| Date | May 2011 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | State and explain | Question number | 6 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
Alkenes are important starting materials for a variety of products.
State and explain the trend of the boiling points of the first five members of the alkene homologous series.
Describe two features of a homologous series.
Below is a schematic diagram representing some reactions of ethene. The letters A–D represent the organic compounds formed from the reactants and catalysts shown.


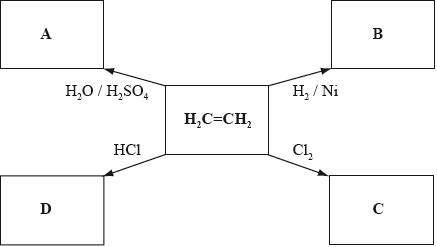
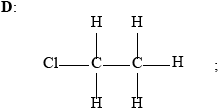
Deduce the structural formulas of compounds A, B, C, and D and state the IUPAC name of compound C.

Describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between pent-1-ene and pentane.
State and explain whether the following molecules are primary, secondary or tertiary halogenoalkanes.
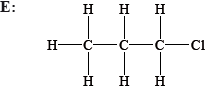
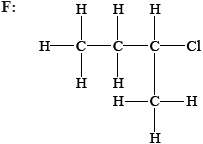
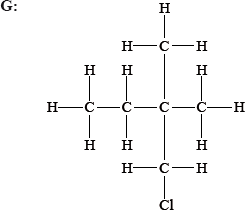
Explain, using equations, the following steps in the free-radical mechanism of the reaction of methane with chlorine.
• Initiation
• Propagation
• Termination
Markscheme
boiling points increase (from the first member to the fifth member);
increasing size of molecule/area of contact/number of electrons (from the first to the fifth member);
strength of intermolecular/van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces increase / more energy required to break the intermolecular bonds (from first member to fifth member);
same general formula;
successive members differ by \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\);
same functional group / similar/same chemical properties;
gradual change in physical properties;
Accept specific physical property such as melting point, boiling point only once.
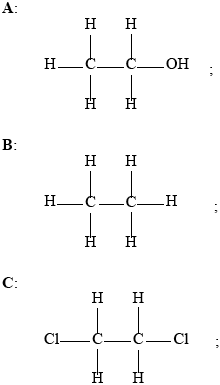
1,2-dichloroethane;
Accept condensed formulas.
Penalize missing hydrogens only once.
add bromine water/bromine;
pentane no change/stays brown and pent-1-ene decolourizes bromine water/bromine;
OR
add acidified \({\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\);
pentane no change/stays purple and pent-1-ene decolourizes acidified \({\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\);
Accept any correct colour change.
Do not accept ‘clear’ instead of ‘colourless’.
E: primary and F: secondary;
G: primary;
G / E: only one alkyl group/2 H atoms attached to the carbon atom attached to the Cl / only one carbon atom attached to the carbon atom attached to the Cl;
F: two alkyl groups/1 H atom attached to the carbon atom attached to the Cl / two carbon atoms attached to the carbon atom attached to the Cl;
Initiation:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{UV}}/h/f/hv/heat}}{\text{2Cl}} \bullet \);
Reference to UV/hf/hν/heat must be included.
Propagation:
\({\text{Cl}} \bullet + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet + {\text{HCl}}\);
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{Cl}} + {\text{Cl}} \bullet \);
Termination:
\({\text{Cl}} \bullet + {\text{Cl}} \bullet \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ / C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet + {\text{ Cl}} \bullet \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{Cl / C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \bullet \to {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_6}\);
Allow representation of radical without \( \bullet \) (e.g. Cl, CH3) if consistent throughout mechanism.
If representation of radical (i.e. \( \bullet \)) is inconsistent, penalize once only.
Examiners report
Although this was the least popular Section B question it tended to be well done by those candidates who attempted it. Part (a) was generally well answered with most candidates able to achieve at least 2 out of the 3 marks. Candidates could state the trend in melting points of the first five members of the alkenes but did not always explain the trend thoroughly.
In part (b) candidates tended to be careless with the use of terminology and used structural or molecular formula rather than general formula when describing a feature of a homologous series. Many candidates also stated that compounds in a homologous series differ by \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)-group but it is successive members that differ by the \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)-group. Greater care in the use of chemical terminology is needed.
The structures in part (c) were well deduced but some candidates were very careless with naming compound C, not taking care with IUPAC nomenclature.
In part (d) candidates were able to identify the bromine test for distinguishing between the alkane and alkene but often did not correctly identify the colour change associated with pent-1-ene and incorrectly suggested that the colour of the bromine changed to clear when it should be colourless.
Part (e) was well done with the exception of identifying structure G as a primary halogenoalkane. Many candidates incorrectly identified it as a tertiary halogenalkane.
Candidates were able to explain with equations the free radical mechanism for the reaction between methane and chlorine. Candidates could only achieve the mark for the initiation step if reference was made to UV with the correct equation. Occasionally candidates incorrectly showed ions rather than radicals in the equations.

