflected back to the train. The speed of sound in stationary air is c.
What whistle frequency is observed on the train after the reflection?
A.
B. (c + u)f
C. (c – u)f
D.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of amplitude xo. Its total energy is 16 J.
What is the kinetic energy of the mass when its displacement is ?
A. 4 J
B. 8 J
C. 12 J
D. 16 J
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.28: Two points illuminated by monochromatic light are separated by a small distance. The light...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
Calculate the mass of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
In carrying out the experiment the student displaced the block horizontally by 4.8 cm from the equilibrium position. Determine the total energy in the oscillation of the wooden block.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Blue light is incident on two narrow slits. Constructive interference takes place along the lines...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Describe the conditions required for an object to perform simple harmonic motion (SHM).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.ii:
Sketch a graph to show the variation with time of the generator output power. Label the time axis with a suitable scale.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i:
Determine the width of one of the slits.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.i:
A wave of amplitude 4.3 m and wavelength 35 m, moves with a speed of 3.4 m s–1. Calculate the maximum vertical speed of the buoy.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii: Suggest the variation in the output voltage from the light sensor that will be observed as the...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelengths of two spectral lines of the light differ by and have a mean wavelength of . The spectral lines are just resolved in the fourth order of the grating. What is the minimum number of grating lines that were illuminated?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.29: White light is incident normally on separate diffraction gratings X and Y. Y has a greater number...
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.27:
A simple pendulum and a mass–spring system oscillate with the same time period. The mass of the pendulum bob and the mass on the spring are initially identical. The masses are halved.
What is when the masses have been changed?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(ii):
Calculate .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The mass of the cylinder is and the cross-sectional area of the cylinder is . The density of water is . Show that the angular frequency of oscillation of the cylinder is about .
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(i): Explain why the frequency recorded by the microphone is lower than the frequency emitted by the...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(ii):
Draw, on the axes, the graph to show how the kinetic energy of the cylinder varies with time during one period of oscillation .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(i):
Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the cylinder.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
Monochromatic light of wavelength passes through a single-slit of width and produces a diffraction pattern on a screen. Which combination of changes to and will cause the greatest decrease in the width of the central maximum?
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Monochromatic light is incident on two identical slits to produce an interference pattern on a...
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State and explain the differences between the pattern on the screen due to the grating and the pattern due to the double slit.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
A transparent liquid forms a parallel-sided thin film in air. The diagram shows a ray I incident on the upper air–film boundary at normal incidence (the rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity).
Reflections from the top and bottom surfaces of the film result in three rays J, K and L. Which of the rays has undergone a phase change of rad?
A. J only
B. J and L only
C. J and K only
D. J, K and L
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.iii:
Calculate the separation of the two slits.
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
A stationary sound source emits waves of wavelength and speed v. The source now moves away from a stationary observer. What are the wavelength and speed of the sound as measured by the observer?
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.ii: Describe the energy changes in the satellite Y-cable system during one cycle of the oscillation.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i:
Explain why zero intensity is observed at position A.
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.27: A spring loaded with mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion. The amplitude of the motion...
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.i:
Estimate the value of k in the following expression.
T =
Give an appropriate unit for your answer. Ignore the mass of the cable and any oscillation of satellite X.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
The distance from the centre of the pattern to A is 4.1 x 10–2 m. The distance from the screen to the slits is 7.0 m.
Calculate the width of each slit.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
The yellow light is made from two very similar wavelengths that produce two lines in the spectrum of sodium. The wavelengths are 588.995 nm and 589.592 nm. These two lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of this diffraction grating. Determine the beam width of the light incident on the diffraction grating.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Explain the condition for w that eliminates reflection for a particular light wavelength in air .
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.i: State the Rayleigh criterion for resolution.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.ii:
The painting contains a pattern of red dots with a spacing of 3 mm. Assume the wavelength of red light is 700 nm. The average diameter of the pupil of a human eye is 4 mm. Calculate the maximum possible distance at which these red dots are distinguished.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
State the phase change when a ray is reflected at B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Calculate, in m s−1, the maximum velocity of vibration of point P when it is vibrating with a frequency of 195 Hz.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.v:
Estimate the displacement needed to double the energy of the string.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii: increasing the distance between the diffraction grating and the screen.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: State the phase difference between the waves at V and Y.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii: State, in terms of λ, the path length between points X and Z.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.iii:
The separation of adjacent slits is d. Show that for the second-order diffraction maximum .
