| Date | May 2018 | Marks available | 1 | Reference code | 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ1 |
| Command term | State | Question number | 3 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
This question is about ethene, C2H4, and ethyne, C2H2.
Ethyne, like ethene, undergoes hydrogenation to form ethane. State the conditions required.
Outline the formation of polyethene from ethene by drawing three repeating units of the polymer.
Under certain conditions, ethyne can be converted to benzene.
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHϴ, for the reaction stated, using section 11 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(g)
Determine the standard enthalpy change, ΔHΘ, for the following similar reaction, using ΔHf values in section 12 of the data booklet.
3C2H2(g) → C6H6(l)
Explain, giving two reasons, the difference in the values for (b)(i) and (ii). If you did not obtain answers, use −475 kJ for (i) and −600 kJ for (ii).
One possible Lewis structure for benzene is shown.
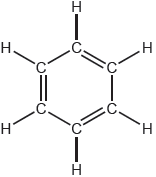
State one piece of physical evidence that this structure is incorrect.
State the characteristic reaction mechanism of benzene.
Markscheme
nickel/Ni «catalyst»
high pressure
OR
heat
Accept these other catalysts: Pt, Pd, Ir, Rh, Co, Ti.
Accept “high temperature” or a stated temperature such as “150 °C”.
[2 marks]
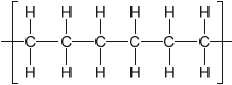
Ignore square brackets and “n”.
Connecting line at end of carbons must be shown.
[1 mark]
ΔHϴ = bonds broken – bonds formed
«ΔHϴ = 3(C≡C) – 6(C=C)benzene/3 × 839 – 6 × 507 / 2517 – 3042 =»
–525 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for +525 «kJ»
Award [1 max] for:
«ΔHϴ = 3(C≡C) – 3(C–C) – 3(C=C) / 3 × 839 – 3 × 346 – 3 × 614 / 2517 – 2880 =» –363 «kJ».
[2 marks]
ΔHΘ = ΣΔHf(products) – ΣΔHf(reactants)
«ΔHΘ = 49 kJ – 3 × 228 kJ =» –635 «kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for “+635 «kJ»”.
[2 marks]
ΔHf values are specific to the compound
OR
bond enthalpy values are averages «from many different compounds»
condensation from gas to liquid is exothermic
Accept “benzene is in two different states «one liquid the other gas»“ for M2.
[2 marks]
equal C–C bond «lengths/strengths»
OR
regular hexagon
OR
«all» C–C have» bond order of 1.5
OR
«all» C–C intermediate between single and double bonds
Accept “all C–C–C bond angles are equal”.
[1 mark]
electrophilic substitution
OR
SE
[1 mark]
Examiners report
Syllabus sections
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3a.ii: Outline the formation of polyethene from ethene by drawing three repeating units of the polymer.
- 17N.3.sl.TZ0.8b.i: State the type of reaction occurring during the titration.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.6b: Explain, with the help of equations, the mechanism of the free-radical substitution reaction...
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.ii: State the observation expected for each reaction giving your reasons.
- 17N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.i: Deduce the type of chemical reaction and the reagents used to distinguish between these...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.27: Which type of reaction occurs between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid? A. Addition B....
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.25: Which compound can be oxidized when heated with an acidified solution of...
- 17N.1.sl.TZ0.24: What is the major product of the reaction between HCl and but-2-ene? A....
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.ii: The aldehyde can be further oxidized to a carboxylic acid. Outline how the experimental...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.i: Formulate the ionic equation for the oxidation of propan-1-ol to the corresponding aldehyde...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ2.26: What is the mechanism for the reaction of propene with iodine in the dark? A. ...
- 18M.2.sl.TZ1.3a.i: Ethyne, like ethene, undergoes hydrogenation to form ethane. State the conditions required.
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.27: Which compound could be formed when CH3CH2CH2OH is heated with acidified potassium...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.26: Which of these reactions proceeds by a free radical mechanism in the presence of UV...
- 18M.1.sl.TZ1.25: What is the product of the reaction between hex-3-ene and steam? A. Hexan-1-ol B. ...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.7c.i: State the organic product of the reaction between 1-chlorobutane, CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl, and aqueous...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3b: Ethyne reacts with chlorine in a similar way to ethene. Formulate equations for the following...
