| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about ethene, C2H4, and ethyne, C2H2.
Ethyne, like ethene, undergoes hydrogenation to form ethane. State the conditions required.
Outline the formation of polyethene from ethene by drawing three repeating units of the polymer.
Under certain conditions, ethyne can be converted to benzene.
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHϴ, for the reaction stated, using section 11 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(g)
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, for the following similar reaction, using ΔHf values in section 12 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(l)
Explain, giving two reasons, the difference in the values for (b)(i) and (ii). If you did not obtain answers, use −475 kJ for (i) and −600 kJ for (ii).
One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown.
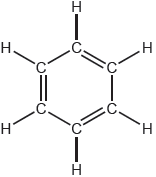
State one piece of physical evidence that this structure is incorrect.
State the characteristic reaction mechanism of benzene.
Markscheme
nickel/Ni «catalyst»
high pressure
OR
heat
Accept these other catalysts: Pt, Pd, Ir, Rh, Co, Ti.
Accept “high temperature” or a stated temperature such as “150 °C”.
[2 marks]
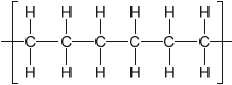
Ignore square brackets and “n”.
Connecting line at end of carbons must be shown.
[1 mark]
ΔHϴ = bonds broken – bonds formed
«ΔHϴ = 3(C≡C) – 6(C=C)benzene/3 × 839 – 6 × 507 / 2517 – 3042 =»
–525 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for +525 «kJ»
Award [1 max] for:
«ΔHϴ = 3(C≡C) – 3(C–C) – 3(C=C) / 3 × 839 – 3 × 346 – 3 × 614 / 2517 – 2880 =» –363 «kJ».
[2 marks]
ΔHΘ = ΣΔHf(products) – ΣΔHf(reactants)
«ΔHΘ = 49 kJ – 3 × 228 kJ =» –635 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for “+635 «kJ»”.
[2 marks]
ΔHf values are specific to the compound
OR
bond enthalpy values are averages «from many different compounds»
condensation from gas to liquid is exothermic
Accept “benzene is in two different states «one liquid the other gas»“ for M2.
[2 marks]
equal C–C bond «lengths/strengths»
OR
regular hexagon
OR
«all» C–C have» bond order of 1.5
OR
«all» C–C intermediate between single and double bonds
Accept “all C–C–C bond angles are equal”.
[1 mark]
electrophilic substitution
OR
SE
[1 mark]
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.27: Which structural formula represents a secondary halogenoalkane? A. ...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.4a: State the names of two functional groups in D-fructose.
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.35: What is the name of...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8c: Clomifene, a fertility drug, whose three-dimensional structure is represented below, also has...
- 13M.3.hl.TZ2.D3b.i: Because it contains several –OH groups and an amine group, doxycycline is slightly polar....
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9a.i: Draw the structural formulas of the two geometrical isomers of 1-chloro-but-2-ene.
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9a.ii: Explain why 1-chloro-but-2-ene shows geometrical isomerism.
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.26: How many structural isomers exist with the formula...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.5f.iv: State the type of hybridization of the carbon and nitrogen atoms in...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.1a: State the names of the three organic functional groups in aspirin.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6a: State and explain the trend of the boiling points of the first five members of the alkene...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.26: Which organic molecule is not a structural isomer of pentan-1-ol? A. pentan-2-ol B. ...
- 12M.1.hl.TZ2.32: What is the name of...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.20a: Compare and contrast the functional groups present in methadone and diamorphine (heroin),...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: State the typical reactions that benzene and cyclohexene undergo with bromine.
- 17M.3.sl.TZ1.10b.i: Describe the difference in their structures.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.24: What is the order of increasing boiling point? A. C4H10 < CH3COOH < CH3CH2CHO <...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.28: How many structural isomers of C6H14 exist? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
- 259336: This is an example question for the example test. You can delete this question.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.26: Applying IUPAC rules, what is the name of...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7e: Compound C can be oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to form compound F. (i) ...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.36: Which functional groups are present in...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.5b: Deduce the structural formula of two isomers of the molecule above with the same functional...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7b: Describe what is meant by the term structural isomers.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.vii: Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of this product, S.
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.27: Which compound is not an isomer of hexane? A. ...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.ii: State the meaning of the term structural isomers.