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i: using a light source with a smaller wavelength.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8b:
Monochromatic light of wavelength 633 nm is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diffraction maxima incident on a screen are detected and their angle θ to the central beam is determined. The graph shows the variation of sinθ with the order n of the maximum. The central order corresponds to n = 0.
Determine a mean value for the number of slits per millimetre of the grating.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
The diagram shows the diffraction pattern for light passing through a single slit.
What is
A. 0.01
B. 0.02
C. 1
D. 2
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelength lines 600.0 nm and 601.5 nm are...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.29: On approaching a stationary observer, a train sounds its horn and decelerates at a constant rate....
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.26: Which is correct for the tangential acceleration of a simple pendulum at small amplitudes? A. It...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Light passes through a diffraction grating. Which quantity must be decreased to improve...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass–spring system oscillates vertically with a period of at the surface of the Earth. The gravitational field strength at the surface of Mars is . What is the period of the same mass–spring system on the surface of Mars?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A train is moving in a straight line away from a stationary observer when the train horn emits a sound of frequency . The speed of the train is where is the speed of sound. What is the frequency of the horn as heard by the observer?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iv:
Calculate, in terms of g, the maximum acceleration of P.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A mass at the end of a vertical spring and a simple pendulum perform oscillations on Earth that...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Monochromatic light is incident on 4 rectangular, parallel slits. The first principal maximum is...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.29: Two lines X and Y in the emission spectrum of hydrogen gas are measured by an observer stationary...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3c:
The wavelength of the light in the beam when emitted by the galaxy was 621.4 nm.
Explain, without further calculation, what can be deduced about the relative motion of the galaxy and the Earth.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ in air is incident normally on a thin film of refractive index n. The film is surrounded by air. The intensity of the reflected light is a minimum. What is a possible thickness of the film?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.ii:
Calculate the speed of the block as it passes the equilibrium position.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.i:
Calculate the angular separation between the central peak and the missing peak in the double-slit interference intensity pattern. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.i:
Calculate the time taken for the block to return to the equilibrium position for the first time.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.ii:
Deduce, in mm, the width of one slit.
-
18M.3.HL.TZ1.11b.i:
determine the initial energy.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating of N lines per unit length. The angle between the first orders is θ1.
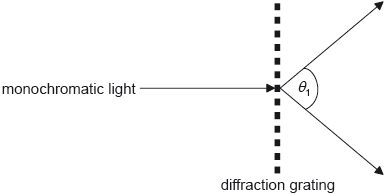
What is the wavelength of the light?
A.
B. N sin θ1
C. N sin
D.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
A train is approaching an observer with constant speed
where c is the speed of sound in still air. The train emits sound of wavelength λ. What is the observed speed of the sound and observed wavelength as the train approaches?
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5c:
The slit separation is increased. Outline one change observed on the screen.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.ii:
Show that the period of oscillation of the ball is about 6 s.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.iii:
The amplitude of oscillation is 0.12 m. On the axes, draw a graph to show the variation with time t of the velocity v of the ball during one period.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5a:
Monochromatic light from two identical lamps arrives on a screen.
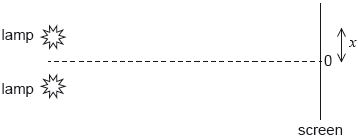
The intensity of light on the screen from each lamp separately is I0.
On the axes, sketch a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity I of light on the screen.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5b:
Monochromatic light from a single source is incident on two thin, parallel slits.
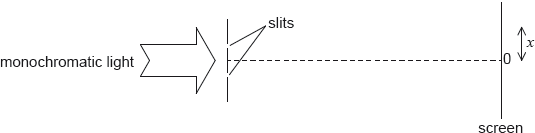
The following data are available.
The intensity I of light at the screen from each slit separately is I0. Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity of light on the screen for this arrangement.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.24: A simple pendulum bob oscillates as shown. ...
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.25: A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a single slit and a diffraction pattern forms on the...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.26: A simple pendulum undergoes simple harmonic motion. The gravitational potential energy of the...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.27: When monochromatic light is incident on a single slit a diffraction pattern forms on a...