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3a.ii: Outline the formation of polyethene from ethene by drawing three repeating units of the polymer.
- 18M.2.hl.TZ1.3a.i: Ethyne, like ethene, undergoes hydrogenation to form ethane. State the conditions required.
- 18M.1.hl.TZ2.35: Which is the correct combination of substitution reaction mechanisms?
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.40: Which would be the most effective method to distinguish between liquid propan-1-ol and...
- 18M.1.hl.TZ1.33: Which monomer could create this polymer? A. But-2-ene B. But-1-ene C. ...
- 17M.3.hl.TZ2.3c.ii: Suggest, giving one reason, whether this is an addition or condensation reaction.
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.ii: Deduce the structural formula of the main organic product when hex-1-ene reacts with hydrogen...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.7b.i: Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.6b: The overall equation for monochlorination of methane is: CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) +...
- 17M.2.hl.TZ2.2a.v: Identify one organic functional group that can react with acidified K2Cr2O7(aq).
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.6c: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer with the following structure. State the structural...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.6b: Bromine was added to hexane, hex-1-ene and benzene. Identify the compound(s) which will react...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ2.6a: Using relevant equations, show the initiation and the propagation steps for this reaction.
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.26: Which conditions are used to convert ethanol to ethanal? A. Excess oxidizing agent and...
- 17M.1.sl.TZ2.25: Which describes the reaction between a halogen and ethane?
- 17M.3.hl.TZ1.9a: Deduce the repeating unit of the polymer and the other product of the reaction.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: State the typical reactions that benzene and cyclohexene undergo with bromine.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.6a: Discuss the physical evidence for the structure of benzene.
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5d: Chloroethene, C2H3Cl, can undergo polymerization. Draw a section of the polymer with three...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5b: Formulate equations for the two propagation steps and one termination step in the formation...
- 17M.2.sl.TZ1.5a: Ethane, C2H6, reacts with chlorine in sunlight. State the type of this reaction and the name...
- 17M.1.hl.TZ1.35: What is the major product of the reaction between 2-methylbut-2-ene and hydrogen bromide? A....
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.17b: Oseltamivir does not possess the carboxyl group needed for activity until it is chemically...
- 16N.3.sl.TZ0.2b: In trial 3, the students noticed that after heating, the crucible had turned black on the...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.5b: Both propane and propene react with bromine. (i) State an equation and the condition...
- 16N.2.sl.TZ0.1d: Ethane-1,2-diol can be oxidized first to ethanedioic acid, (COOH)2, and then to carbon...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.26: Which type of reaction occurs when methanol and propanoic acid react together in the presence...
- 16N.1.sl.TZ0.25: Which monomer is used to form the polymer with the following repeating unit? A....
- 16M.2.hl.TZ0.5a: (i) State the term that is used to describe molecules that are related to each other in the...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Compound B is related to compound A. (i) State the term that is used to describe molecules...
- 16M.2.sl.TZ0.4a: (i) State the name, applying IUPAC rules, of compound A. (ii) Draw a section, showing three...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.26: What is the mechanism of the reaction between ethane and chlorine in...
- 16M.1.sl.TZ0.25: Which compound can both be esterified and turn acidified potassium dichromate(VI)...
- 15M.1.hl.TZ1.35: What is the product of the addition of chlorine, \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\), to...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.5a: State an equation for the formation of ethanol from ethene and the necessary reaction...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.5d: State the equation for the acid-catalysed reaction of ethanol with propanoic acid and state...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6a: State the equation for the reaction between methane and bromine to form bromomethane.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6b.i: Explain, using equations, the complete free-radical mechanism for the reaction of methane...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.6b.ii: Bromomethane reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide. State the organic product of this reaction.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ1.7a.i: Ethanol is a primary alcohol that can be oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI)....
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10a.i: Deduce the full structural formula of compound A.
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10a.iii: Describe the colour change observed when excess but-2-ene reacts with bromine to form...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10b: (i) Outline two reasons why the polymerization of alkenes is of economic...
- 15M.2.hl.TZ2.10g: Deduce the equation for the complete combustion of compound C.