- 10M.3.sl.TZ1.G3b: Explain how the reaction of benzene with bromine provides chemical evidence that benzene does...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ1.35: What is the IUPAC name for...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.2a: Calculate the value for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethene obtained using the average...
- 09M.1.hl.TZ2.38: What is the IUPAC name of the compound...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which is a tertiary halogenoalkane? A. ...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.10a: State the IUPAC name for leucine.
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.24: Which alcohols are oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution when heated? A....
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.26: What is the name of the compound with this molecular structure applying IUPAC rules? A. ...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.ii: The mass and 1H\(\,\)NMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons,...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.ii: The mass and 1H NMR spectra of product X are shown below. Deduce, giving your reasons, its...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.36: Which compounds can be reduced? I. C2H4II. CH3COOHIII. CH3CHO A. I and II...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.6b: Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.i: Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react...
- 17M.3.hl.TZ2.20a.iii: Suggest two absorbances, other than the absorbances due to the ring structure and C–H bonds,...
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.34: Which is a secondary alcohol?
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.29: In which pair are both compounds secondary?
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which properties are features of a homologous series? I. Same general formula II. ...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ2.28: Which compound is an isomer of octane,...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.9a: Apply IUPAC rules to state the names of the four compounds.
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.6a: Draw the structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene.
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.25: What is the name of the following molecule applying IUPAC rules? A. ...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8d.i: Draw any two other isomers of P.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.4b.i: Deduce the full structural formula for both compounds, showing all the bonds...
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.6e.i: Apply IUPAC rules to name the ester, CH3COOCH2CH3(aq).
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which statement about a homologous series is correct? A. Members of the series differ by...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.5f: (i) Deduce the structural formula of each isomer. (ii) Identify the isomer from part...
- 10N.3.sl.TZ0.G1: (a) Describe the structure of benzene, C6H6. (b) State two pieces of evidence that...
- 10M.2.hl.TZ1.7a: Below are four structural isomers with molecular formula...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.7a.v: Identify the class of alcohols that propan-2-ol belongs to and state the name of the organic...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.ii: Based on its \({K_{\text{a}}}\) value, state and explain whether benzoic acid is a strong or...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.28: Which of the following are isomers of pentane? I. 2-methylpentane II. ...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.29: Which of the following pairs are members of the same homologous series? A. ...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: Describe two features of a homologous series.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6d: Describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between pent-1-ene and pentane.
- 12M.1.sl.TZ2.26: Consider the compound...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.6d.i: Compare the formation of sigma (\(\sigma \)) and pi (\(\pi \)) bonds between the carbon atoms...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.9b.i: State the IUPAC names of each of the compounds, D, E, F and G. D: E: F: G:
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.5a: (i) State the term that is used to describe molecules that are related to each other in the...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.6a: Discuss the physical evidence for the structure of benzene.
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.6c.i: One possible product, X, of the reaction of ethane with chlorine has the...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which compound contains a secondary carbon atom? A. CH3CH(Cl)CH(CH3)2 B. ...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.24: Which functional group is present in paracetamol? A. Carboxyl B. Amino C. ...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.v: Identify one organic functional group that can react with acidified K2Cr2O7(aq).
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.ii: Identify the functional group that shows stretching at 1710 cm–1 in the infrared spectrum of...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which are structural isomers? I. CH3CH2OH and CH3OCH3 II. HOCH2CH3...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.7a: The Kekulé structure of benzene suggests it should readily undergo addition reactions. ...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ2.2a: Describe two differences, other than the number of atoms, between the models of ethane and...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.7b: \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\) exists as three isomers. Identify the...
- 14M.3.hl.TZ2.3e: Y is an isomer of X, which contains the same functional groups. Deduce the structural formula...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6a: Applying IUPAC rules, state the name of A.
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6g.ii: State the homologous series to which D belongs.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8a.i: Outline three features of a homologous series.
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.iii: X is an isomer of C4H8 and has the structural formula shown below. Apply IUPAC rules to...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6b.i: Draw the ester functional group.
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.27: Which order is correct when the following substances are arranged in order of increasing...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: Ethanol is part of the homologous series of alcohols. Describe two features of a homologous...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.6c: (i) Below are four structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.2a.i: State the equation for the reaction of propanoic acid with water.