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident normally on a thin liquid film of refractive index that is suspended in air. The rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity.
What is the minimum thickness of the film so that the reflected light undergoes constructive interference?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A beam of light containing two different wavelengths is incident on a diffraction grating. The...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Explain why q will perform simple harmonic oscillations when it is released.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Calculate the period of oscillations of q.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.ii: State what will happen to the width of the primary maxima.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
A plate performs simple harmonic oscillations with a frequency of 39 Hz and an amplitude of 8.0 cm.
Show that the maximum speed of the oscillating plate is about 20 m s−1.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.i: State what will happen to the angular position of the primary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.iii: State what will happen to the intensity of the secondary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: State what is meant by the Doppler effect.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
Sound of frequency 2400 Hz is emitted from a stationary source towards the oscillating plate in (b). The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency of the sound that is received back at the source after reflection at the plate.
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii: Calculate the angle between the first-order line of the red light in the hydrogen spectrum and...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a diffraction grating. The grating spacing is d. The angles between the different orders are shown on the diagram.
What is the expression for the wavelength of light used?
A.
B.
C. d sin α
D. d sin β
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.27: The graph shows the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light when monochromatic...
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
The light illuminates a width of 3.5 mm of the grating. The deuterium and hydrogen red lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of the diffraction grating. Show that the grating spacing of the diffraction grating is about 2 × 10–6 m.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
An ambulance siren emits a sound of frequency 1200 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s–1. The ambulance moves towards a stationary observer at a constant speed of 40 m s–1. What is the frequency heard by the observer?
A. Hz
B. Hz
C. Hz
D. Hz
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) has a period T and total energy E. The amplitude of oscillations is halved. What are the new period and total energy of the system?
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.iii: The light source is changed so that white light is incident on the diffraction grating. Outline...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Light of wavelength is diffracted after passing through a very narrow single slit of width . The intensity of the central maximum of the diffracted light is . The slit width is doubled.
What is the intensity of central maximum and the angular position of the first minimum?
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
An observer with an eye of pupil diameter views the headlights of a car that emit light of wavelength . The distance between the headlights is .
What is the greatest distance between the observer and the car at which the images of the headlights will be resolved by the observer’s eye?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
Outline two reasons why both models predict that the motion is simple harmonic when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6d:
The graph shows for model A the variation with of elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring.
Describe the graph for model B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.3d:
Loudspeaker A is switched off. Loudspeaker B moves away from M at a speed of 1.5 m s−1 while emitting a frequency of 3.0 kHz.
Determine the difference between the frequency detected at M and that emitted by B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Determine the time period of the system when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
Outline, without calculation, the change to the time period of the system for the model represented by graph B when is large.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
A simple pendulum has a time period on the Earth. The pendulum is taken to the Moon where the gravitational field strength is that of the Earth.
What is the time period of the pendulum on the Moon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A train is sounding its whistle when approaching a train station. Three statements about the...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
In two different experiments, white light is passed through a single slit and then is either refracted through a prism or diffracted with a diffraction grating. The prism produces a band of colours from M to N. The diffraction grating produces a first order spectrum P to Q.
What are the colours observed at M and P?
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Determine the amplitude of oscillation for test 1.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iv: In test 2, the maximum elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring is 44 J. When t = 0 the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Deduce .
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
The motion sensor operates by detecting the sound waves reflected from the base of the mass. The sensor compares the frequency detected with the frequency emitted when the signal returns.
The sound frequency emitted by the sensor is 35 kHz. The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency change detected by the sensor for test 2.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.3ei:
Calculate the frequency heard by the observer.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Deduce, in W m-2, the intensity at M.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.8cii:
Show that, due to single slit diffraction, the intensity at a point on the screen a distance of 28 mm from M is zero.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8ci: Suggest why, after this change, the intensity at P will be less than that at M.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.i: Calculate, in m, the length of the thread. State your answer to an appropriate number of...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of the object.