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.24: Which species can oxidize ethanol to ethanoic acid? A. \({{\text{I}}^ - }\) B. ...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.28: Which statements about the chlorine free radical are correct? I. It has 18...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.29: Which statement is correct about the polymerization of ethene to poly(ethene)? A. The...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ1.26: Which compound could be X in the two-stage reaction...
- 15M.1.sl.TZ2.28: Which statements are correct for the reaction of ethene with bromine in the absence of...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.2a: State the equation for the reaction between methane and bromine to form bromomethane.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.2b: Explain, using equations, the complete free-radical mechanism for the reaction of methane...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.5a: (i) State an equation for the formation of ethanol from ethene and the necessary reaction...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.i: Deduce the full structural formula of compound A.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7g.ii: Deduce the equation for the complete combustion of compound C.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ1.7c.i: Ethanol is a primary alcohol that can be oxidized by acidified potassium dichromate(VI)....
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.4b: Ethane, a member of the homologous series of alkanes, can react with bromine. Explain the...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.iii: Describe the colour change observed when excess but-2-ene reacts with bromine to form...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7b: State the names of the reagents D and E.
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7c: (i) Outline two reasons why the polymerization of alkenes is of economic...
- 15M.2.sl.TZ2.7d: Compound C, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{9}}}{\text{OH}}\), can also be formed...
- 14M.1.hl.TZ2.39: What is the structural formula of the ester formed by reacting propanoic acid with...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.4a: State the conditions necessary for this reaction.
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.6a: Alcohols with the molecular formula...
- 14M.2.hl.TZ1.8d.i: Deduce the mechanism for the reaction using equations and curly arrows to represent the...
- 14M.1.sl.TZ1.29: For the reaction pathway below, what are the names for the first and second...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.6b: (i) Deduce the oxidation number of chromium in...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.7d: (i) Identify the reagent necessary for this reaction to occur. (ii) Deduce the...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ1.7f: Bromoethene, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHBr}}\), can undergo polymerization....
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.3b: Combustion also often forms carbon and carbon monoxide. Outline what reaction conditions...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.3c: (i) State the type of polymerization that occurs. (ii) Draw the structure of a...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6b: State the reagent required to convert A into B.
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6c: (i) State the conditions required for this reaction to occur. (ii) Outline why it...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6e: A can also be converted into C without going via B. State the reagent and conditions required.
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6f: (i) State why C is not readily oxidized by acidified potassium...
- 14M.2.sl.TZ2.6g.i: State the conditions required for this reaction to occur.
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.34: Which product is formed when bromine water is added to propene,...
- 14N.1.hl.TZ0.36: Which of these repeating units is present in the polymer poly(propene)?
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.9c: (i) Determine the organic product formed when each of the compounds is heated under...
- 14N.2.hl.TZ0.9f: (i) Pentanoic acid reacts with ethanol. State the structural formula of the organic...
- 14N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which equation represents a propagation step in the reaction of methane with bromine? A. ...
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.4d: State a balanced equation for the complete combustion of D-fructose.
- 14N.2.sl.TZ0.7c: Determine the organic product formed when each of the compounds is heated under reflux with...
- 14N.3.sl.TZ0.26d: Propanone could also be formed from propene by reaction with steam over an acidic catalyst,...
- 13N.1.hl.TZ0.39: What is the organic product of the reaction between butan-1-ol and ethanoic acid on heating...
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8a: State the other substances required to convert 2-methylbut-2-ene to 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
- 13N.2.hl.TZ0.8b: Explain whether you would expect 2-methylbutan-2-ol to react with acidified potassium...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.27: What is the function of the ultraviolet light used in the reaction between ethane and...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.2c: Traces of butane, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{10}}}}\), are also found...
- 13N.1.sl.TZ0.29: Which organic product forms in the following...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.2a: Complete the overall equation for this reaction by stating the...
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.2b: State the type of mechanism by which this reaction occurs.
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.6b: State the other substances required to convert 2-methylbut-2-ene to 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
- 13N.2.sl.TZ0.6c: Explain whether you would expect 2-methylbutan-2-ol to react with acidified potassium...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.ii: Describe a test to distinguish but-2-ene from butane, including what is observed in each case.
