| Date | November 2014 | Marks available | 3 | Reference code | 14N.3.sl.TZ0.26 |
| Level | SL | Paper | 3 | Time zone | TZ0 |
| Command term | Explain | Question number | 26 | Adapted from | N/A |
Question
The cumene process is used for the production of both propanone and phenol. The overall reaction is shown in the equation below.
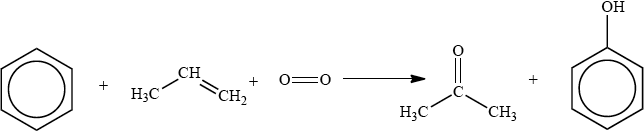
This process is important in the polymer industry. Propanone can be converted into methyl methacrylate, the monomer used to make Perspex®, and phenol is used in phenol-methanal resins, which are important thermosetting plastics.
State and explain how the presence of a halogen substituent might affect the acidity of carboxylic acids.
Propanone could also be formed from propene by reaction with steam over an acidic catalyst, followed by oxidation of the product.
The reaction of propene with water can yield two possible products. Explain, in terms of the stability of the intermediate carbocations, why one is formed in much greater quantities than the other.
Markscheme
halogens make them more acidic;
halogens are electron withdrawing;
Accept halogens (can be) electronegative.
reduces charge on/stabilizes anion formed / weakens O–H bond / makes it easier to lose \({{\text{H}}^ + }\) ion;
Accept decreases pKa.
Accept causes anion to be weaker base.
one product involves a primary carbocation and other a secondary carbocation;
secondary carbocation is more stable (than the primary carbocation, and hence this produces the major product);
alkyl groups reduce charge on carbon atom (through an inductive effect);
Positive inductive effect of alkyl groups alone not enough for M3.
Examiners report
(a) (i) was well done by the better candidates only, but most candidates only scored one mark in (ii) and no marks in (iii).
(d) was very poorly answered. Some knew that there was an inductive effect but did not understand what this meant, namely that through the positive inductive effect the alkyl groups reduce the charge on the carbon atom.