What is the velocity of the object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.21: A train approaches a station and sounds a horn of constant frequency and constant intensity. An...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.17: A mass on a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position. Which graph represents the...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.ii:
Label on the graph with the letter X a point where the speed of the pendulum is half that of its initial speed.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.iii:
The mass of the pendulum bob is 75 g. Show that the maximum speed of the bob is about 0.7 m s–1.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iv: The speed after the collision of the bob and the object was measured using a sensor. This sensor...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
The headlights of a car emit light of wavelength 400 nm and are separated by 1.2 m. The headlights are viewed by an observer whose eye has an aperture of 4.0 mm. The observer can just distinguish the headlights as separate images. What is the distance between the observer and the headlights?
A. 8 km
B. 10 km
C. 15 km
D. 20 km
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.22: Two stars are viewed with a telescope using a green filter. The images of the stars are just...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
A transparent liquid film of refractive index 1.5 coats the outside of a glass lens of higher refractive index. The liquid film is used to eliminate reflection from the lens at wavelength λ in air.
What is the minimum thickness of the liquid film coating and the phase change at the liquid–glass interface?
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.29: In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the distance between fringes is too small to be...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
The four pendulums shown have been cut from the same uniform sheet of board. They are attached to the ceiling with strings of equal length.
Which pendulum has the shortest period?
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoes simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude 0. When the displacement of the object is , the speed of the object is . What is the speed when the displacement is 0?
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.29: Sea waves move towards a beach at a constant speed of 2.0 m s–1. They arrive at the beach with a...
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is normally incident on a diffraction grating of spacing 3λ. What is the angle between the two second-order maxima?
A.
B.
C.
D. >90° so no second orders appear
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
calculate the smallest value of d that will result in destructive interference between ray X and ray Y.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): state, in terms of d, the path difference between the reflected rays X and Y.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Light of frequency 500 THz is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern. The...
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(ii):
Estimate, in rad, the smallest angular separation of two distinct point sources of light of wavelength 656 nm that can be resolved by the eye of this observer.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Predict whether reflected ray X undergoes a phase change.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii): discuss a practical advantage of this arrangement.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(i): Draw, on the axes, the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light incident on the...
Sub sections and their related questions
9.1 – Simple harmonic motion
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
A particle is oscillating with simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude x0 and maximum kinetic energy Ek. What is the potential energy of the system when the particle is a distance 0.20x0 from its maximum displacement?
A. 0.20Ek
B. 0.36Ek
C. 0.64Ek
D. 0.80Ek
- 17M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A pendulum oscillating near the surface of the Earth swings with a time period T. What is the...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7a:
Describe the conditions required for an object to perform simple harmonic motion (SHM).
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7b:
Calculate the mass of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7c:
In carrying out the experiment the student displaced the block horizontally by 4.8 cm from the equilibrium position. Determine the total energy in the oscillation of the wooden block.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ1.7d:
A second identical spring is placed in parallel and the experiment in (b) is repeated. Suggest how this change affects the fractional uncertainty in the mass of the block.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass oscillates with simple harmonic motion (SHM) of amplitude xo. Its total energy is 16 J.
What is the kinetic energy of the mass when its displacement is ?
A. 4 J
B. 8 J
C. 12 J
D. 16 J
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.i:
A wave of amplitude 4.3 m and wavelength 35 m, moves with a speed of 3.4 m s–1. Calculate the maximum vertical speed of the buoy.
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.2b.ii:
Sketch a graph to show the variation with time of the generator output power. Label the time axis with a suitable scale.
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.27: A spring loaded with mass m oscillates with simple harmonic motion. The amplitude of the motion...
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.i:
Estimate the value of k in the following expression.
T =
Give an appropriate unit for your answer. Ignore the mass of the cable and any oscillation of satellite X.
- 17N.2.HL.TZ0.2f.ii: Describe the energy changes in the satellite Y-cable system during one cycle of the oscillation.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.26: A mass at the end of a vertical spring and a simple pendulum perform oscillations on Earth that...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.i:
Calculate the time taken for the block to return to the equilibrium position for the first time.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.1e.ii:
Calculate the speed of the block as it passes the equilibrium position.
-
18M.3.HL.TZ1.11b.i:
determine the initial energy.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.24: A simple pendulum bob oscillates as shown. ...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.ii:
Show that the period of oscillation of the ball is about 6 s.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.1d.iii:
The amplitude of oscillation is 0.12 m. On the axes, draw a graph to show the variation with time t of the velocity v of the ball during one period.
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM) has a period T and total energy E. The amplitude of oscillations is halved. What are the new period and total energy of the system?