- 13M.2.hl.TZ1.9a.iii: 2-bromobutane can be produced from but-2-ene. State the equation of this reaction using...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.27: Which steps are involved in the free-radical mechanism of the bromination of ethane in the...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ1.28: Which substance can be polymerized to produce the polymer below? A. But-1-ene B. ...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.5c: Describe, using an equation, the oxidation by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) of the...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8a.ii: Describe a test to distinguish ethene from ethane, including what is observed in each case.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8a.iii: Bromoethane can be produced either from ethene or from ethane. State an equation for each...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8b.i: State the equation for the reaction of...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ1.8c.v: Describe, using an equation, how...
- 13M.1.hl.TZ2.33: What are possible products of the incomplete combustion of propan-2-ol? A. carbon...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8d.iii: State the structural formula of the organic products, Q, R, S and T, formed in the following...
- 13M.2.hl.TZ2.8d.v: State the structural formula of the organic product formed, U, when R is heated under reflux...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.28: What are possible products of the incomplete combustion of propane? A. carbon monoxide,...
- 13M.1.sl.TZ2.29: Which equation represents a propagation step in the mechanism for the reaction between...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.3a.ii: State the name of the compound formed that is responsible for this decreased pH value.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.iv: Draw the structure of poly(chloroethene) showing two repeating units.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iii:
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.iv: Identify a suitable catalyst used in the reaction to form R.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.v: P, CH3CH=CHCH3, reacts with HBr to form CH3CHBrCH2CH3. Suggest one suitable mechanism for the...
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.viii: P can undergo a polymerization reaction. Draw two repeating units of the resulting polymer.
- 13M.2.sl.TZ2.7c.vi: State the structural formula of the organic product formed, S, when Q is heated under reflux...
- 12N.2.hl.TZ0.1f.iii: One important use of chlorine is in the synthesis of poly(chloroethene), PVC. Identify the...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.iv: State the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of X with HBr to form Y.
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.vii: Deduce the structural formula of the organic product formed when Z is oxidized by heating...
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which compound would decolourize bromine water in the dark? A. ...
- 12N.1.sl.TZ0.29: Some methane gas is burned in a limited supply of oxygen. Which products could form? I. ...
- 12N.2.sl.TZ0.6a.v: Y reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq), to form an alcohol, Z. Identify whether Z...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.2c: Identify the structural formula of an isomer of but-2-ene which does not decolourize bromine...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.2d: (i) Outline two reasons why the polymers of the alkenes are of economic importance. (ii)...
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.5c: State the reagent and conditions needed for reaction 1.
- 10N.2.hl.TZ0.5d: Reaction 1 involves a free-radical mechanism. Describe the stepwise mechanism, by giving...
- 10N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which monomer could be used to form a polymer with the following repeating unit? A. ...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.2b: Bromine water, Br2(aq), can be used to distinguish between the alkanes and the alkenes. (i)...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.2c: (i) Outline two reasons why the polymers of the alkenes are of economic importance. (ii)...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.4e: State the name of the product and identify the type of reaction which occurs between ethene...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.5d: Reaction 1 involves a free-radical mechanism. Describe the stepwise mechanism, by giving...
- 10N.2.sl.TZ0.5c: (i) State the reagent and conditions needed for reaction 1. (ii) State the...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.34: Which reaction occurs via a free-radical mechanism? A. ...
- 09N.1.hl.TZ0.38: What is the name of the ester formed when...
- 09N.1.sl.TZ0.28: Which substance is not produced during the combustion of alkanes? A. ...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Both \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}\) and...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7a.i: State an equation for the reaction of...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.ii: On reaction with acidified potassium dichromate(VII), two of the isomers are oxidised in two...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.iii: A third isomer is oxidized in one step. Draw the structural formula of the organic product...
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.v: Identify the isomer which resists oxidation by acidified potassium dichromate(VI).
- 09N.2.sl.TZ0.7b.iv: State the colour change that takes place in these oxidation reactions.
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.3a.ii: Draw a section of poly(chloroethene) containing six carbon atoms.
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.3b.ii: State the reagents and conditions necessary to prepare ethanoic acid from ethanol in the...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ1.6c: (i) Below are four structural isomers of alcohols with molecular formula...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ1.G2b: (i) bromine. (ii) hydrogen bromide.
- 10M.3.sl.TZ1.G2a: Explain how a bromine molecule is able to act as an electrophile.
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.28: What happens when a few drops of bromine water are added to excess hex-1-ene and the mixture...