- 09M.3.sl.TZ1.D1c.i: Identify the amine functional group in the morphine molecule below by drawing a ring around...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6c: Below is a schematic diagram representing some reactions of ethene. The letters A–D represent...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.27: Which of the structures below is an aldehyde? A. ...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.7a: (i) State the meaning of the term isomers. (ii) Deduce the structural formulas of...
- 11N.2.hl.TZ0.9b.iv: Discuss the volatility of E compared to F.
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which molecule contains an ester group? A. ...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Deduce the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of butan-1-ol.
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Compound B is related to compound A. (i) State the term that is used to describe molecules...
- 16M.3.sl.TZ0.8b: (i) State the name of the functional group circled in the DHEA molecule shown below. (ii)...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.5a: Draw the full structural formulas of propane and propene.
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.23: The structure of a drug used to treat symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is shown below. Which...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ1.7c: State the reagents used to convert benzene to nitrobenzene and the formula of...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5a: Ethane, C2H6, reacts with chlorine in sunlight. State the type of this reaction and the name...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7a.iii: Suggest the structural formula of this compound.
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the name of this compound, using IUPAC rules? A. 3-methylbutan-3-ol B....
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.24: Which compounds belong to the same homologous series? A. CHCCH2CH3, CHCCH2CH2CH3 B. ...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.39: What is the structural formula of the ester formed by reacting propanoic acid with...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ1.34: What is the IUPAC name for...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.26: Which statement is correct for members of the same homologous series? A. They have the...
- 14M.3.sl.TZ2.20b: State one piece of chemical evidence proving benzene does not contain alternate single and...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.9b: (i) Define the term structural isomers. (ii) Identify the two compounds in the...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.5a: Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of this molecule.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8c.iii: Deduce whether C4H9Br is a primary or tertiary halogenoalkane.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8c.iv: Determine the structural formula of C4H9Br.
- 13M.3.sl.TZ1.A1a: Draw the two possible structures of compound P.
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.26: Which three compounds can be considered to be a homologous series? A. ...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.ii: Draw a circle around each of these two functional groups in the structure above and label...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.i: Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of P.
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which of the following substances are structural isomers of each other? I. ...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.2a: State the name of the alkene shown.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.7a.iv: Propan-2-ol is an isomer of propan-1-ol. Draw the structure of propan-2-ol.
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.1a: Identify the organic functional group present in both vegetable oil and biodiesel.
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.27: What is the IUPAC name for...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.iii: Determine the hydrogen ion concentration and the pH of a...
- 11M.3.sl.TZ2.D2b.i: State the name of the functional group circled on the structure of caffeine.
- 12M.3.sl.TZ1.G1: The structure of benzene originally described by August Kekulé is shown below. Explain,...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.5a: (i) Distinguish between the terms empirical formula and molecular formula. Empirical...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.24: ...
- 16M.3.hl.TZ0.26a: Identify the functional group circled in the structure of oseltamivir.
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.9b: The structures of two molecules, X and Y, are shown below. (i) Justify why both these...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.1b: Determine the average oxidation state of carbon in ethene and in...
- 17M.3.sl.TZ1.15b: Deduce the formula of the biodiesel formed when the vegetable oil shown is reacted with the...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5c.i: One possible product, X, of the reaction of ethane with chlorine has the...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7c.i: State the reagents and the name of the mechanism for the nitration of benzene.
- 17N.1.hl.TZ0.38: Which functional group is responsible for the pKb of 4.1 in this compound? A. Amido B....
- 18M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.iii: Pyridine, like benzene, is an aromatic compound. Outline what is meant by an aromatic compound.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.5c: Identify the homologous series to which ethanol belongs and state two features of a...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.4a: State two features of a homologous series.
- 14M.3.sl.TZ2.3e: (i) Deduce the structural formula of Y. (ii) Predict one difference between the...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the name of the alkane shown in the diagram below, applying IUPAC rules? A. ...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.7b: (i) Define the term structural isomers. (ii) Identify the two compounds in the...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the name of...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.3a: Identify the name of the functional group circled in the structure of carboplatin.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8d.vi: Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of this product, U.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8d.ii: Apply IUPAC rules to state the names of all the straight-chain isomers of compounds of...
- 10N.1.hl.TZ0.37: Which compound is an amide? A. CH3COOCH3 B. CH3CONH2 C. CH3NH2 D. ...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.2c: Identify the structural formula of an isomer of but-2-ene which does not decolourize bromine...