-
19M.1.HL.TZ2.16:
An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of the object.
What is the velocity of the object?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.17: A mass on a spring is displaced from its equilibrium position. Which graph represents the...
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.i: Calculate, in m, the length of the thread. State your answer to an appropriate number of...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.ii:
Label on the graph with the letter X a point where the speed of the pendulum is half that of its initial speed.
-
19M.2.HL.TZ1.6a.iii:
The mass of the pendulum bob is 75 g. Show that the maximum speed of the bob is about 0.7 m s–1.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
The four pendulums shown have been cut from the same uniform sheet of board. They are attached to the ceiling with strings of equal length.
Which pendulum has the shortest period?
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.26:
An object undergoes simple harmonic motion (shm) of amplitude 0. When the displacement of the object is , the speed of the object is . What is the speed when the displacement is 0?
A. 0
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.27:
A simple pendulum and a mass–spring system oscillate with the same time period. The mass of the pendulum bob and the mass on the spring are initially identical. The masses are halved.
What is when the masses have been changed?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7b:
The mass of the cylinder is and the cross-sectional area of the cylinder is . The density of water is . Show that the angular frequency of oscillation of the cylinder is about .
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(i):
Determine the maximum kinetic energy of the cylinder.
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.7c(ii):
Draw, on the axes, the graph to show how the kinetic energy of the cylinder varies with time during one period of oscillation .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iii:
Calculate, in m s−1, the maximum velocity of vibration of point P when it is vibrating with a frequency of 195 Hz.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.v:
Estimate the displacement needed to double the energy of the string.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.26: Which is correct for the tangential acceleration of a simple pendulum at small amplitudes? A. It...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A mass–spring system oscillates vertically with a period of at the surface of the Earth. The gravitational field strength at the surface of Mars is . What is the period of the same mass–spring system on the surface of Mars?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.8b.iv:
Calculate, in terms of g, the maximum acceleration of P.
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.26: A simple pendulum undergoes simple harmonic motion. The gravitational potential energy of the...
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.i: Explain why q will perform simple harmonic oscillations when it is released.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.3b.ii:
Calculate the period of oscillations of q.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8b:
A plate performs simple harmonic oscillations with a frequency of 39 Hz and an amplitude of 8.0 cm.
Show that the maximum speed of the oscillating plate is about 20 m s−1.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
A simple pendulum has a time period on the Earth. The pendulum is taken to the Moon where the gravitational field strength is that of the Earth.
What is the time period of the pendulum on the Moon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.ii:
Deduce .
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iii:
Determine the amplitude of oscillation for test 1.
- 22M.2.HL.TZ2.6a.iv: In test 2, the maximum elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring is 44 J. When t = 0 the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
Outline two reasons why both models predict that the motion is simple harmonic when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Determine the time period of the system when is small.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6c:
Outline, without calculation, the change to the time period of the system for the model represented by graph B when is large.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.6d:
The graph shows for model A the variation with of elastic potential energy Ep stored in the spring.
Describe the graph for model B.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.7c.ii:
Deduce whether the motion of Z is simple harmonic.
9.2 – Single-slit diffraction
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.iii:
Calculate the separation of the two slits.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ2.25: A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a single slit and a diffraction pattern forms on the...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.8cii:
Show that, due to single slit diffraction, the intensity at a point on the screen a distance of 28 mm from M is zero.
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Light of frequency 500 THz is incident on a single slit and forms a diffraction pattern. The...
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(i): Draw, on the axes, the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light incident on the...
-
21M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
The diagram shows the diffraction pattern for light passing through a single slit.
What is
A. 0.01
B. 0.02
C. 1
D. 2
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.29:
Monochromatic light of wavelength passes through a single-slit of width and produces a diffraction pattern on a screen. Which combination of changes to and will cause the greatest decrease in the width of the central maximum?
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.27: When monochromatic light is incident on a single slit a diffraction pattern forms on a...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
Light of wavelength is diffracted after passing through a very narrow single slit of width . The intensity of the central maximum of the diffracted light is . The slit width is doubled.
What is the intensity of central maximum and the angular position of the first minimum?
9.3 – Interference
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.27: Monochromatic light is incident on a double slit. Both slits have a finite width. The light then...
