| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 18M.3.sl.TZ2.2 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Describe | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Organic molecules can be visualized using three-dimensional models built from kits such as that pictured below.
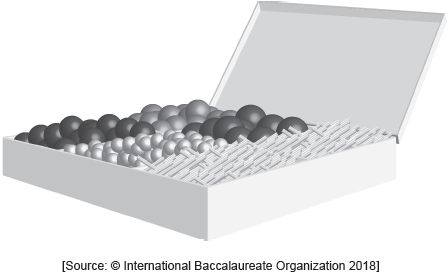
Describe two differences, other than the number of atoms, between the models of ethane and ethene constructed from the kit shown.
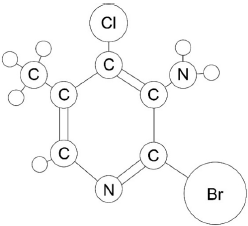
The above ball and stick model is a substituted pyridine molecule (made of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, bromine and chlorine atoms). All atoms are shown and represented according to their relative atomic size.
Label each ball in the diagram, excluding hydrogens, as a carbon, C, nitrogen, N, bromine, Br, or chlorine, Cl.
Suggest one advantage of using a computer generated molecular model compared to a ball and stick 3-D model.
Pyridine, like benzene, is an aromatic compound.
Outline what is meant by an aromatic compound.
Markscheme
Any two of:
Ethene: «carbon–carbon» double bond AND Ethane: «carbon–carbon» single bond
ethene has a shorter carbon–carbon bond «than ethane»
Ethene: planar/two-dimensional/2-D AND Ethane: tetrahedral «carbons»/three-dimensional/3-D
OR
Ethene: each carbon surrounded by three electron domains AND Ethane: each carbon surrounded by four electron domains
OR
different molecular geometries/shapes
rotation about carbon–carbon inhibited/blocked in ethene AND not in ethane
«H–C–C/H–C–H» bond angles different
OR
Ethene: «bond angles approximately» 120° AND Ethane: 109.5/109°
Do not accept “different number of atoms/hydrogens/bonds” etc.
Accept “Ethene: unsaturated AND Ethane: saturated” OR “Ethene: has a double bond AND Ethane: does not” OR “Ethene: two flexible bonds between carbon atoms AND Ethane: one”.
Accept any reasonable physical description of the two different molecular models based on a variety of kits for M1.
For ethene, accept any bond angle in the range 117–122°.
Award [2] if any two of the concepts listed are shown in a correctly labelled or annotated diagram.
Award [1 max] for two correct statements for either molecule but with no comparison given to the other.
Award [1 max] for suitable unlabeled diagrams of both compounds.
[2 marks]
6 carbon atoms labelled in correct positions
both nitrogen atoms labelled in correct positions
bromine AND chlorine atoms labelled in correct positions
[3 marks]
accurate bond angles/lengths can be measured
OR
«using mathematical functions» can calculate expected shapes based on energy minimizations
OR
better visualization of possible bond rotations/conformation/modes of vibration
OR
can visualize macromolecules/proteins/DNA
OR
hydrogen bonding «networks» can be generated/allows intermolecular forces «of attraction» to be simulated
OR
more variety of visualization representations/can observe space filling
OR
can produce an electron density map/electrostatic potential map
OR
once model is generated file can be saved for future use/computer models can be shared globally by scientists
OR
helps design molecules of biological significance/assists in drug design «using libraries»
OR
can predict molecular interactions with solvents/can predict physical properties/can predict spectral data/can examine crystal structures
OR
«often» easier to construct/modify «model»
Accept “precise” for “accurate”.
Accept “computer generated structural representation is normally what is expected in order to be published «in a scientific journal»”.
Accept “easier to see different sizes of atoms/atomic radii”.
[1 mark]
bonds within ring have resonance
OR
contains delocalized «conjugated pi» electrons in ring
There must be reference to a ring or cyclic structure.
Accept “alternating single and double bonds in a ring”.
Accept “ring which shows resonance/delocalization”.
Accept “follows Hückel/4n +2 rule”.
Do not accept “contains one or more benzene rings”.
[1 mark]

