| Date | May 2013 | Marks available | 2 | Reference code | 13M.3.hl.TZ2.D3 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ2 |
| Command term | Identify and State | Question number | D3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
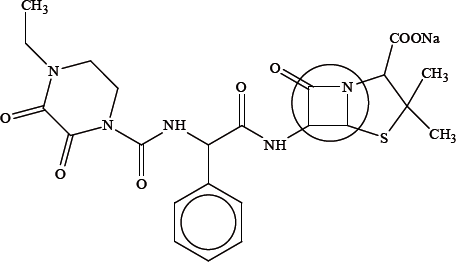
The structure of a drug is shown below:
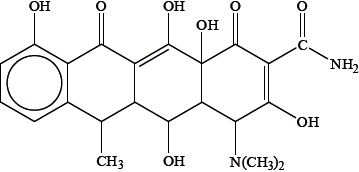
Another drug that can have a similar effect to the one shown in (a) is doxycycline, shown below.
Identify the class of drugs to which this particular drug belongs.
Explain the high reactivity of the part of the drug that is enclosed in the circle.
Suggest why the drug is administered as its sodium salt.
Because it contains several –OH groups and an amine group, doxycycline is slightly polar. Identify the amine group by drawing a circle around it on the structure above and state whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
Suggest one way in which the polarity of doxycycline could be substantially increased.
Deduce the number of chiral carbon atoms in doxycycline and explain why chirality is important when considering its action in the body.
Markscheme
penicillin(s)/antibacterial(s)/antibiotic;
(\(\beta \)-lactam) ring is strained;
Accept stressed.
sp3 and sp2 hybridization;
bond angles are 90° / less than 120° and 109.5° / OWTTE;
(the sodium salt) makes the penicillin ionic/more polar;
this increases its solubility in water/more concentrated in bloodstream / makes it more able to be absorbed by the body / OWTTE;
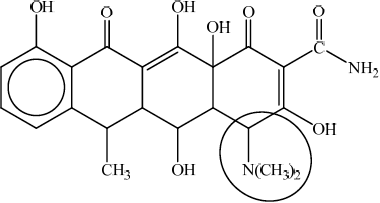 ;
;
Circle must go around the N atom (joined to the two CH3 groups) and not include more than the two CH3 groups and the carbon atom in the ring directly bonded to it.
Accept a circle around the –N(CH3)2 without including the carbon atom of the ring.
tertiary;
M2 can only be awarded if M1 is correct.
react with hydrochloric acid/any other named strong acid / convert the amine group into a salt/ammonium ion/its hydrochloride/any other named product;
Accept amino for amine group.
react with sodium hydroxide/\({\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }\) / convert a phenolic/OH group on the benzene ring/ into a phenoxide ion/sodium salt;
six/6;
The different enantiomers/isomers may have different physiological/pharmacological effects on the body / one enantiomer benefits the body, the other might not / OWTTE;
Accept a specific example such as thalidomide.
Accept one enantiomer could have a toxic effect.
Do not allow just “has different effects”.
Examiners report
Part a) (i) was very well answered overall.
In a) (ii) while many candidates showed familiarity with the \(\beta \)-lactam ring, not as many were able to convey arguments that allowed them to score.
Good candidates achieved at least one mark in a) iii) for the increase in polarity although often answers for this question were vague and just referenced an increase in solubility’ without specifying ‘in water’. The reason for converting the drug into a sodium salt was often incorrectly linked to digestion as opposed to making the molecule more polar.
A fair number of candidates incorrectly circled the NH2 group of the amide group and classified this as a primary amine.
Many had difficulty explaining how to make the drug more polar in b) ii).
Most candidates obtained second mark in this question and very few identified the correct number of chiral carbons.

