| Date | November 2010 | Marks available | 6 | Reference code | 10N.2.hl.TZ0.2 |
| Level | HL | Paper | 2 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Deduce, Explain, Outline, and State | Question number | 2 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
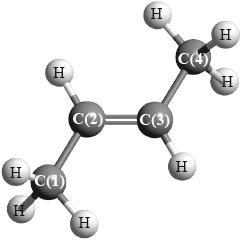
But-2-ene is a straight-chain alkene with formula \({{\text{C}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}\). The molecule contains both \(\sigma \) and \(\pi \) bonds.
The polymerization of the alkenes is one of the most significant reactions of the twentieth century.
(i) Explain the formation of the \(\pi \) bond.
(ii) For each of the carbon atoms, C(1) and C(2), identify the type of hybridization shown.
C(1):
C(2):
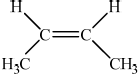
But-2-ene shows geometrical isomerism. Draw the structural formula and state the name of the other geometrical isomer.
Identify the structural formula of an isomer of but-2-ene which does not decolourize bromine water, Br2(aq).
(i) Outline two reasons why the polymers of the alkenes are of economic importance.
(ii) State the type of polymerization reaction shown by the alkene in part (a).
(iii) Deduce the structure of the resulting polymer showing three repeating units.
(iv) Explain why monomers are often gases or volatile liquids, but polymers are solids.
Markscheme
(i) (bond formed by) sideways overlap;
(of) p orbitals;
Marks awarded either from sketch or from explanation.
(ii) C(l) is sp3 and C(2) is sp2;
 ;
;
cis but-2-ene/Z-but-2-ene;
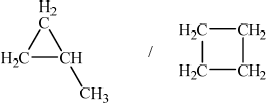 ;
;
(i) synthesis of materials not naturally available/plastics;
chemically unreactive materials produced;
wide range of uses/physical properties / versatile;
cheap;
large industry;
uses a limited natural resource;
Award [2] for any two.
(ii) addition;
(iii) 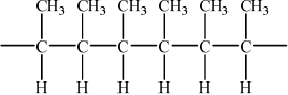 ;
;
Must show continuation bonds.
Ignore bracket around the 6 carbons.
Must have 6 carbons joined to each other along chain.
(iv) monomers are smaller molecules / have smaller surface area than polymers;
Accept monomers have lower molecular mass.
with weaker intermolecular/Van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces;
Accept opposite argument for polymers.
Examiners report
This question was generally well answered and many high scores were seen. Most candidates were able to explain the formation of \(\pi \) bonds in (a) and identify the type of hybridization present.
Many candidates drew structures which were not geometric isomers in (b) with but-1-ene a common incorrect answer.
In (c) only the best candidates were able to identify a cycloalkane as a saturated isomer and it was fairly common to find structures that included double bonds despite the guidance in the question.
The economic importance of addition polymers was well known in (d) with most candidates stating that they were plastics with versatile properties and low cost.
Addition polymerisation was well recalled but a large number of candidates made mistakes with the structure of the polymer. Continuation bonds, for example, were often missing from the ends. Many understood in terms of molecular size, why polymers have higher boiling points than monomers but not all correctly attributed it to the stronger van der Waals forces between the molecules.