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9c.i: State whether this reaction is SN1 or SN2.
- 09M.2.hl.TZ1.3b: Determine the value for the enthalpy of hydrogenation of ethene using the values for the...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.26: Which three compounds can be considered to be a homologous series? A. ...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.i: Ethanol to ethyl ethanoate.
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.28: What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A. 2-methylbutane B. ...
- 12M.3.hl.TZ2.D3d: (i) Identify the \(\beta \)-lactam ring by drawing a circle around it. (ii) Explain...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4d: Based on the types of intermolecular force present, explain why butan-1-ol has a higher...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.7a: One example of a homologous series is the alcohols. Describe two features of a homologous...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.ii: State the reagents and reaction conditions used to convert X to Y and X to Z. X to Y: X to Z:
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.2c: The other monomer used in the production of polyurethane is compound Z shown below. (i)...
- 17M.3.sl.TZ1.10b.ii: Explain why the difference in their structures affects their melting points.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5d: Chloroethene, C2H3Cl, can undergo polymerization. Draw a section of the polymer with three...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.6a: Using relevant equations, show the initiation and the propagation steps for this reaction.
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.6b: The overall equation for monochlorination of methane is: CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) +...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.9b.i: Hydrogenation of propene produces propane. Calculate the standard entropy change, ΔS θ, for...
- 17M.3.hl.TZ2.3c.iii: Subsequent steps proceed under differing conditions, forming the dendrimer polymer with the...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.25: What is the name of this compound, using IUPAC rules? A. 1,1-dimethylpropanoic...
- 18M.3.sl.TZ2.2b.i: The above ball and stick model is a substituted pyridine molecule (made of carbon, hydrogen,...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10a.ii: Apply IUPAC rules to name compound A.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.27: Applying IUPAC rules, what is the name of the compound? A. ...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.ii: Apply IUPAC rules to name compound A.
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Deduce the empirical formula of D-fructose.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.3a.ii: State the name of the compound formed that is responsible for this decreased pH value.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.i: Identify the names of two functional groups present in cortisone. 1. 2.
- 09M.1.hl.TZ1.34: Identify the functional group present in...
- 09M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.i: Calculate the \({K_{\text{a}}}\) value of benzoic acid,...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.i: State the name of one structural isomer of pentane.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.25: What are the functional groups in the aspirin...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ1.27: Which molecule has a tertiary nitrogen? A. (CH3)2NH B. (C2H5)4N+I− C. ...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ2.37: In which order should the reagents be used to convert benzene into phenylamine (aniline)?
- 17M.3.sl.TZ2.10a: Identify the functional groups which are present in only one structure of glucose.
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.iii: Deduce the name of the class of compound formed when the product of (c)(i) reacts with...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10e: Compound C, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{OH}}\), can be oxidized by...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.3a: State a balanced equation for the complete combustion of nonane.
- 14M.3.sl.TZ2.20a: Describe the structure of benzene.
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.7a: Apply IUPAC rules to state the name of compound 1.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.i: Outline three features of a homologous series.
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.26: How many non-cyclic structural isomers exist with the molecular formula...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.27: What is the name of the following compound applying IUPAC rules? A. ...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.ii: X is a straight-chain structural isomer of P. Draw the structure of X.
- 09N.2.hl.TZ0.9a.iii: Draw the structural formula of one isomer of...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.4a.i: Identify the boiling points for each of the isomers A, B and C and state a reason for your...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.i: Draw four structural isomers of molecular formula...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ1.G3a: Describe two different types of physical evidence which show that benzene does not contain...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.27: What is the structural formula of 2,3-dibromo-3-methylhexane? A. ...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4c: Determine the standard enthalpy change, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\),...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.i: The IUPAC name of X is 4-methylpentan-1-ol. State the IUPAC names of Y and Z. Y: Z:
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.23: ...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.4a: (i) State the name, applying IUPAC rules, of compound A. (ii) Draw a section, showing three...
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.2b: One important industrial use of phosgene is the production of polyurethanes. Phosgene is...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.35: What is the major product of the reaction between 2-methylbut-2-ene and hydrogen bromide? A....
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3d: One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown. State one piece of physical evidence...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ2.9a.i: Deduce the structural formulas of the two possible isomers.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.24: What are possible names of a molecule with molecular formula C4H10O? I. ...