-
16N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating that has a slit separation of . What is the greatest number of maxima that can be observed using this arrangement?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 7
D. 9 - 17M.1.HL.TZ1.27: For fringes to be observed in a double-slit interference experiment, the slits must emit waves...
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Blue light is incident on two narrow slits. Constructive interference takes place along the lines...
-
17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.i:
Determine the width of one of the slits.
- 17M.2.HL.TZ2.4c.ii: Suggest the variation in the output voltage from the light sensor that will be observed as the...
- 17N.1.HL.TZ0.28: Monochromatic light is incident on two identical slits to produce an interference pattern on a...
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
A transparent liquid forms a parallel-sided thin film in air. The diagram shows a ray I incident on the upper air–film boundary at normal incidence (the rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity).
Reflections from the top and bottom surfaces of the film result in three rays J, K and L. Which of the rays has undergone a phase change of rad?
A. J only
B. J and L only
C. J and K only
D. J, K and L
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.i:
Explain why zero intensity is observed at position A.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6a.ii:
The distance from the centre of the pattern to A is 4.1 x 10–2 m. The distance from the screen to the slits is 7.0 m.
Calculate the width of each slit.
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.i:
State and explain the differences between the pattern on the screen due to the grating and the pattern due to the double slit.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ1.27:
Monochromatic light of wavelength λ in air is incident normally on a thin film of refractive index n. The film is surrounded by air. The intensity of the reflected light is a minimum. What is a possible thickness of the film?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Monochromatic light is incident on 4 rectangular, parallel slits. The first principal maximum is...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.i:
Calculate the angular separation between the central peak and the missing peak in the double-slit interference intensity pattern. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3b.ii:
Deduce, in mm, the width of one slit.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.26:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident on a diffraction grating of N lines per unit length. The angle between the first orders is θ1.

What is the wavelength of the light?
A.
B. N sin θ1
C. N sin
D.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5a:
Monochromatic light from two identical lamps arrives on a screen.

The intensity of light on the screen from each lamp separately is I0.
On the axes, sketch a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity I of light on the screen.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5b:
Monochromatic light from a single source is incident on two thin, parallel slits.

The following data are available.
The intensity I of light at the screen from each slit separately is I0. Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation with distance x on the screen of the intensity of light on the screen for this arrangement.
-
18M.2.HL.TZ2.5c:
The slit separation is increased. Outline one change observed on the screen.
- 18N.1.HL.TZ0.27: The graph shows the variation with diffraction angle of the intensity of light when monochromatic...
-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
A beam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a diffraction grating. The grating spacing is d. The angles between the different orders are shown on the diagram.
What is the expression for the wavelength of light used?
A.
B.
C. d sin α
D. d sin β
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.ii: Calculate the angle between the first-order line of the red light in the hydrogen spectrum and...
- 18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.iii: The light source is changed so that white light is incident on the diffraction grating. Outline...
-
19M.2.HL.TZ2.3ei:
Calculate the frequency heard by the observer.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8a: Deduce, in W m-2, the intensity at M.
- 19M.2.HL.TZ2.8ci: Suggest why, after this change, the intensity at P will be less than that at M.
- 19M.1.HL.TZ1.29: In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the distance between fringes is too small to be...
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
A transparent liquid film of refractive index 1.5 coats the outside of a glass lens of higher refractive index. The liquid film is used to eliminate reflection from the lens at wavelength λ in air.
What is the minimum thickness of the liquid film coating and the phase change at the liquid–glass interface?
-
19N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light of wavelength λ is normally incident on a diffraction grating of spacing 3λ. What is the angle between the two second-order maxima?
A.
B.
C.
D. >90° so no second orders appear
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10a:
Predict whether reflected ray X undergoes a phase change.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(i): state, in terms of d, the path difference between the reflected rays X and Y.
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(ii):
calculate the smallest value of d that will result in destructive interference between ray X and ray Y.
- 19N.2.HL.TZ0.10b(iii): discuss a practical advantage of this arrangement.
- 20N.1.HL.TZ0.29: White light is incident normally on separate diffraction gratings X and Y. Y has a greater number...
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6a:
State the phase change when a ray is reflected at B.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6b:
Explain the condition for w that eliminates reflection for a particular light wavelength in air .