- 10M.1.sl.TZ2.29: What is the product of the following...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.7a.i: The reaction of alkenes with bromine water provides a test for unsaturation in the...
- 10M.2.sl.TZ2.7c: (i) Deduce the structural formulas of the two alcohol isomers of molecular formula...
- 10M.3.sl.TZ2.G2: Hydrolysis of aliphatic and aromatic halides occurs under different conditions. State an...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.28: When bromine water is shaken with a liquid organic compound, it is rapidly decolourized. What...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ1.29: Which conditions are required to obtain a good yield of a carboxylic acid when ethanol is...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ1.7a.iii: When propan-1-ol is oxidized using a warm acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI) two...
- 09M.3.sl.TZ1.D3b.i: Describe the colour change of potassium dichromate(VI) when it reacts with ethanol.
- 09M.1.hl.TZ2.33: What structural feature must a molecule have in order to undergo addition...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.29: Which equations represent the incomplete combustion of methane? I. ...
- 09M.1.sl.TZ2.26: What is the product of the oxidation of butan-2-ol? A. But-2-ene B. Butanoic...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.vi: Ethene can be converted into ethanol by direct hydration in the presence of a catalyst...
- 09M.2.sl.TZ2.6a.iv: Ethanol can be oxidized using acidified potassium dichromate,...
- 11M.1.hl.TZ1.36: What is the correct order of reaction types in the following sequence?
- 11M.2.hl.TZ1.7b: Deduce an equation for the reaction between propanoic acid and methanol. Identify the...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6e: State and explain whether the following molecules are primary, secondary or tertiary...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ1.26: Which of the following statements about alkenes is not correct? A. They have reactive...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6c: Below is a schematic diagram representing some reactions of ethene. The letters A–D represent...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6f: Explain, using equations, the following steps in the free-radical mechanism of the reaction...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ1.6d: Describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between pent-1-ene and pentane.
- 11M.1.hl.TZ2.38: Which reactants could be used to form the compound below? A. Butanoic acid and...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.v: Explain why it is necessary to carry out the reaction under acidic conditions.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.i: Describe the colour change that will be observed in the reaction.
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.iv: Deduce the half-equation for the oxidation of ethanol to ethanal and hence the overall redox...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.7d.vi: Identify the organic product formed if excess potassium dichromate is used and the reaction...
- 11M.2.hl.TZ2.8b.v: The product \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{11}}}}{\text{OH}}\) formed from the...
- 11M.1.sl.TZ2.28: What product is formed when...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.ii: Both propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol can be oxidized in aqueous solution by potassium...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.i: State the equation for the complete combustion of...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.7b.iii: State the name(s) and structure(s) of the organic product(s) that can be formed when each of...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6b.i: State the conditions necessary for the hydrogenation reaction to occur.
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.i: Describe a chemical test that could be used to distinguish between propane and propene. In...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.ii: Under certain conditions propene can polymerize to form poly(propene). State the type of...
- 11M.2.sl.TZ2.6c.iii: Other than polymerization, state one reaction of alkenes which is of economic importance.
- 12M.2.hl.TZ2.10a.i: State the names of two organic compounds required to produce ethyl methanoate and state...
- 12M.2.hl.TZ2.10b.iii: State and explain how the rate of step II would differ if 2-chlorobutane was used instead of...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.5a: (i) Distinguish between the terms empirical formula and molecular formula. Empirical...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.7b: (i) Explain why alkanes have low reactivity. (ii) Outline the meaning of the term...
- 12M.2.sl.TZ2.7c: (i) Identify a suitable catalyst for this reaction. (ii) But-2-ene can be converted...
- 12M.3.sl.TZ2.F2b: Describe how an oil can be converted into a fat.
- 11N.1.hl.TZ0.34: Which compound is produced in the reaction between but-2-ene and steam? A. ...
- 11N.1.hl.TZ0.36: Which compound is the major product of the reaction when 1-bromobutane is heated with...
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.28: From which monomer is this polymer made?
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.25: Which equation represents the initiation reaction when methane reacts with chlorine in the...
- 11N.1.sl.TZ0.29: What is the organic product of the reaction between 2-chlorobutane and sodium hydroxide...
- 11N.2.sl.TZ0.4b: Deduce the balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of butan-1-ol.