- 21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.i: State the Rayleigh criterion for resolution.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.i: State the phase difference between the waves at V and Y.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.ii: State, in terms of λ, the path length between points X and Z.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8a.iii:
The separation of adjacent slits is d. Show that for the second-order diffraction maximum .
-
21M.2.HL.TZ2.8b:
Monochromatic light of wavelength 633 nm is normally incident on a diffraction grating. The diffraction maxima incident on a screen are detected and their angle θ to the central beam is determined. The graph shows the variation of sinθ with the order n of the maximum. The central order corresponds to n = 0.
Determine a mean value for the number of slits per millimetre of the grating.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.i: using a light source with a smaller wavelength.
- 21M.2.HL.TZ2.8c.ii: increasing the distance between the diffraction grating and the screen.
-
21N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Monochromatic light of wavelength in air is incident normally on a thin liquid film of refractive index that is suspended in air. The rays are shown at an angle to the normal for clarity.
What is the minimum thickness of the film so that the reflected light undergoes constructive interference?
A.B.
C.
D.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.i: State what will happen to the angular position of the primary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.ii: State what will happen to the width of the primary maxima.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8d.iii: State what will happen to the intensity of the secondary maxima.
-
22M.1.HL.TZ2.30:
In two different experiments, white light is passed through a single slit and then is either refracted through a prism or diffracted with a diffraction grating. The prism produces a band of colours from M to N. The diffraction grating produces a first order spectrum P to Q.
What are the colours observed at M and P?
9.4 – Resolution
- 16N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A diffraction grating is used to observe light of wavelength 400 nm. The light illuminates 100...
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6b:
Airports use radar to track the position of aircraft. The waves are reflected from the aircraft and detected by a large circular receiver. The receiver must be able to resolve the radar images of two aircraft flying close to each other.
The following data are available.
Diameter of circular radar receiver = 9.3 m Wavelength of radar = 2.5 cm Distance of two aircraft from the airport = 31 kmCalculate the minimum distance between the two aircraft when their images can just be resolved.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.28: Two points illuminated by monochromatic light are separated by a small distance. The light...
-
17N.2.HL.TZ0.6b.ii:
The yellow light is made from two very similar wavelengths that produce two lines in the spectrum of sodium. The wavelengths are 588.995 nm and 589.592 nm. These two lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of this diffraction grating. Determine the beam width of the light incident on the diffraction grating.
-
18N.2.HL.TZ0.5b.i:
The light illuminates a width of 3.5 mm of the grating. The deuterium and hydrogen red lines can just be resolved in the second-order spectrum of the diffraction grating. Show that the grating spacing of the diffraction grating is about 2 × 10–6 m.
-
19M.1.HL.TZ1.30:
The headlights of a car emit light of wavelength 400 nm and are separated by 1.2 m. The headlights are viewed by an observer whose eye has an aperture of 4.0 mm. The observer can just distinguish the headlights as separate images. What is the distance between the observer and the headlights?
A. 8 km
B. 10 km
C. 15 km
D. 20 km
-
19N.2.HL.TZ0.10c(ii):
Estimate, in rad, the smallest angular separation of two distinct point sources of light of wavelength 656 nm that can be resolved by the eye of this observer.
-
20N.1.HL.TZ0.28:
Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelengths of two spectral lines of the light differ by and have a mean wavelength of . The spectral lines are just resolved in the fourth order of the grating. What is the minimum number of grating lines that were illuminated?
A.
B.
C.
D.
-
21M.2.HL.TZ1.6c.ii:
The painting contains a pattern of red dots with a spacing of 3 mm. Assume the wavelength of red light is 700 nm. The average diameter of the pupil of a human eye is 4 mm. Calculate the maximum possible distance at which these red dots are distinguished.
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.28: Light is incident on a diffraction grating. The wavelength lines 600.0 nm and 601.5 nm are...
- 21M.1.HL.TZ2.27: Light passes through a diffraction grating. Which quantity must be decreased to improve...
- 21N.1.HL.TZ0.29: A beam of light containing two different wavelengths is incident on a diffraction grating. The...
-
22M.1.HL.TZ1.31:
An observer with an eye of pupil diameter views the headlights of a car that emit light of wavelength . The distance between the headlights is .
What is the greatest distance between the observer and the car at which the images of the headlights will be resolved by the observer’s eye?
A.
B.
C.
D.
9.5 – Doppler effect
-
16N.2.HL.TZ0.6a:
Police use radar to detect speeding cars. A police officer stands at the side of the road and points a radar device at an approaching car. The device emits microwaves which reflect off the car and return to the device. A change in frequency between the emitted and received microwaves is measured at the radar device.
The frequency change Δf is given by
where f is the transmitter frequency, v is the speed of the car and c is the wave speed.
The following data are available.
Transmitter frequency f = 40 GHz Δf = 9.5 kHz Maximum speed allowed = 28 m s–1(i) Explain the reason for the frequency change.
(ii) Suggest why there is a factor of 2 in the frequency-change equation.
(iii) Determine whether the speed of the car is below the maximum speed allowed.
-
17M.1.HL.TZ1.28:
A train moving at speed u relative to the ground, sounds a whistle of constant frequency f as it moves towards a vertical cliff face.
The sound from the whistle reaches the cliff face and is reflected back to the train. The speed of sound in stationary air is c.
What whistle frequency is observed on the train after the reflection?
A.
B. (c + u)f
C. (c – u)f
D.
- 17M.1.HL.TZ2.29: A train travelling in a straight line emits a sound of constant frequency f. An observer at...
-
17N.1.HL.TZ0.30:
A stationary sound source emits waves of wavelength and speed v. The source now moves away from a stationary observer. What are the wavelength and speed of the sound as measured by the observer?
- 18M.1.HL.TZ1.29: Two lines X and Y in the emission spectrum of hydrogen gas are measured by an observer stationary...
-
18M.2.HL.TZ1.3c:
The wavelength of the light in the beam when emitted by the galaxy was 621.4 nm.
Explain, without further calculation, what can be deduced about the relative motion of the galaxy and the Earth.
-
18M.1.HL.TZ2.27:
A train is approaching an observer with constant speed
where c is the speed of sound in still air. The train emits sound of wavelength λ. What is the observed speed of the sound and observed wavelength as the train approaches?

-
18N.1.HL.TZ0.29:
An ambulance siren emits a sound of frequency 1200 Hz. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s–1. The ambulance moves towards a stationary observer at a constant speed of 40 m s–1. What is the frequency heard by the observer?
A. Hz
B. Hz
C. Hz
D. Hz
- 19M.2.HL.TZ1.6b.iv: The speed after the collision of the bob and the object was measured using a sensor. This sensor...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.21: A train approaches a station and sounds a horn of constant frequency and constant intensity. An...
- 19M.1.HL.TZ2.22: Two stars are viewed with a telescope using a green filter. The images of the stars are just...
- 19N.1.HL.TZ0.29: Sea waves move towards a beach at a constant speed of 2.0 m s–1. They arrive at the beach with a...
- 20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(i): Explain why the frequency recorded by the microphone is lower than the frequency emitted by the...
-
20N.2.HL.TZ0.4d(ii):
Calculate .
- 21M.1.HL.TZ1.29: On approaching a stationary observer, a train sounds its horn and decelerates at a constant rate....
-
21M.1.HL.TZ2.28:
A train is moving in a straight line away from a stationary observer when the train horn emits a sound of frequency . The speed of the train is where is the speed of sound. What is the frequency of the horn as heard by the observer?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- 21N.2.HL.TZ0.8a: State what is meant by the Doppler effect.
-
21N.2.HL.TZ0.8c:
Sound of frequency 2400 Hz is emitted from a stationary source towards the oscillating plate in (b). The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency of the sound that is received back at the source after reflection at the plate.
- 22M.1.HL.TZ2.31: A train is sounding its whistle when approaching a train station. Three statements about the...
-
22M.2.HL.TZ2.6b:
The motion sensor operates by detecting the sound waves reflected from the base of the mass. The sensor compares the frequency detected with the frequency emitted when the signal returns.
The sound frequency emitted by the sensor is 35 kHz. The speed of sound is 340 m s−1.
Determine the maximum frequency change detected by the sensor for test 2.
-
22M.2.HL.TZ1.3d:
Loudspeaker A is switched off. Loudspeaker B moves away from M at a speed of 1.5 m s−1 while emitting a frequency of 3.0 kHz.
Determine the difference between the frequency detected at M and that emitted by B.
